
The history of ancient Israel and Judah begins in the Southern Levant region of Western Asia during the Late Bronze Age and Early Iron Age. "Israel" as a people or tribal confederation appears for the first time in the Merneptah Stele, an inscription from ancient Egypt that dates to about 1208 BCE, with the people group possibly being older. According to modern archaeology, ancient Israelite culture developed as an outgrowth from the Semitic Canaanites. Two related Israelite polities known as the Kingdom of Israel (Samaria) and the Kingdom of Judah had emerged in the region by Iron Age II.

Hezekiah, or Ezekias, was the son of Ahaz and the 13th king of Judah according to the Hebrew Bible.

Yahweh was an ancient Levantine deity, and national god of the Israelite kingdoms of Israel and Judah. Though no consensus exists regarding the deity's origins, scholars generally contend that Yahweh emerged as a "divine warrior" associated first with Seir, Edom, Paran and Teman, and later with Canaan. The origins of his worship reach at least to the early Iron Age, and likely to the Late Bronze Age, if not somewhat earlier.

The Israelites were a group of Semitic-speaking tribes in the ancient Near East who, during the Iron Age, inhabited a part of Canaan.

Jeconiah, also known as Coniah and as Jehoiachin, was the nineteenth and penultimate king of Judah who was dethroned by the King of Babylon, Nebuchadnezzar II in the 6th century BCE and was taken into captivity. He was the son and successor of King Jehoiakim, and the grandson of King Josiah. Most of what is known about Jeconiah is found in the Hebrew Bible. Records of Jeconiah's existence have been found in Iraq, such as the Jehoiachin's Rations Tablets. These tablets were excavated near the Ishtar Gate in Babylon and have been dated to c. 592 BCE. Written in cuneiform, they mention Jeconiah and his five sons as recipients of food rations in Babylon.
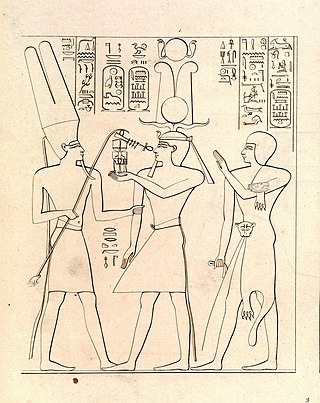
Hedjkheperre Setepenre Shoshenq I —also known as Shashank or Sheshonk or Sheshonq I—was a pharaoh of ancient Egypt and the founder of the Twenty-second Dynasty of Egypt. Of Meshwesh ancestry, Shoshenq I was the son of Nimlot A, Great Chief of the Ma, and his wife Tentshepeh A, a daughter of a Great Chief of the Ma herself; Shoshenq was thus the nephew of Osorkon the Elder, a Meshwesh king of the 21st Dynasty. He is generally presumed to be the Shishak mentioned in the Hebrew Bible, and his exploits are carved on the Bubastite Portal at Karnak.
Edwin Richard Thiele was an American Seventh-day Adventist missionary in China, an editor, archaeologist, writer, and Old Testament professor. He is best known for his chronological studies of the kingdoms of Judah and Israel.
Shishak, also spelled Shishaq or Susac, was, according to the Hebrew Bible, an Egyptian pharaoh who sacked Jerusalem in the 10th century BCE. He is usually identified with the pharaoh Shoshenq I.

Israel Finkelstein is an Israeli archaeologist, professor emeritus at Tel Aviv University and the head of the School of Archaeology and Maritime Cultures at the University of Haifa. Finkelstein is active in the archaeology of the Levant and is an applicant of archaeological data in reconstructing biblical history. He is also known for applying the exact and life sciences in archaeological and historical reconstruction. Finkelstein is the current excavator of Megiddo, a key site for the study of the Bronze and Iron Ages in the Levant.

The Kings of Judah were the monarchs who ruled over the ancient Kingdom of Judah. According to the biblical account, this kingdom was founded after the death of Saul, when the tribe of Judah elevated David to rule over it. After seven years, David became king of a reunited Kingdom of Israel. However, in about 930 BCE the united kingdom split, with ten of the twelve Tribes of Israel rejecting Solomon's son Rehoboam as their king. The tribes of Judah and Benjamin remained loyal to Rehoboam, and re-formed the Kingdom of Judah, while the other entity continued to be called the Kingdom of Israel, or just Israel.

The United Monarchy is a political entity described in the deuteronomistic history of the Hebrew Bible as, under the reigns of Saul, David, and Solomon, encompassing the territories of both the later Kingdom of Judah and Samarian Kingdom of Israel. Whether the United Monarchy existed is a matter of ongoing academic debate, and scholars remain divided between those who support the historicity of the biblical narrative, those who doubt or dismiss it, and those who support the kingdom's theoretical existence while maintaining that the biblical narrative is exaggerated. Proponents of the kingdom's existence traditionally date it to between c. 1047 BCE and c. 930 BCE.

The Omrides or Omride dynasty were the ruling dynasty of the Kingdom of Samaria founded by King Omri. According to the Bible, the Omride rulers of Israel were Omri, Ahab, Ahaziah and Jehoram. Ahab's daughter Athaliah also became queen regnant of the Kingdom of Judah.

The chronology of the Bible is an elaborate system of lifespans, 'generations', and other means by which the Masoretic Hebrew Bible measures the passage of events from the creation to around 164 BCE. It was theological in intent, not historical in the modern sense, and functions as an implied prophecy whose key lies in the identification of the final event. The passage of time is measured initially by adding the ages of the Patriarchs at the birth of their firstborn sons, later through express statements, and later still by the synchronised reigns of the kings of Israel and Judah.
Gerald "Gary" Neil Knoppers was a professor in the Department of Theology at University of Notre Dame. He wrote books and articles regarding a range of Old Testament and ancient Near Eastern topics. He is particularly renowned for his work on 1 Chronicles, writing I Chronicles 1 – 9 and I Chronicles 10 – 29, which together comprise a very significant treatment of the work of the Chronicler. In May 2005 the Canadian Society of Biblical Studies/Societe canadienne des Etudes bibliques granted the R. B. Y. Scott Award to Knoppers for his two-volume Anchor Bible commentary on I Chronicles

The siege of Jerusalem was a military campaign carried out by Nebuchadnezzar II, king of the Neo-Babylonian Empire, in which he besieged Jerusalem, then capital of the Kingdom of Judah. The city surrendered, with king Jeconiah of Judah deported to Babylon and replaced by his Babylonian-appointed uncle, Zedekiah. The siege was recorded by both the Hebrew Bible and the Babylonian Nebuchadnezzar Chronicle.
The Mysterious Numbers of the Hebrew Kings (1951) is a reconstruction of the chronology of the kingdoms of Israel and Judah by Edwin R. Thiele. The book was originally his doctoral dissertation and is widely regarded as the definitive work on the chronology of Hebrew Kings. The book is considered the classic and comprehensive work in reckoning the accession of kings, calendars, and co-regencies, based on biblical and extra-biblical sources.

Yehud, also known as Yehud Medinata or Yehud Medinta, was an administrative province of the Achaemenid Persian Empire in the region of Judea that functioned as a self-governing region under its local Jewish population. The province was a part of the Persian satrapy of Eber-Nari, and continued to exist for two centuries until its incorporation into the Hellenistic empires following the conquests of Alexander the Great.

Moshe Garsiel is professor emeritus of Bible at Bar-Ilan University.













