
A router is a networking device that forwards data packets between computer networks. Routers perform the traffic directing functions on the Internet. Data sent through the internet, such as a web page or email, is in the form of data packets. A packet is typically forwarded from one router to another router through the networks that constitute an internetwork until it reaches its destination node.

A web server is computer software and underlying hardware that accepts requests via HTTP, the network protocol created to distribute web pages, or its secure variant HTTPS. A user agent, commonly a web browser or web crawler, initiates communication by making a request for a specific resource using HTTP, and the server responds with the content of that resource or an error message. The server can also accept and store resources sent from the user agent if configured to do so.

In computing, a server is a piece of computer hardware or software that provides functionality for other programs or devices, called "clients". This architecture is called the client–server model. Servers can provide various functionalities, often called "services", such as sharing data or resources among multiple clients, or performing computation for a client. A single server can serve multiple clients, and a single client can use multiple servers. A client process may run on the same device or may connect over a network to a server on a different device. Typical servers are database servers, file servers, mail servers, print servers, web servers, game servers, and application servers.

In computer networking, a proxy server is a server application or appliance that acts as an intermediary for requests from clients seeking resources from servers that provide those resources. A proxy server thus functions on behalf of the client when requesting service, potentially masking the true origin of the request to the resource server.
Universal Plug and Play (UPnP) is a set of networking protocols that permits networked devices, such as personal computers, printers, Internet gateways, Wi-Fi access points and mobile devices to seamlessly discover each other's presence on the network and establish functional network services. UPnP is intended primarily for residential networks without enterprise-class devices.

Correspondence chess is chess or variant chess played by various forms of long-distance correspondence, often through a correspondence chess server, a public internet chess forum, email, or the postal system. Less common methods that have been employed include fax, homing pigeon and phone. It is in contrast to over-the-board (OTB) chess, where the players sit at a chessboard at the same time, or play at the same time remotely.
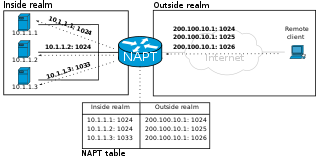
In computer networking, port forwarding or port mapping is an application of network address translation (NAT) that redirects a communication request from one address and port number combination to another while the packets are traversing a network gateway, such as a router or firewall. This technique is most commonly used to make services on a host residing on a protected or masqueraded (internal) network available to hosts on the opposite side of the gateway, by remapping the destination IP address and port number of the communication to an internal host.
Internet security is a branch of computer security specifically related to not only Internet, often involving browser security and the World Wide Web, but also network security as it applies to other applications or operating systems as a whole. Its objective is to establish rules and measures to use against attacks over the Internet. The Internet represents an insecure channel for exchanging information, which leads to a high risk of intrusion or fraud, such as phishing, online viruses, trojans, worms and more.
In computer science and networking in particular, a session is a temporary and interactive information interchange between two or more communicating devices, or between a computer and user. A session is established at a certain point in time, and then ‘torn down’ - brought to an end - at some later point. An established communication session may involve more than one message in each direction. A session is typically stateful, meaning that at least one of the communicating parties needs to hold current state information and save information about the session history in order to be able to communicate, as opposed to stateless communication, where the communication consists of independent requests with responses.
A gateway is a piece of networking hardware used in telecommunications for telecommunications networks that allows data to flow from one discrete network to another. Gateways are distinct from routers or switches in that they communicate using more than one protocol to connect a bunch of networks and can operate at any of the seven layers of the open systems interconnection model (OSI).
An Internet bot, web robot, robot or simply bot, is a software application that runs automated tasks (scripts) over the Internet. Typically, bots perform tasks that are simple and repetitive, much faster than a person could. The most extensive use of bots is for web crawling, in which an automated script fetches, analyzes and files information from web servers. More than half of all web traffic is generated by bots.
Networking hardware, also known as network equipment or computer networking devices, are electronic devices which are required for communication and interaction between devices on a computer network. Specifically, they mediate data transmission in a computer network. Units which are the last receiver or generate data are called hosts, end systems or data terminal equipment.
Internet fax, e-fax, or online fax is the use of the internet and internet protocols to send a fax (facsimile), rather than using a standard telephone connection and a fax machine. A distinguishing feature of Internet fax, compared to other Internet communications such as email, is the ability to exchange fax messages with traditional telephone-based fax machines.
Inter-domain routing is data flow control and interaction between Primary Domain Controller (PDC) computers. This type of computer uses various computer protocols and services to operate. It is most commonly used to multicast between internet domains.
The Zlob Trojan, identified by some antiviruses as Trojan.Zlob, is a Trojan horse which masquerades as a required video codec in the form of ActiveX. It was first detected in late 2005, but only started gaining attention in mid-2006.
Remote Desktop Services (RDS), known as Terminal Services in Windows Server 2008 and earlier, is one of the components of Microsoft Windows that allow a user to take control of a remote computer or virtual machine over a network connection. RDS is Microsoft's implementation of thin client architecture, where Windows software, and the entire desktop of the computer running RDS, are made accessible to any remote client machine that supports Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP). User interfaces are displayed from the server onto the client system and input from the client system is transmitted to the server - where software execution takes place. This is in contrast to application streaming systems, like Microsoft App-V, in which computer programs are streamed to the client on-demand and executed on the client machine.
Usenet is a worldwide distributed discussion system available on computers. It was developed from the general-purpose Unix-to-Unix Copy (UUCP) dial-up network architecture. Tom Truscott and Jim Ellis conceived the idea in 1979, and it was established in 1980. Users read and post messages to one or more categories, known as newsgroups. Usenet resembles a bulletin board system (BBS) in many respects and is the precursor to Internet forums that became widely used. Discussions are threaded, as with web forums and BBSs, though posts are stored on the server sequentially.
BITNET was a co-operative U.S. university computer network founded in 1981 by Ira Fuchs at the City University of New York (CUNY) and Greydon Freeman at Yale University. The first network link was between CUNY and Yale.
A Mobile Web Server is software designed for modern-day smartphones to host personal web servers, through the use of open sourced software, such as, i-jetty, an open source software, based on jetty. I-jetty is an open source web container, serving Java-based web content such as, servlets and JSPs. Jetty is written in Java and its API is available as a set of JARs. Developers can instantiate a jetty container as an object, instantly adding network and web connectivity to a stand-alone Java app. Jetty is built for scalable performance allowing tens of thousands of HTTP connections and hundreds of thousands of simultaneous web socket connections. Jetty is optimized and known for creating small memory footprints, increasing scalability and performance.






