
In computing, BIOS is firmware used to provide runtime services for operating systems and programs and to perform hardware initialization during the booting process. The firmware comes pre-installed on the computer's motherboard.
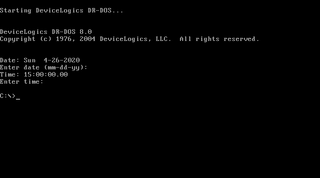
DR-DOS is a disk operating system for IBM PC compatibles, originally developed by Gary A. Kildall's Digital Research, Inc. and derived from Concurrent PC DOS 6.0, which was an advanced successor of CP/M-86. Upon its introduction in 1988, it was the first DOS that attempted to be compatible with IBM PC DOS and MS-DOS.

GEM is a discontinued operating environment released by Digital Research in 1985. GEM is known primarily as the native graphical user interface of the Atari ST series of computers, providing a WIMP desktop. It was also available for IBM PC compatibles and shipped with some models from Amstrad. GEM is used as the core for some commercial MS-DOS programs, the most notable being Ventura Publisher. It was ported to other computers that previously lacked graphical interfaces, but never gained traction. The final retail version of GEM was released in 1988.

FreeGEM released in 1999 is a windowing system based on Digital Research's GEM which was first released in 1985. GEM stands for "Graphics Environment Manager".
Star Trek is the code name that was given to a secret prototype project, running a port of Macintosh System 7 and its applications on Intel-compatible x86 personal computers. The project, starting in February 1992, was conceived in collaboration between Apple Computer, who provided the majority of engineers, and Novell, who at the time was one of the leaders of cross-platform file-servers. The plan was that Novell would market the resulting OS as a challenge to Microsoft Windows, but the project was discontinued in 1993 and never released, although components were reused in other projects. The project was named after the Star Trek science fiction franchise with the slogan "To boldly go where no Mac has gone before".
CONFIG.SYS is the primary configuration file for the DOS and OS/2 operating systems. It is a special ASCII text file that contains user-accessible setup or configuration directives evaluated by the operating system's DOS BIOS during boot. CONFIG.SYS was introduced with DOS 2.0.

ViewMAX is a CUA-compliant file manager supplied with DR DOS versions 5.0 and 6.0. It is based on a cut-down runtime version of Digital Research's GEM/3 graphical user interface modified to run only a single statically built application, the ViewMAX desktop. Support for some unneeded functions has been removed whilst some new functions were added at the same time. Nevertheless, the systems remained close enough for ViewMAX to recognize GEM desktop accessories automatically and to allow some native GEM applications to be run inside the ViewMAX environment. Many display drivers for GEM 3.xx could be used by ViewMAX as well, enabling ViewMAX to be used with non-standard display adapters and higher resolutions than possible using the default set of ViewMAX drivers. Also, Digital Research's SID86, the symbolic instruction debugger that shipped with DR DOS 3.xx and provided dedicated functions to debug GEM applications, could be used for ViewMAX as well.
GEOS is a computer operating environment, graphical user interface (GUI), and suite of application software. Originally released as PC/GEOS, it runs on MS-DOS-based, IBM PC compatible computers. Versions for some handheld platforms were also released and licensed to some companies.

American Megatrends International, LLC, doing business as AMI, is an international hardware and software company, specializing in PC hardware and firmware. The company was founded in 1985 by Pat Sarma and Subramonian Shankar. It is headquartered in Building 800 at 3095 Satellite Boulevard in unincorporated Gwinnett County, Georgia, United States, near the city of Duluth, and in the Atlanta metropolitan area.
Lineo was a thin client and embedded systems company spun out of Caldera Thin Clients by 20 July 1999.

Arachne is an Internet suite containing a graphical web browser, email client, and dialer. Originally, Arachne was developed by Michal Polák under his xChaos label, a name he later changed into Arachne Labs. It was written in C and compiled using Borland C++ 3.1. Arachne has since been released under the GPL as Arachne GPL.

Phoenix Technologies Ltd. is an American company that designs, develops and supports core system software for personal computers and other computing devices. The company's products – commonly referred to as BIOS or firmware – support and enable the compatibility, connectivity, security and management of the various components and technologies used in such devices. Phoenix Technologies and IBM developed the El Torito standard.
Computer hardware or software is said to be bug compatible if it exactly replicates an undesirable feature of a previous version. The phrase is found in the Jargon File.
FlexOS is a discontinued modular real-time multiuser multitasking operating system (RTOS) designed for computer-integrated manufacturing, laboratory, retail and financial markets. Developed by Digital Research's Flexible Automation Business Unit in Monterey, California, in 1985.

MS-DOS is an operating system for x86-based personal computers mostly developed by Microsoft. Collectively, MS-DOS, its rebranding as IBM PC DOS, and a few operating systems attempting to be compatible with MS-DOS, are sometimes referred to as "DOS". MS-DOS was the main operating system for IBM PC compatibles during the 1980s, from which point it was gradually superseded by operating systems offering a graphical user interface (GUI), in various generations of the graphical Microsoft Windows operating system.

DOS is a family of disk-based operating systems for IBM PC compatible computers. The DOS family primarily consists of IBM PC DOS and a rebranded version, Microsoft's MS-DOS, both of which were introduced in 1981. Later compatible systems from other manufacturers include DR-DOS (1988), ROM-DOS (1989), PTS-DOS (1993), and FreeDOS (1994). MS-DOS dominated the IBM PC compatible market between 1981 and 1995.

Wyse Technology, Inc., or simply Wyse, was an independent American manufacturer of cloud computing systems. Wyse are best remembered for their video terminal line introduced in the 1980s, which competed with the market-leading Digital. They also had a successful line of IBM PC compatible workstations in the mid-to-late 1980s. But starting late in the decade, Wyse were outcompeted by companies such as eventual parent Dell. Current products include thin client hardware and software as well as desktop virtualization solutions. Other products include cloud software-supporting desktop computers, laptops, and mobile devices. Dell Cloud Client Computing is partnered with IT vendors such as Citrix, IBM, Microsoft, and VMware.
Caldera, Inc. was a Canopy-funded software company founded in October 1994 and incorporated on 25 January 1995 by former Novell employees Bryan Wayne Sparks, Ransom H. Love and others to develop the Caldera Network Desktop (CND) and later create a Linux distribution named OpenLinux (COL). The company was originally based in Provo and later in Orem, Utah, USA.
In computing, a hardware code page (HWCP) refers to a code page supported natively by a hardware device such as a display adapter or printer. The glyphs to present the characters are stored in the alphanumeric character generator's resident read-only memory and are thus not user-changeable. They are available for use by the system without having to load any font definitions into the device first. Startup messages issued by a PC's System BIOS or displayed by an operating system before initializing its own code page switching logic and font management and before switching to graphics mode are displayed in a computer's default hardware code page.

DR-WebSpyder is a DOS web browser, mail client and operating system runtime environment that was developed by Caldera UK in 1997. It was based on the DR-DOS operating system and networking components from Novell as well as the Arachne web browser by Michal Polák of xChaos software. The system was designed to run on low-end desktop systems, but being able to boot and execute from disk as well as from ROM or network, it was also tailored for x86-based thin clients and embedded systems with or without disk drives. Using the web browser as its principal user interface, it could be also used for kiosk systems and set-top boxes. It was ported to Linux in 1999 under the name Embrowser and was renamed Embedix Browser in 2000.













