Related Research Articles

Pope Victor II, born Gebhard of Dollnstein-Hirschberg, was the head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 13 April 1055 until his death in 1057. Victor II was one of a series of German-born popes who led the Gregorian Reform.

Year 1036 (MXXXVI) was a leap year starting on Thursday of the Julian calendar.
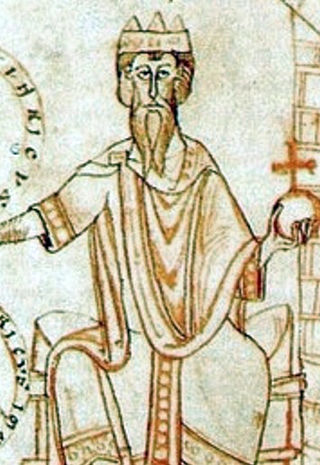
Conrad II, also known as Conrad the Elder and Conrad the Salic, was the emperor of the Holy Roman Empire from 1027 until his death in 1039. The first of a succession of four Salian emperors, who reigned for one century until 1125, Conrad ruled the kingdoms of Germany, Italy and Burgundy.

Conrad, a member of the Hohenstaufen dynasty, was the only son of Emperor Frederick II from his second marriage with Queen Isabella II of Jerusalem. He inherited the title of King of Jerusalem upon the death of his mother in childbed. Appointed Duke of Swabia in 1235, his father had him elected King of Germany and crowned King of Italy in 1237. After the emperor was deposed and died in 1250, he ruled as King of Sicily until his death.

Gisela of Burgundy, a member of the royal Elder House of Welf, was Duchess of Bavaria from about 972 to 976 and again from 985 to 995, by her marriage with Duke Henry the Wrangler. She was the mother of Emperor Henry II.

The Prince-Archbishopric of Salzburg was an ecclesiastical principality and state of the Holy Roman Empire. It comprised the secular territory ruled by the archbishops of Salzburg, as distinguished from the much larger Catholic diocese founded in 739 by Saint Boniface in the German stem duchy of Bavaria. The capital of the archbishopric was Salzburg, the former Roman city of Iuvavum.

Wolfgang of Regensburg was bishop of Regensburg in Bavaria from Christmas 972 until his death. He is a saint in the Catholic and Eastern Orthodox churches. He is regarded as one of the three great German saints of the 10th century, the other two being Ulrich of Augsburg and Conrad of Constance. Towards the end of his life Wolfgang withdrew as a hermit to a solitary spot, in the Salzkammergut region of Upper Austria. Soon after Wolfgang's death many churches chose him as their patron saint, and various towns were named after him.

The House of Hohenlohe is a former German princely and ducal dynasty. It ruled an immediate territory within the Holy Roman Empire which was divided between several branches. In 1806 the area of Hohenlohe was 1,760 km² and its estimated population was 108,000. The motto of the house is "ex flammis orior" (english: From flames I rise). The Lords of Hohenlohe were elevated to the rank of imperial counts in 1450, and from 1744 the territory and its rulers were princely. In 1825, the German Confederation recognized the right of all members of the house to be styled Serene Highness , with the title Fürst for the heads of its branches, and princes/princesses for the other members. From 1861 the Hohenlohe-Oehringen line was also ducal and the dukes of the Duchy of Ujest.

Boniface III, son of Tedald of Canossa and the father of Matilda of Tuscany, was the most powerful north Italian prince of his age. By inheritance he was count of Brescia, Canossa, Ferrara, Florence, Lucca, Mantua, Modena, Pisa, Pistoia, Parma, Reggio, and Verona from 1007 and, by appointment, margrave of Tuscany from 1027 until his assassination in 1052.
Gebhard II, called Gebhard von Hohenwart, was the bishop of Regensburg from 1023 to 17 March 1036.
Gebhard I, known as Gebhard of Swabia, was the Bishop of Regensburg from 994 until his death.
The Bishopric of Merseburg was an episcopal see on the eastern border of the medieval Duchy of Saxony with its centre in Merseburg, where Merseburg Cathedral was constructed. The see was founded in 967 by Emperor Otto I at the same time in the same manner as those of Meissen and Zeitz, all suffragan dioceses of the Archbishopric of Magdeburg as part of a plan to bind the adjacent Slavic ("Wendish") lands in the Saxon Eastern March beyond the Saale River more closely to the Holy Roman Empire.

Gertrude of Sulzbach was German queen from 1138 until her death as the second wife of the Hohenstaufen king Conrad III.
Engelbert II, a member of the House of Sponheim, was Margrave of Istria and Carniola from about 1103/07 until 1124. In 1123, he succeeded his elder brother Henry as Duke of Carinthia and Margrave of Verona which he held until his retirement in 1135.

The Archdiocese of Salzburg is a Latin Church archdiocese of the Catholic Church in Austria. The archdiocese is one of two Austrian archdioceses, serving alongside the Archdiocese of Vienna.

Henry III, called the Black or the Pious, was Holy Roman Emperor from 1046 until his death in 1056. A member of the Salian dynasty, he was the eldest son of Conrad II and Gisela of Swabia.

The Counts of Lenzburg were a comital family in the Duchy of Swabia in the 11th and 12th centuries, controlling substantial portions of the pagi of Aargau and Zürichgau.
Count Berengar II of Sulzbach, sometimes known as Berengar I of Sulzbach, was Count of Sulzbach in Bavaria. Berengar was a leader of the reform party. He sided with Pope Gregory VII during the Investiture Controversy in opposition to Henry IV, Holy Roman Emperor, and supported Henry V in his successful rebellion against his father. He is known as the founder of several abbeys.
References
- ↑ Wolfram, Herwig (2006). Conrad II, 990-1039: Emperor of Three Kingdoms. p. 88. ISBN 9780271027388.
- 1 2 New Advent website, Ratisbon
- ↑ "Gebhard III. von Hohenlohe Bishop of Regensburg (1036-1060)". manfred-hiebl.de.