
The western tanager, is a medium-sized American songbird. Formerly placed in the tanager family (Thraupidae), other members of its genus and it are classified in the cardinal family (Cardinalidae). The species's plumage and vocalizations are similar to other members of the cardinal family.
Articles on forestry topics include:.

Diameter at breast height, or DBH, is a standard method of expressing the diameter of the trunk or bole of a standing tree. DBH is one of the most common dendrometric measurements.
A cruising rod is a simple device used to quickly estimate the number of pieces of lumber yielded by a given piece of timber. Similarly to a yardstick, it is a rod with markings. The estimation is carried out as follows. Standing at arm's length from the tree, estimate its average diameter by taking a note on the rod's markings. Walk away to see the whole tree; hold the rod upright at the distance from the eye at which the rod and the tree appear of the same diameter; the noted mark on the rod will show an approximate location of an 2.4-metre (8 ft) log cut along the tree height.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and guide to forestry:
Basal area is the cross-sectional area of trees at breast height. It is a common way to describe stand density. In forest management, basal area usually refers to merchantable timber and is given on a per hectare or per acre basis. If one cut down all the merchantable trees on an acre at 4.5 feet (1.4 m) off the ground and measured the square inches on the top of each stump (πr*r), added them all together and divided by square feet, that would be the basal area on that acre. In forest ecology, basal area is used as a relatively easily-measured surrogate of total forest biomass and structural complexity, and change in basal area over time is an important indicator of forest recovery during succession .

Carya tomentosa, commonly known as mockernut hickory, mockernut, white hickory, whiteheart hickory, hognut, bullnut, is a species of tree in the walnut family Juglandaceae. The most abundant of the hickories, and common in the eastern half of the United States, it is long lived, sometimes reaching the age of 500 years. A straight-growing hickory, a high percentage of its wood is used for products where strength, hardness, and flexibility are needed. The wood makes excellent fuel wood, as well. The leaves turn yellow in Autumn.

Tree taper is the degree to which a tree's stem or bole decreases in diameter as a function of height above ground. Within Forestry and for the purposes of timber production, trees with a high degree of taper are said to have poor form, while those with low taper have good form. The opposite is the case for open-grown amenity trees. The form of a tree is sometimes quantified by the Girard form class, which is the ratio, expressed as a percentage, of the butt-log scaling diameter to diameter at breast height.

A diameter tape (D-tape) is a measuring tape used to estimate the diameter of a cylinder object, typically the stem of a tree or pipe. A diameter tape has either metric or imperial measurements reduced by the value of π. This means the tape measures the diameter of the object. It is assumed that the cylinder object is a perfect circle. The diameter tape provides an approximation of diameter; most commonly used in dendrometry.

Tree allometry establishes quantitative relations between some key characteristic dimensions of trees and other properties. To the extent these statistical relations, established on the basis of detailed measurements on a small sample of typical trees, hold for other individuals, they permit extrapolations and estimations of a host of dendrometric quantities on the basis of a single measurements.
A volume table is a chart to aid in the estimation of standing timber volume. These tables are based on volume equations and use correlations between certain aspects of a tree to estimate the volume to a degree of certainty. The diameter at breast height (DBH) and the merchantable height are used to determine the total volume. Difficulties occur when estimating the form class of the tree in question. The Mesavage and Girard form classes used to classify the trees to decide which volume table should be used. These volume tables are also based on different log rules such a Scribner, Doyle, and International 1⁄4 in (6.4 mm) scale. In order to be effective, the proper form class must be selected as well as accurate DBH and height measurements.
Forest inventory is the systematic collection of data and forest information for assessment or analysis. An estimate of the value and possible uses of timber is an important part of the broader information required to sustain ecosystems. When taking forest inventory the following are important things to measure and note: species, diameter at breast height (DBH), height, site quality, age, and defects. From the data collected one can calculate the number of trees per acre, the basal area, the volume of trees in an area, and the value of the timber. Inventories can be done for other reasons than just calculating the value. A forest can be cruised to visually assess timber and determine potential fire hazards and the risk of fire. The results of this type of inventory can be used in preventive actions and also awareness. Wildlife surveys can be undertaken in conjunction with timber inventory to determine the number and type of wildlife within a forest. The aim of the statistical forest inventory is to provide comprehensive information about the state and dynamics of forests for strategic and management planning. Merely looking at the forest for assessment is called taxation.
Stand density index is a measure of the stocking of a stand of trees based on the number of trees per unit area and diameter at breast height (DBH) of the tree of average basal area, also known as the quadratic mean diameter. It may also be defined as the degree of crowding within stocked areas, using various growing space ratios based on crown length or diameter, tree height or diameter, and spacing. Stand density index is usually well correlated with stand volume and growth, and several variable-density yield tables have been created using it. Basal area, however, is usually satisfactory as a measure of stand density index and because it is easier to calculate it is usually preferred over SDI. Stand density index is also the basis for Stand density management diagrams.
The Biltmore stick is a tool used by foresters to estimate tree trunk diameter at breast height. The tool very often includes a hypsometer scale to estimate height as well. It looks much like an everyday yardstick. With practice a Biltmore stick is considered to be exceptionally accurate, often within half an inch on diameters. Some foresters use the tool regularly, however, many prefer to use more accurate tools such as a diameter tape to measure diameter at breast height (DBH) and a clinometer to measure height. On the other end of the spectrum, some foresters consider the use of a Biltmore stick to be no more accurate than their own visual estimates, and make it practice for their surveys to be largely completed in this manner.
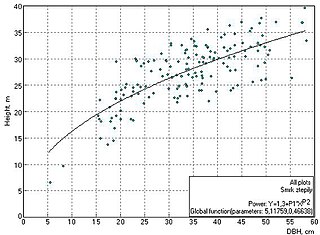
Dendrometry is the branch of forestry that is concerned with the measurement of the various dimensions of trees, such as their diameter, size, shape, age, overall volume, thickness of the bark, etc., as well as the statistical properties of tree stands, including measures of central tendency and dispersion of these quantities, wood density, or yearly growth, for instance.
In forestry, quadratic mean diameter or QMD is a measure of central tendency which is considered more appropriate than arithmetic mean for characterizing the group of trees which have been measured. For n trees, QMD is calculated using the quadratic mean formula:

Pseudotsuga menziesii var. menziesii, commonly known as Coast Douglas-fir, Pacific Douglas-fir, Oregon pine, or Douglas spruce, is an evergreen conifer native to western North America from west-central British Columbia, Canada southward to central California, United States. In Oregon and Washington its range is continuous from the Cascades crest west to the Pacific Coast Ranges and Pacific Ocean. In California, it is found in the Klamath and California Coast Ranges as far south as the Santa Lucia Mountains with a small stand as far south as the Purisima Hills, Santa Barbara County. In the Sierra Nevada it ranges as far south as the Yosemite region. It occurs from near sea level along the coast to 1,800 metres (5,900 ft) in the California Mountains. Further inland, coast Douglas-fir is replaced by Rocky Mountain or interior Douglas-fir. Interior Douglas-fir intergrades with coast Douglas-fir in the Cascades of northern Washington and southern British Columbia.
Tree volume is one of many parameters that are measured to document the size of individual trees. Tree volume measurements serve a variety of purposes, some economic, some scientific, and some for sporting competitions. Measurements may include just the volume of the trunk, or the volume of the trunk and the branches depending on the detail needed and the sophistication of the measurement methodology.
Judson Freeman Clark was a Canadian forester and mycologist. He is famous for publishing in 1906, what is now known as the International 1/8-Inch Log Rule, which he modified in 1917 for 1/4-inch saw kerf.






