Related Research Articles

In amniotes, the clitoris is a female sex organ. In humans, it is the vulva's most erogenous area and generally the primary anatomical source of female sexual pleasure. The clitoris is a complex structure, and its size and sensitivity can vary. The visible portion, the glans, of the clitoris is typically roughly the size and shape of a pea and is estimated to have at least 8,000 nerve endings.
Clitoridectomy or clitorectomy is the surgical removal, reduction, or partial removal of the clitoris. It is rarely used as a therapeutic medical procedure, such as when cancer has developed in or spread to the clitoris. Commonly, non-medical removal of the clitoris is performed during female genital mutilation.

In mammals and other animals, the vagina is the elastic, muscular reproductive organ of the female genital tract. In humans, it extends from the vestibule to the cervix. The outer vaginal opening is normally partly covered by a thin layer of mucosal tissue called the hymen. At the deep end, the cervix bulges into the vagina. The vagina allows for copulation and birth. It also channels menstrual flow, which occurs in humans and closely related primates as part of the menstrual cycle.
Genital modifications are forms of body modifications applied to the human sexual organs. The term genital enhancement is generally used for genital modifications that improve the recipient's quality of life in result in positive health outcomes. The term genital mutilation is used for genital modifications that drastically diminish the recipient's quality of life and result in adverse health outcomes, whether physical or mental.

The female reproductive system is made up of the internal and external sex organs that function in the reproduction of new offspring. The human female reproductive system is immature at birth and develops to maturity at puberty to be able to produce gametes, and to carry a fetus to full term. The internal sex organs are the vagina, uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries. The female reproductive tract includes the vagina, uterus, and fallopian tubes and is prone to infections. The vagina allows for sexual intercourse and childbirth, and is connected to the uterus at the cervix. The uterus or womb accommodates the embryo, which develops into the fetus. The uterus also produces secretions, which help the transit of sperm to the fallopian tubes, where sperm fertilize ova produced by the ovaries. The external sex organs are also known as the genitals and these are the organs of the vulva including the labia, clitoris, and vaginal opening.
Gender-affirming surgery for female-to-male transgender people includes a variety of surgical procedures that alter anatomical traits to provide physical traits more comfortable to the trans man's male identity and functioning.
Gender-affirming surgery for male-to-female transgender women or transfeminine non-binary people describes a variety of surgical procedures that alter the body to provide physical traits more comfortable and affirming to an individual's gender identity and overall functioning.
Vaginoplasty is any surgical procedure that results in the construction or reconstruction of the vagina. It is a type of genitoplasty. Pelvic organ prolapse is often treated with one or more surgeries to repair the vagina. Sometimes a vaginoplasty is needed following the treatment or removal of malignant growths or abscesses to restore a normal vaginal structure and function. Surgery to the vagina is done to correct congenital defects to the vagina, urethra and rectum. It may correct protrusion of the urinary bladder into the vagina (cystocele) and protrusion of the rectum (rectocele) into the vagina. Often, a vaginoplasty is performed to repair the vagina and its attached structures due to trauma or injury.
Genital reconstructive surgery may refer to:

The labia are the major externally visible portions of the vulva. In humans and other primates, there are two pairs of labia: the labia majora are large and thick folds of skin that cover the vulva's other parts while the labia minora are the inner folds of skin between the outer labia that surround and protect the urethral and vaginal openings.

Labiaplasty is a plastic surgery procedure for creating or altering the labia minora and the labia majora, the folds of skin of the human vulva. It is a type of vulvoplasty. There are two main categories of women seeking cosmetic genital surgery: those with conditions such as intersex, and those with no underlying condition who experience physical discomfort or wish to alter the appearance of their vulvas because they believe they do not fall within a normal range.

Vaginectomy is a surgery to remove all or part of the vagina. It is one form of treatment for individuals with vaginal cancer or rectal cancer that is used to remove tissue with cancerous cells. It can also be used in gender-affirming surgery. Some people born with a vagina who identify as trans men or as nonbinary may choose vaginectomy in conjunction with other surgeries to make the clitoris more penis-like (metoidioplasty), construct of a full-size penis (phalloplasty), or create a relatively smooth, featureless genital area.

Anthony Atala is an American bioengineer, urologist, and pediatric surgeon. He is the W.H. Boyce professor of urology, the founding director of the Wake Forest Institute for Regenerative Medicine, and the chair of the Department of Urology at Wake Forest School of Medicine in North Carolina. His work focuses on the science of regenerative medicine: "a practice that aims to refurbish diseased or damaged tissue using the body's own healthy cells".

Clitoral hood reduction, also termed clitoral hoodectomy, clitoral unhooding, clitoridotomy, or (partial) hoodectomy, is a plastic surgery procedure for reducing the size and the area of the clitoral hood in order to further expose the glans of the clitoris.
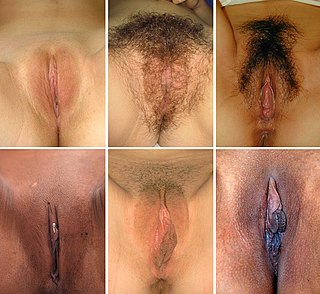
In mammals, the vulva consists of the external female genitalia. The human vulva includes the mons pubis, labia majora, labia minora, clitoris, vulval vestibule, urinary meatus, vaginal opening, hymen, and Bartholin's and Skene's vestibular glands. The vulva includes the entrance to the vagina, which leads to the uterus, and provides a double layer of protection for this by the folds of the outer and inner labia. Pelvic floor muscles support the structures of the vulva. Other muscles of the urogenital triangle also give support.
Vaginal transplantation is procedure whereby donated or laboratory-grown vagina tissue is used to create a 'neovagina'. It is most often used in women who have vaginal aplasia.
Regeneration in humans is the regrowth of lost tissues or organs in response to injury. This is in contrast to wound healing, or partial regeneration, which involves closing up the injury site with some gradation of scar tissue. Some tissues such as skin, the vas deferens, and large organs including the liver can regrow quite readily, while others have been thought to have little or no capacity for regeneration following an injury.
Genitoplasty is plastic surgery to the genitals. Genitoplasties may be reconstructive to repair injuries, and damage arising from cancer treatment, or congenital disorders, endocrine conditions, or they may be cosmetic.
Sexual anomalies, also known as sexual abnormalities, are a set of clinical conditions due to chromosomal, gonadal and/or genitalia variation. Individuals with congenital (inborn) discrepancy between sex chromosome, gonadal, and their internal and external genitalia are categorised as individuals with a disorder of sex development (DSD). Afterwards, if the family or individual wishes, they can partake in different management and treatment options for their conditions.
References
- 1 2 "Bioengineered corporal tissue for structural and functional restoration of the penis". 2009 Chen, K. Eberli, D. Yoo, J. and Atala, A. 2009 Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences107 No 8, pp. 3346-3350.
- ↑ "Bone regeneration and stem cells." 2011 Arvidson, K. et al. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine15, No 4, pp. 718-746.
- ↑ "Regenerative Medicine: Regrowing Body Parts". March 23, 2008 CBS
- ↑ "Engineered Rabbit Penises Raise Human Hopes." 2009 Keim, B. Wired Science
- ↑ "Italian doctor builds new, more natural vagina". 2007 Brown, S. Reuters
- ↑ "Patent application title: Vaginal Tissue Regeneration Device and Method for Regeneration of Vaginal Lining using Vibration Therapy" Archived 2013-09-21 at the Wayback Machine . May 2012 Barnard, E. and Wilhite M. Patent application number: 20120136287
- ↑ "Regeneration of Vaginal Tissue with non-systemic vaginal administration of Estrogen" May 2009 Lyle, J. Patent application number: 20090124584
- ↑ "Surgical Techniques: Reconstructive Surgery of the Clitoris after Ritual Excision." 2006 Foldes, Pierre J. Sex Medicine3 pp. 1091-1094
- ↑ Reconstructive surgery after female genital mutilation: a prospective cohort study. Foldes, P. et al. Lancet380 Issue 9837 pp. 134-141
- ↑ "DoD; Dept of Army -- USAMRAA; Armed Forces Institute of Regenerative Medicine -II (AFIRM II)." Archived 2012-10-31 at the Wayback Machine Retrieved 2012-8-23