The term built environment refers to human-made conditions and is often used in architecture, landscape architecture, urban planning, public health, sociology, and anthropology, among others. These curated spaces provide the setting for human activity and were created to fulfill human desires and needs. The term can refer to a plethora of components including the traditionally associated buildings, cities, public infrastructure, transportation, open space, as well as more conceptual components like farmlands, dammed rivers, wildlife management, and even domesticated animals.
Applied psychology is the use of psychological methods and findings of scientific psychology to solve practical problems of human and animal behavior and experience. Educational and organizational psychology, business management, law, health, product design, ergonomics, behavioural psychology, psychology of motivation, psychoanalysis, neuropsychology, psychiatry and mental health are just a few of the areas that have been influenced by the application of psychological principles and scientific findings. Some of the areas of applied psychology include counseling psychology, industrial and organizational psychology, engineering psychology, occupational health psychology, legal psychology, school psychology, sports psychology, community psychology, neuropsychology, medical psychology and clinical psychology, evolutionary psychology, human factors, forensic psychology and traffic psychology. In addition, a number of specialized areas in the general area of psychology have applied branches. However, the lines between sub-branch specializations and major applied psychology categories are often mixed or in some cases blurred. For example, a human factors psychologist might use a cognitive psychology theory. This could be described as human factor psychology or as applied cognitive psychology. When applied psychology is used in the treatment of behavioral disorders there are many experimental approaches to try and treat an individual. This type of psychology can be found in many of the subbranches in other fields of psychology.
Community psychology is concerned with the community as the unit of study. This contrasts with most psychology which focuses on the individual. Community psychology also studies the community as a context for the individuals within it, and the relationships of the individual to communities and society. Community psychologists seek to understand the functioning of the community, including the quality of life of persons within groups, organizations and institutions, communities, and society. They aim to enhance the quality of life through collaborative research and action.
Environmental psychology is a branch of psychology that explores the relationship between humans and the external world. It examines the way in which the natural environment and our built environments shape us as individuals. Environmental psychology emphasizes how humans change the environment and how the environment changes humans' experiences and behaviors. The field defines the term environment broadly, encompassing natural environments, social settings, built environments, learning environments, and informational environments. According to an article on APA Psychnet, environmental psychology is when a person thinks of a plan, travels to a certain place, and follows through with the plan throughout their behavior.
Robert Sommer is an internationally known Environmental Psychologist and held the position of Distinguished Professor of Psychology Emeritus at the University of California, Davis. Sommer wrote 14 books and over 600 articles, he was best known for his book Personal Space: The Behavioral Basis of Design (1969), which discusses the influence of the environment on human activities.
Cultural psychology is the study of how cultures reflect and shape their members' psychological processes.
Susan Camille Saegert, Guadalupe, Texas is Professor of Environmental Psychology at the CUNY Graduate Center. She was previously Professor of Human and Organizational Development at Vanderbilt University in Nashville, TN.

Livability or liveability is the degree to which a place is good for living. Livability refers to the concerns that are related to the long-term wellbeing of individuals and communities. It encompasses factors like neighborhood amenities, including parks, open space, walkways, grocery shops and restaurants as well as environmental quality, safety and health. It also incorporates things like cost and friendliness. These features contribute to the pleasantness and accessibility of communities. Additionally, livability considers the availability and quality of public transport, educational institutions and healthcare facilities. It also considers the overall cultural and social atmosphere of a place, including the presence of diverse recreational activities and community engagement opportunities. All these factors combined create an environment that enhances the overall quality of life for residents.
Evolutionary developmental psychology (EDP) is a research paradigm that applies the basic principles of evolution by natural selection, to understand the development of human behavior and cognition. It involves the study of both the genetic and environmental mechanisms that underlie the development of social and cognitive competencies, as well as the epigenetic processes that adapt these competencies to local conditions.
Irwin Altman, is a social psychologist who earned his B.A. degree from New York University in 1951, his M.A. degree from the University of Maryland in 1954 and his Ph.D. from the University of Maryland in 1957. He is active in many groups and associations including the International Association of Applied Psychology, American Psychological Association, American Association for the Advancement of Science, American Association of University Professors, Society for the Psychological Study of Social Issues, Society of Experimental Social Psychology, Society of Personality and Social Psychology, Association for the Study of Man-Environment Relations, Environmental Design Research Association, and the Western Psychological Association. He is currently an emeritus faculty member at the University of Utah, Salt Lake City.
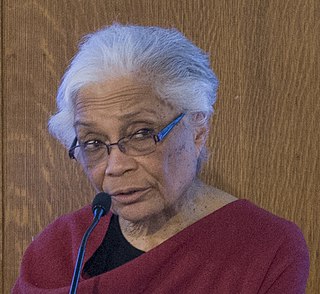
Sharon Egretta Sutton, is an American architect, educator, visual artist, and author. Her work is focused on community-based participatory research and design. She is a professor emerita at the University of Washington. In 1984, she became the first African American woman to become a full professor in an accredited architectural degree program while teaching at the University of Michigan. She has also taught at Parsons School of Design, and Columbia University.
Leanne Rivlin is an originator of the Environmental Psychology Doctoral Program at the CUNY Graduate Center in the late 1960s.
Conservation psychology is the scientific study of the reciprocal relationships between humans and the rest of nature, with a particular focus on how to encourage conservation of the natural world. Rather than a specialty area within psychology itself, it is a growing field for scientists, researchers, and practitioners of all disciplines to come together and better understand the Earth and what can be done to preserve it. This network seeks to understand why humans hurt or help the environment and what can be done to change such behavior. The term "conservation psychology" refers to any fields of psychology that have understandable knowledge about the environment and the effects humans have on the natural world. Conservation psychologists use their abilities in "greening" psychology and make society ecologically sustainable. The science of conservation psychology is oriented toward environmental sustainability, which includes concerns like the conservation of resources, conservation of ecosystems, and quality of life issues for humans and other species.
Cindi Katz, a geographer, is Professor in Environmental Psychology, Earth and Environmental Sciences, American Studies, and Women's Studies at the CUNY Graduate Center. Her work concerns social reproduction and the production of space, place and nature; children and the environment; the consequences of global economic restructuring for everyday life; the privatization of the public environment, the intertwining of memory and history in the geographical imagination, and the intertwined spatialities of homeland and home-based security. She is known for her work on social reproduction and everyday life, research on children's geographies, her intervention on "minor theory", and the notion of counter-topography, which is a means of recognizing the historical and geographical specificities of particular places while inferring their analytic connections to specific material social practices.

Robert E. Kraut is an American social psychologist who studies human-computer interaction, online communities, internet use, group coordination, computers in organizations, and the role of visual elements in interpersonal communication. He is a Herbert Simon Professor of Human-computer Interaction at the Human-Computer Interaction Institute at Carnegie Mellon University.
Allan W. Wicker studied with the founders of ecological psychology, Roger G. Barker and Herbert Wright, in the social psychology program at the University of Kansas, where he earned the Ph.D. in 1967. He taught at the University of Wisconsin, Milwaukee and the University of Illinois, Champaign-Urbana before taking a position at Claremont Graduate School in 1971, where he was a professor of psychology until early retirement in 1999. He is currently an emeritus professor.
Interior design psychology is a field within environmental psychology, which concerns the environmental conditions of the interior. It is a direct study of the relationship between an environment and how that environment affects the behavior of its inhabitants, intending to maximize the positive effects of this relationship. Through interior design psychology, the performance and efficiency of the space and the well-being of the individual are improved. Figures like Walter Benjamin, Sigmund Freud, John B. Calhoun and Jean Baudrillard have shown that by incorporating this psychology into design one can control an environment and to an extent, the relationship and behavior of its inhabitants. An example of this is seen through the rat experiments conducted by Calhoun in which he noted the aggression, killing and changed sexual tendencies amongst rats. This experiment created a stark behavioral analogy between the rat's behavior and inhabitation in high-rise building projects in the US after WWII, an example of which is the Pruitt-Igoe development in St Louis demolished in 1972 only 21 years after being erected.

Urban planning, also known as town planning, city planning, regional planning, or rural planning in specific contexts, is a technical and political process that is focused on the development and design of land use and the built environment, including air, water, and the infrastructure passing into and out of urban areas, such as transportation, communications, and distribution networks and their accessibility. Traditionally, urban planning followed a top-down approach in master planning the physical layout of human settlements. The primary concern was the public welfare, which included considerations of efficiency, sanitation, protection and use of the environment, as well as effects of the master plans on the social and economic activities. Over time, urban planning has adopted a focus on the social and environmental bottom-lines that focus on planning as a tool to improve the health and well-being of people while maintaining sustainability standards. Sustainable development was added as one of the main goals of all planning endeavors in the late 20th century when the detrimental economic and the environmental impacts of the previous models of planning had become apparent. Similarly, in the early 21st century, Jane Jacobs's writings on legal and political perspectives to emphasize the interests of residents, businesses and communities effectively influenced urban planners to take into broader consideration of resident experiences and needs while planning.
Susan Saltzman Fainstein is an American educator and scholar of urban planning. Fainstein is currently a Senior Research Fellow at the Harvard University Graduate School of Design. Her research and writing has focused on the distributive effects of urban development strategies and megaprojects, the role of democracy and community control in local public institutions, and establishing a moral theory of "the just city."
Pro-environmental behaviour is behaviour that a person consciously chooses in order to minimize the negative impact of their actions on the environment. Barriers to pro-environmental behaviour are the numerous factors that hinder individuals when they try to adjust their behaviours toward living more sustainable lifestyles. Generally, these barriers can be separated into larger categories: psychological, social/cultural, financial and structural. Psychological barriers are considered internal, where an individual's knowledge, beliefs and thoughts affect their behaviour. Social and cultural barriers are contextual, where an individual's behaviour is affected by their surroundings. Financial barriers are simply a lack of funds to move toward more sustainable behaviour. Structural barriers are external and often impossible for an individual to control, such as lack of governmental action, or locality of residence that promotes car use as opposed to public transit.