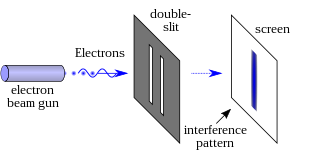
In modern physics, the double-slit experiment is a demonstration that light and matter can display characteristics of both classically defined waves and particles; moreover, it displays the fundamentally probabilistic nature of quantum mechanical phenomena. This type of experiment was first performed by Thomas Young in 1801, as a demonstration of the wave behavior of visible light. At that time it was thought that light consisted of either waves or particles. With the beginning of modern physics, about a hundred years later, it was realized that light could in fact show behavior characteristic of both waves and particles. In 1927, Davisson and Germer demonstrated that electrons show the same behavior, which was later extended to atoms and molecules. Thomas Young's experiment with light was part of classical physics long before the development of quantum mechanics and the concept of wave–particle duality. He believed it demonstrated that Christiaan Huygens' wave theory of light was correct, and his experiment is sometimes referred to as Young's experiment or Young's slits.

A microscope is a laboratory instrument used to examine objects that are too small to be seen by the naked eye. Microscopy is the science of investigating small objects and structures using a microscope. Microscopic means being invisible to the eye unless aided by a microscope.
Wave–particle duality is the concept in quantum mechanics that every particle or quantum entity may be described as either a particle or a wave. It expresses the inability of the classical concepts "particle" or "wave" to fully describe the behaviour of quantum-scale objects. As Albert Einstein wrote:
It seems as though we must use sometimes the one theory and sometimes the other, while at times we may use either. We are faced with a new kind of difficulty. We have two contradictory pictures of reality; separately neither of them fully explains the phenomena of light, but together they do.
Matter waves are a central part of the theory of quantum mechanics, being half of wave–particle duality. All matter exhibits wave-like behavior. For example, a beam of electrons can be diffracted just like a beam of light or a water wave.

Sumio Iijima is a Japanese physicist and inventor, often cited as the inventor of carbon nanotubes. Although carbon nanotubes had been observed prior to his "invention", Iijima's 1991 paper generated unprecedented interest in the carbon nanostructures and has since fueled intense research in the area of nanotechnology.

Jack Steinberger was a German-born American physicist noted for his work with neutrinos, the subatomic particles considered to be elementary constituents of matter. He was a recipient of the 1988 Nobel Prize in Physics, along with Leon M. Lederman and Melvin Schwartz, for the discovery of the muon neutrino. Through his career as an experimental particle physicist, he held positions at the University of California, Berkeley, Columbia University (1950–68), and the CERN (1968–86). He was also a recipient of the United States National Medal of Science in 1988, and the Matteucci Medal from the Italian Academy of Sciences in 1990.

Alec Nigel Broers, Baron Broers, is a British electrical engineer.

David John Hugh Cockayne FRS FInstP was Professor in the physical examination of materials in the Department of Materials at the University of Oxford and professorial fellow at Linacre College from 2000 to 2009. He was the president of the International Federation of Societies for Microscopy from 2003 till 2007, then vice-president 2007 to 2010.

Virgilio Tosi was an Italian documentary filmmaker and historian of early film.

Ernst G. Bauer is a German-American physicist known for his studies in the field of surface science, thin film growth and nucleation mechanisms and the invention in 1962 of the Low Energy Electron Microscopy (LEEM). In the early 1990s, he extended the LEEM technique in two directions by developing Spin-Polarized Low Energy Electron Microscopy (SPLEEM) and Spectroscopic Photo Emission and Low Energy Electron Microscopy (SPELEEM). He is currently Distinguished Research Professor Emeritus at the Arizona State University.

The Istituto Italiano di Tecnologia (IIT) (in English: Italian Institute of Technology) is a scientific research centre based in Genoa (Italy, EU). Its main goal is the advancement of science, in Italy and worldwide, through projects and discoveries oriented to applications and technology. Some account IIT as the best Italian scientific research centre.
Knut W. Urban is a German physicist. He has been the Director of the Institute of Microstructure Research at Forschungszentrum Jülich from 1987 to 2010.

John Gordon King (1925–2014) was an English-born American physicist who was the Francis Friedman Professor of Physics (emeritus) at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, the former director of MIT’s Molecular Beam Laboratory, and the former associate director of MIT’s Research Laboratory of Electronics.

Antonio Ereditato is an Italian physicist, currently associate researcher at Fermilab, Batavia, USA, and Emeritus professor at the University of Bern, Switzerland, where he has been Director of the Laboratory for High Energy Physics from 2006 to 2020. From 2021 to 2022 he has been Visiting Professor at the Yale University, USA. He carried out research activities in the field of experimental neutrino physics, of weak interactions and strong interactions with experiments conducted at CERN, in Japan, at Fermilab in United States and at the LNGS in Italy. Ereditato has accomplished several R&D studies on particle detectors: wire chambers, calorimeters, time projection chambers, nuclear emulsions, detectors for medical applications.

Harald Rose is a German physicist.

Peter Jenni, is an experimental particle physicist working at CERN. He is best known as one of the "founding fathers" of the ATLAS experiment at the CERN Large Hadron Collider together with a few other colleagues. He acted as spokesperson of the ATLAS Collaboration until 2009. ATLAS is a world-wide collaboration which started in 1992 involving roughly 3,000 physicists at 183 institutions in 38 countries. Jenni was directly involved in the experimental work leading to the discoveries of the W and Z bosons in the 1980s and the Higgs boson in 2012. He is (co-)author of about 1000 publications in scientific journals.

(George) Andrew Davidson Briggs is a British scientist. He is Professor of Nanomaterials in the Department of Materials at the University of Oxford. He is best known for his early work in acoustic microscopy and his current work in materials for quantum technologies.
Massimilla "Milla" Baldo-Ceolin was an Italian particle physicist.
Elmar Zeitler was a German physicist.

Patrizio Bianchi is an Italian economist and academic, current chairholder of the UNESCO Chair in Education, Growth and Equality. He served as minister of education in the Draghi Cabinet from 2021 to 2022.