The Mačva Districtpronounced [mǎtʃʋanskiː ôkruːɡ]) is one of eight administrative districts of Šumadija and Western Serbia. It expands in the western parts of Serbia, in the geographical regions of Mačva, Podrinje, Posavina, and Pocerina. According to the 2011 census results, it has a population of 298,931 inhabitants. The administrative center of the Mačva district is the city of Šabac.

Berkovitsa is a town and ski resort in northwestern Bulgaria. It is the administrative centre of the homonymous Berkovitsa Municipality, Montana Province and is close to the town of Varshets. As of December 2009, it has a population of 13,917 inhabitants.
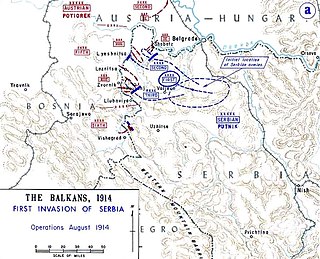
The Battle of Cer was a military campaign fought between Austria-Hungary and Serbia in August 1914 during the early stages of the Serbian Campaign of the First World War. It took place around Cer Mountain and several surrounding villages, as well as the town of Šabac.

Banja Koviljača is a popular tourist and spa town locateded in the city of Loznica, Serbia. Situated on the west border of Serbia by the Drina river, 137 kilometres (85 mi) from Belgrade, it is the oldest spa town in Serbia. As of 2011 census, it has 7,000 inhabitants.

Loznica is a city located in the Mačva District of western Serbia. It lies on the right bank of the Drina river. In 2011 the city had a total population of 19,572, while the administrative area had a population of 79,327.

Lešnica is a village in western Serbia. It is located in the municipality of Loznica, in the Mačva District. Lešnica's current population is 4,731.
The Jerez is a river in western Serbia, a 56 km-long right tributary to the Sava river.
The Jadar region begins roughly at the Osečina and it is divided in two sub-regions: Upper Jadar, which is part of much larger region of Rađevina, and Lower Jadar, which is also part of another, larger region of Podrinje. Center of the Lower Jadar is the town of Loznica, which is not on the Jadar river, but some 10 km to the southwest.

Donja Badanja is a village in western Serbia. It is located in the municipality of Loznica, in the Mačva District. Donja Badanja's current population is 510. According to 1991 census population was 670.

The Drina is a 346 km (215 mi) long international river, which forms a large portion of the border between Bosnia and Herzegovina and Serbia. It is the longest tributary of the Sava River and the longest karst river in the Dinaric Alps which belongs to the Danube river watershed. Its name is derived from the Latin name of the river which in turn is derived from Greek.

The Battle of Loznica involved an attack on the German garrison of that town by the Jadar Chetnik Detachment on 31 August 1941. Following the World War II German-led Axis invasion of Yugoslavia in April 1941, the Kingdom of Yugoslavia was partitioned. At the time, Loznica was part of the German-occupied territory of Serbia, which included Serbia proper, with the addition of the northern part of Kosovo, and the Banat.

The Tronoša Monastery is a Serbian Orthodox monastery between the villages of Tršić and Korenita, in the administrative town of Loznica, in western Serbia. It is ecclesiastically part of the Eparchy of Šabac. According to tradition, the monastery was built by King Stefan Dragutin.
The Capture of Banja Koviljača was a long battle fought by allied forces of Chetnik Detachments of the Yugoslav Army (Chetniks) with Yugoslav Partisans against German forces. On 1 September 1941, the allies attacked German soldiers who were garrisoned in an outpost at Banja Koviljača. This was the beginning of the hostilities of the April war. The Battle of Koviljača reflected skillful command by leaders of the uprising in Serbia.

The Jadar Museum is a history museum located in Loznica, Serbia. It has a permanent collection dedicated to man's activities in the area of Podrinje from prehistory until 1950. The museum is housed in the Old Pharmacy Building, which is the cultural monument of great importance.

Memorial Ossuary Cer was built in the village Tekeriš on the mountain Cer. The remains of the killed Serbian soldiers after the Battle of Cer in the First World War were buried there. Memorial ossuary Cer is on the list of Cultural Monuments of Exceptional Importance.