Tracfort was a short lived French automobile manufacturing venture that lasted from 1933 till late in 1934.

Donnet was a French manufacturing company of the early twentieth century. Founded as Société des Établissements Donnet-Denhaut by Jérôme Donnet and François Denhaut at Neuilly-sur-Seine in 1914, the firm manufactured a highly successful line of patrol flying boats for the French Navy. The company became known simply as Donnet after designer Denhaut left it in 1919, but did not continue to build aircraft for long afterwards.

The Bucciali was a French automobile manufactured from 1922 until 1933.

C.I.M.E., CIME, La Compagnie Industrielle des Moteurs a Explosion,, was a French manufacturer of light proprietary engines, mainly four-cylinder units. CIME also built light automobiles in 1929.

Sénéchal was a French automobile manufacturer between 1921 and 1929.

Automobiles J. Suère was a French manufacturer of automobiles between 1909 and 1931.

Sima Violet was a French manufacturer of cyclecars between 1924 and 1929.

Benjamin was a French manufacturer of cyclecars between 1921 and 1927 and based on the north-west edge of Paris. 1927 was a year of changes which included a name change, and between 1927 and 1929 the company operated under a new name, Benova.

Villard was a French automobile manufacturer between 1925 and 1935.
Société des Nouveaux Ateliers A. Deguingand was a short-lived French automobile manufacturer.
Raymond Siran, Cyclecars D'Yrsan was a French manufacturer of automobiles in the cyclecar class.

Majola was a French producer of engines and automobiles, established in 1908 and producing automobiles from 1911 till 1928.
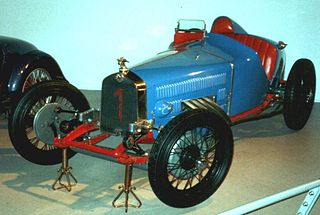
Automobiles Lombard was a French automobile manufacturer which was active from 1927 to 1929.

Maximag was the name of a Swiss automobile, produced by Motosacoche, based at Carouge, a suburb of Geneva, from 1923 till 1928.

Messier was a French automobile manufacturer, based at Montrouge, on the southern edge of Paris, from 1925 till 1931.

Établissements Monotrace S.A. was a French automobile manufacturer, based at Courbevoie, on the edge of Paris, from 1924 till 1930. Although it was presented as a type of automobile, the Monotrace was in some respects more like a motor cycle than a conventional motor car.

Octo was a French automobile manufactured at Courbevoie by Louis Vienne between 1921 and 1928.

Automobiles Oméga-Six was a French automobile manufactured in the Paris region by Gabriel Daubeck between 1922 and 1930.

Lafitte was a French automobile manufactured in Paris from 1923–1928. The 'SA de Construction de Voiturettes Th. Lafitte', owned by Theodore Laffitte, manufactured a light cyclecar which was renowned for its innovative engineering. It incorporated a three-cylinder radial engine mounted in a hinged cage, which was tilted by the driver to engage and vary the ratio of the friction drive to the rear wheels. Uniquely, the 'variable ratio' friction drive consisted of a convex steel flywheel and a concave 'clutch plate' that was faced by wound strips of paper or sometimes leather.
Voiturettes Automobiles A.S. was a sports automobile manufacturer company based in Courbevoie, and later in La Garenne-Colombes, in France. It was established in 1919 by Lucien Jeannin, and existed until 1928.