Related Research Articles

Galba was Roman emperor, ruling from AD 68 to 69. He was the first emperor in the Year of the Four Emperors and assumed the throne following Emperor Nero's suicide.

The Julio-Claudian dynasty comprised the first five Roman emperors: Augustus, Tiberius, Caligula, Claudius, and Nero.
AD 69 (LXIX) was a common year starting on Sunday of the Julian calendar. In the Roman Empire, it was known as the Year of the consulship of Galba and Vinius. The denomination AD 69 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

The 20s decade ran from January 1, AD 20, to December 31, AD 29.

The 30s decade ran from January 1, AD 30, to December 31, AD 39.
AD 20 (XX) was a leap year starting on Monday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Marcus Valerius Messalla Barbatus and Cotta. The denomination 20 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
AD 36 (XXXVI) was a leap year starting on Sunday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Allenius and Plautius. The denomination AD 36 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Gaius Julius Vindex was a Roman governor in the province of Gallia Lugdunensis. He was of a noble Gallic family of Aquitania and was one of the men belonging to a faction of Empress Agrippina, the mother of Nero. Vindex had taken part in a conspiracy against the emperor in 59. However, with the assassination of Agrippina by Nero, this faction was dissolved.

Gaius Caesar was the grandson and heir to the throne of Roman emperor Augustus, alongside his younger brother Lucius Caesar. Although he was born to Marcus Vipsanius Agrippa and Julia, Augustus' only daughter, Gaius and his younger brother, Lucius Caesar, were raised by their grandfather as his adopted sons and joint-heirs to the empire. He would experience an accelerated political career befitting a member of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, with the Roman Senate allowing him to advance his career without first holding a quaestorship or praetorship, offices that ordinary senators were required to hold as part of the cursus honorum.
The gens Sulpicia was one of the most ancient patrician families at ancient Rome, and produced a succession of distinguished men, from the foundation of the Republic to the imperial period. The first member of the gens who obtained the consulship was Servius Sulpicius Camerinus Cornutus, in 500 BC, only nine years after the expulsion of the Tarquins, and the last of the name who appears on the consular list was Sextus Sulpicius Tertullus in AD 158. Although originally patrician, the family also possessed plebeian members, some of whom may have been descended from freedmen of the gens.

Legio V Alaudae, sometimes also known as Gallica, was a legion of the Roman army founded in 52 BC by the general Gaius Julius Caesar. It was levied in Transalpine Gaul to fight the armies of Vercingetorix, and was the first Roman legion to comprise non-citizens. Historians disagree whether the legion was destroyed during the Batavian rebellion in AD 70, or during the First Battle of Tapae.
Legio I Germanica,, was a legion of the Imperial Roman army, possibly founded in 48 BC by Julius Caesar to fight for him in the civil war against Pompey. The title germanic is a reference to its service in the Germanic Wars, rather than the place of origin of its soldiers. After the Revolt of the Batavi, the remaining men of the Germanica were added to Galba's seventh legion, which became VII Gemina. The emblem of Legio I is unknown, but it was probably Taurus, like all the other legions levied by Caesar.

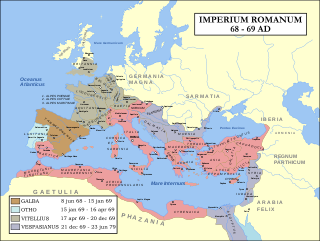
The Year of the Four Emperors, AD 69, was the first civil war of the Roman Empire, during which four emperors ruled in succession: Galba, Otho, Vitellius, and Vespasian. It is considered an important interval, marking the transition from the Julio-Claudians, the first imperial dynasty, to the Flavian dynasty. The period witnessed several rebellions and claimants, with shifting allegiances and widespread turmoil in Rome and the provinces.
Mamercus Aemilius Scaurus was a Roman rhetorician, poet and senator. Tacitus writes that Scaurus was "a man of distinguished rank and ability as an advocate, but of infamous life." He was suffect consul from July to the end of the year AD 21, with Gnaeus Tremellius as his colleague.
Decimus Haterius Agrippa was a Roman plebeian tribune, praetor and consul. He was the son of the orator and senator Quintus Haterius and his wife Vipsania.

De vita Caesarum, commonly known as The Twelve Caesars, is a set of twelve biographies of Julius Caesar and the first 11 emperors of the Roman Empire written by Gaius Suetonius Tranquillus. The group are: Julius Caesar, Augustus, Tiberius, Caligula, Claudius, Nero, Galba, Otho, Vitellius, Vespasian, Titus, Domitian.
Scribonia Magna, known in modern historical sources as Scribonia Crassi, was a Roman noblewoman. Scribonia was descended from Pompey.
Quintus Sulpicius Camerinus Peticus was a Roman senator during the reign of Nero.

Publius Sulpicius Quirinius, also translated as Cyrenius, was a Roman aristocrat. After the banishment of the ethnarch Herod Archelaus from the tetrarchy of Judea in AD 6, Quirinius was appointed legate governor of Syria, to which the province of Judaea had been added for the purpose of a census.
Gaius Sulpicius Galba was a Roman senator, who was active during the reign of Augustus. He was suffect consul in 5 BC as the colleague of Quintus Haterius, succeeding Lucius Vinicius.