The House of Hanover is a European royal house with roots tracing back to the 17th century. Its members, known as Hanoverians, ruled Hanover, Great Britain, Ireland, and the British Empire at various times during the 17th to 20th centuries. Originating as a cadet branch of the House of Welf in 1635, also known then as the House of Brunswick-Lüneburg, the Hanoverians ascended to prominence with Hanover's elevation to an Electorate in 1692. In 1714 George I, prince-elector of Hanover and a descendant of King James VI and I, assumed the throne of Great Britain and Ireland, marking the beginning of Hanoverian rule over the British Empire. At the end of his line, Queen Victoria's death in 1901, the throne of the United Kingdom passed to her eldest son Edward VII, a member of the House of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha, through his father Albert, Prince Consort. The last reigning members of the House of Hanover lost the Duchy of Brunswick in 1918 when Germany became a republic and abolished royalty and nobility.
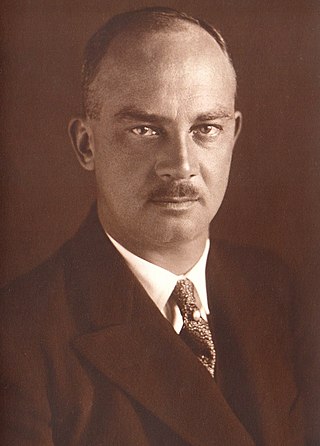
Ernest Augustus ; 17 November 1887 – 30 January 1953) was Duke of Brunswick from 2 November 1913 to 8 November 1918. He was a grandson of George V of Hanover, thus a Prince of Hanover and a Prince of the United Kingdom. He was also a maternal grandson of Christian IX of Denmark and the son-in-law of German Emperor Wilhelm II. The Prussians had deposed King George from the Hanoverian throne in 1866, but his marriage ended the decades-long feud between the Prussians and the Hanoverians.

The Hanoverian or Hannoveraner is a German breed or stud-book of warmblood sport horse. As with other German warmblood breeds, eligibility for registration depends on performance rather than ancestry.

The Kingdom of Hanover was established in October 1814 by the Congress of Vienna, with the restoration of George III to his Hanoverian territories after the Napoleonic era. It succeeded the former Electorate of Hanover, and joined 38 other sovereign states in the German Confederation in June 1815. The kingdom was ruled by the House of Hanover, a cadet branch of the House of Welf, in personal union with Great Britain between 1714 and 1837. Since its monarch resided in London, a viceroy, usually a younger member of the British royal family, handled the administration of the Kingdom of Hanover.

Karl Wilhelm Rudolf von Bennigsen was a German politician descended from an old Hanoverian family.

The King of Hanover was the official title of the head of state and hereditary ruler of the Kingdom of Hanover, beginning with the proclamation of King George III of the United Kingdom, as "King of Hanover" during the Congress of Vienna, on 12 October 1814 at Vienna, and ending with the kingdom's annexation by Prussia on 20 September 1866.
The German-Hanoverian Party, also known as the Guelph Party, was an agrarian, federalist political party in the German Empire and the Weimar Republic. It represented the interests of Hanoverian separatists and regionalists that sought to restore the overthrown House of Welf and separate from Prussia to either become a kingdom within Germany or to become independent outright. The party was a part of the anti-Prussian faction in the Reichstag and closely cooperated with the Catholic Centre Party, including opposing Kulturkampf and centralization legislations.

The Hanover Hound is a breed of dog sometimes referred to as a Hanoverian Hound. It is a hunting and tracking dog descended from bloodhounds of medieval times. It was first introduced into France in the 1980s and is still a very rare breed. It was crossbred with the Bavarian Hound, which gave rise to the Bavarian Mountain Hound.

Wanna is a village and a municipality in the integrated municipality of Land Hadeln, Lower Saxony, Germany.

Bad Münder is a town in the Hamelin-Pyrmont district, Lower Saxony, Germany. It is on the south side of the Deister hills in the Deister-Süntel valley, about 15 kilometres (9.3 mi) northeast of Hamelin. The city with 16 districts has about 17,400 inhabitants (2020). The district Bad Münder is the administrative centre with about 8,000 inhabitants.

The Christian-National Peasants' and Farmers' Party was an agrarian political party of Weimar Germany. It developed from the German National People's Party (DNVP) in 1928.

Neuenkirchen is a municipality in the Land Hadeln collective municipality within the district of Cuxhaven, in Lower Saxony, Germany.
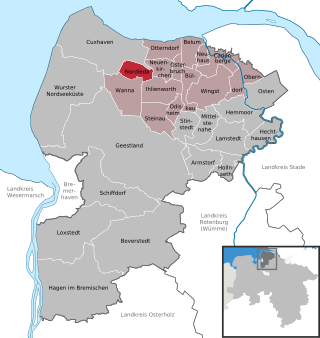
Nordleda is a municipality in the district of Cuxhaven, in Lower Saxony, Germany.

Odisheim is a municipality in the district of Cuxhaven, in Lower Saxony, Germany.

Steinau in the Land of Hadeln is a municipality in the district of Cuxhaven, in Lower Saxony, Germany.

The Rhinelander, or Rheinisches Reitpferd, is a German warmblood breed of sport horse. It is traditionally bred at the Warendorf State Stud, which it shares with the Westphalian, and is bred to the same standard as the Westphalian and other German warmbloods, such as the Bavarian Warmblood, Mecklenburger, Brandenburger, and Württemberger.
The Stade Region emerged in 1823 by an administrative reorganisation of the dominions of the Kingdom of Hanover, a sovereign state, whose then territory is almost completely part of today's German federal state of Lower Saxony. Until 1837 the Kingdom of Hanover was ruled in personal union by the Kings of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland.
The German Chancery, also known as the Hanoverian Chancery, was the official name given to the office of the Hanoverian ministry in London during the years of personal union between Great Britain and the Electorate of Hanover from 1714 until 1837. The office ceased upon the accession of Queen Victoria in the United Kingdom and King Ernest Augustus in Hanover in 1837.
The Lower Saxony State Party was a short lived regionalist political party in Germany.

Elections to the Constituent Reichstag of the North German Confederation were held on 12 February 1867, with run-off elections during the following weeks. The National Liberal Party emerged as the largest party, winning 80 seats and receiving strong support in Hanover, Kassel and Nassau. Voter turnout was around 65% in Prussian constituencies. After the Constituent Reichstag had drawn up and agreed a constitution, fresh elections were held in August.