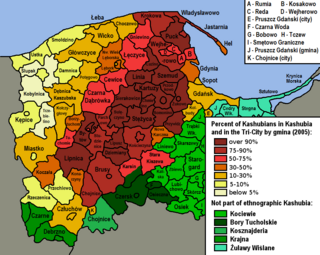
The Kashubians, also known as Cassubians or Kashubs, are a Lechitic ethnic group native to the historical region of Pomerania, including its eastern part called Pomerelia, in north-central Poland. Their settlement area is referred to as Kashubia. They speak the Kashubian language, which is classified as a separate language closely related to Polish.

The Pomeranian language is in the Pomeranian group of Lechitic languages within the West Slavic languages.

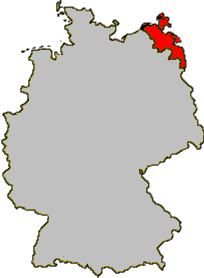
Pomerania is a historical region on the southern shore of the Baltic Sea in Central Europe, split between Poland and Germany. The central and eastern part belongs to the West Pomeranian, Pomeranian and Kuyavian-Pomeranian voivodeships of Poland, while the western part belongs to the German states of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania and Brandenburg.

West Pomeranian Voivodeship is a voivodeship (province) in northwestern Poland. Its capital and largest city is Szczecin. Its area equals 22,892.48 km2 (8,838.84 sq mi), and in 2021, it was inhabited by 1,682,003 people.
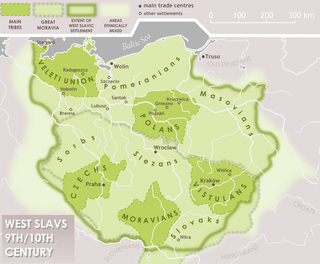
The Pomeranians, first mentioned as such in the 10th century, were a West Slavic tribe, which from the 5th to the 6th centuries had settled at the shore of the Baltic Sea between the mouths of the Oder and Vistula Rivers. They spoke the Pomeranian language that belonged to the Lechitic languages, a branch of the West Slavic language family.

East Low German is a group of Low German dialects spoken in north-eastern Germany as well as by minorities in northern Poland. Together with West Low German dialects, it forms a dialect continuum of the Low German language. Before 1945, the dialect was spoken along the entire then-German-settled Baltic Coast from Mecklenburg, through Pomerania, West Prussia into certain villages of the East Prussian Klaipėda Region.

The history of Pomerania starts shortly before 1000 AD, with ongoing conquests by newly arrived Polan rulers. Before that, the area was recorded nearly 2000 years ago as Germania, and in modern times Pomerania has been split between Germany and Poland. Its name comes from the Old Polish po more, which means "(land) at the sea".
The Pomeranian Evangelical Church was a Protestant regional church in the German state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, serving the citizens living in Hither Pomerania. The Pomeranian Evangelical Church was based on the teachings brought forward by Martin Luther and other Reformators during the Reformation. It combined Lutheran and Reformed traditions. The seat of the church was Greifswald, the bishop's preaching venue was the former Collegiate Church of St. Nicholas in Greifswald.
East Pomeranian or Farther Pomeranian is an East Low German dialect moribund in Europe, which used to be spoken in the region of Farther Pomerania when it was part of the German Province of Pomerania, until World War II, and today is part of Poland. Currently, the language survives mainly in Brazil, where it is spoken by descendants of German immigrants of the 19th century and where it was given its own script by the linguist Ismael Tressmann. It has co-official status in 11 Brazilian municipalities and has been recognized as a historical and cultural heritage of the Brazilian state of Espírito Santo. East Pomeranian is also spoken in central Wisconsin and parts of Iowa, in the United States.

Mecklenburgisch-Vorpommersch is a Low German dialect spoken in the German state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern. It belongs to the East Low German group.

Gdańsk Pomerania is the main geographical region within Pomerelia in northern Poland, covering the bulk of Pomeranian Voivodeship. In contrast to Pomerelia and its synonyms, the term does not cover the historical areas of Chełmno Land and Michałów Land, sometimes with the addition of Lubawa Land.

Farther Pomerania, Hinder Pomerania, Rear Pomerania or Eastern Pomerania, is a subregion of the historic region of Pomerania in north-western Poland, mostly within the West Pomeranian Voivodeship, while its easternmost parts are within the Pomeranian Voivodeship.
Pomeranian is an adjective referring to the historical region of Pomerania, which is divided between Poland and Germany.

The Samborides or House of Sobiesław were a ruling dynasty in the historic region of Pomerelia. They were first documented about 1155 as governors (princeps) in the Eastern Pomeranian lands serving the royal Piast dynasty of Poland, and from 1227 ruled as autonomous princes until 1294, at which time the dynasty died out. The subsequent war for succession between the Polish Piast dynasty, the Imperial Margraviate of Brandenburg and the State of the Teutonic Order resulted in the Teutonic takeover of Gdańsk (Danzig) in 1308.

The Pomeranian Voivodeship was a unit of administrative division and local government in the Kingdom of Poland and the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth from 1454/1466 until the First partition of Poland in 1772. From 1613 the capital was at Skarszewy.

The Pomeranians are a German people native to the historical region of Pomerania. In modern times, its population inhabits Germany, including the state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern. Nowadays there are about five million descendants of Germans in Brazil, a part of these Brazilians are of Pomeranian origin.

Pomerania during the Early Middle Ages covers the History of Pomerania from the 7th to the 11th centuries.

Pomerania during the High Middle Ages covers the history of Pomerania in the 12th and 13th centuries.

Historical Western Pomerania, also called Cispomerania,Fore Pomerania, Front Pomerania or Hither Pomerania, is the western extremity of the historic region of Pomerania forming the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, located mostly in north-eastern Germany, with a small portion in north-western Poland.

The coat of arms of the West Pomeranian Voivodeship, Poland depicts a red griffin with yellow (golden) beak and claws on the white (silver) background. The coat of arms was created by Jerzy Bąk and adopted in 2000.















