
In optics, chromatic aberration (CA), also called chromatic distortion, color aberration, color fringing, or purple fringing, is a failure of a lens to focus all colors to the same point. It is caused by dispersion: the refractive index of the lens elements varies with the wavelength of light. The refractive index of most transparent materials decreases with increasing wavelength. Since the focal length of a lens depends on the refractive index, this variation in refractive index affects focusing. Since the focal length of the lens varies with the color of the light different colors of light are brought to focus at different distances from the lens or with different levels of magnification. Chromatic aberration manifests itself as "fringes" of color along boundaries that separate dark and bright parts of the image.

Stereoscopy is a technique for creating or enhancing the illusion of depth in an image by means of stereopsis for binocular vision. The word stereoscopy derives from Greek στερεός (stereos) 'firm, solid' and σκοπέω (skopeō) 'to look, to see'. Any stereoscopic image is called a stereogram. Originally, stereogram referred to a pair of stereo images which could be viewed using a stereoscope.

An image scanner is a device that optically scans images, printed text, handwriting, or an object and converts it to a digital image. The most common type of scanner used in the home and the office is the flatbed scanner, where the document is placed on a glass bed. A sheetfed scanner, which moves the page across an image sensor using a series of rollers, may be used to scan one page of a document at a time or multiple pages, as in an automatic document feeder. A handheld scanner is a portable version of an image scanner that can be used on any flat surface. Scans are typically downloaded to the computer that the scanner is connected to, although some scanners are able to store scans on standalone flash media.
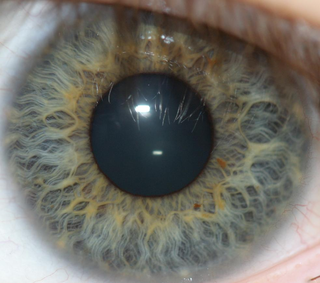
Iris recognition is an automated method of biometric identification that uses mathematical pattern-recognition techniques on video images of one or both of the irises of an individual's eyes, whose complex patterns are unique, stable, and can be seen from some distance. The discriminating powers of all biometric technologies depend on the amount of entropy they are able to encode and use in matching. Iris recognition is exceptional in this regard, enabling the avoidance of "collisions" even in cross-comparisons across massive populations. Its major limitation is that image acquisition from distances greater than a meter or two, or without cooperation, can be very difficult. However, the technology is in development and iris recognition can be accomplished from even up to 10 meters away or in a live camera feed.

Color photography is photography that uses media capable of capturing and reproducing colors. By contrast, black-and-white or gray-monochrome photography records only a single channel of luminance (brightness) and uses media capable only of showing shades of gray.

An autostereogram is a two-dimensional (2D) image that can create the optical illusion of a three-dimensional (3D) scene. Autostereograms use only one image to accomplish the effect while normal stereograms require two. The 3D scene in an autostereogram is often unrecognizable until it is viewed properly, unlike typical stereograms. Viewing any kind of stereogram properly may cause the viewer to experience vergence-accommodation conflict.

A facial recognition system is a technology potentially capable of matching a human face from a digital image or a video frame against a database of faces. Such a system is typically employed to authenticate users through ID verification services, and works by pinpointing and measuring facial features from a given image.
The McCollough effect is a phenomenon of human visual perception in which colorless gratings appear colored contingent on the orientation of the gratings. It is an aftereffect requiring a period of induction to produce it. For example, if someone alternately looks at a red horizontal grating and a green vertical grating for a few minutes, a black-and-white horizontal grating will then look greenish and a black-and-white vertical grating will then look pinkish. The effect is remarkable because, although it diminishes rapidly with repeated testing, it has been reported to last up to 2.8 months when exposure to testing is limited.
The implicit-association test (IAT) is an assessment intended to detect subconscious associations between mental representations of objects (concepts) in memory. Its best-known application is the assessment of implicit stereotypes held by test subjects, such as associations between particular racial categories and stereotypes about those groups. The test has been applied to a variety of belief associations, such as those involving racial groups, gender, sexuality, age, and religion but also the self-esteem, political views, and predictions of the test taker. The implicit-association test is the subject of significant academic and popular debate regarding its validity, reliability, and usefulness in assessing implicit bias.

The British Rail Class 28 diesel-electric locomotives, known variously as 'Metrovicks', 'Crossleys' or 'Co-Bos', were built under the Pilot Scheme for diesel locomotives as part of the British Railways 1955 Modernisation Plan.
In online marketing, a landing page, sometimes known as a "lead capture page", "single property page", "static page", "squeeze page" or a "destination page", is a single web page that appears in response to clicking on a search engine optimized search result, marketing promotion, marketing email or an online advertisement. The landing page will usually display directed sales copy that is a logical extension of the advertisement, search result or link. Landing pages are used for lead generation. The actions that a visitor takes on a landing page are what determine an advertiser's conversion rate. A landing page may be part of a microsite or a single page within an organization's main web site.

Image stitching or photo stitching is the process of combining multiple photographic images with overlapping fields of view to produce a segmented panorama or high-resolution image. Commonly performed through the use of computer software, most approaches to image stitching require nearly exact overlaps between images and identical exposures to produce seamless results, although some stitching algorithms actually benefit from differently exposed images by doing high-dynamic-range imaging in regions of overlap. Some digital cameras can stitch their photos internally.

High-speed photography is the science of taking pictures of very fast phenomena. In 1948, the Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers (SMPTE) defined high-speed photography as any set of photographs captured by a camera capable of 69 frames per second or greater, and of at least three consecutive frames. High-speed photography can be considered to be the opposite of time-lapse photography.

Color motion picture film refers both to unexposed color photographic film in a format suitable for use in a motion picture camera, and to finished motion picture film, ready for use in a projector, which bears images in color.
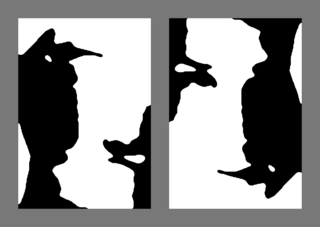
The Mooney Face Test, developed by Craig M. Mooney, was first introduced in his 1957 article “Age in the development of closure ability in children.” Participants in the test are shown series of black and white distorted photographs, presented in such a way that would require them to perform closure. The law of closure is one of the seven Gestalt principles that describes a tendency of our perception to view an incomplete object as continuing and complete. The test assumes that perception is based on the collected information taken from the different regions of the image, which then constitute a holistic representation of a face. Today, there are many iterations of the Mooney Face Test, a number of which contain images that involve image color inversion and facial feature scrambling.
The Facial Recognition Technology (FERET) program was a government-sponsored project that aimed to create a large, automatic face-recognition system for intelligence, security, and law enforcement purposes. The program began in 1993 under the combined leadership of Dr. Harry Wechsler at George Mason University (GMU) and Dr. Jonathon Phillips at the Army Research Laboratory (ARL) in Adelphi, Maryland and resulted in the development of the Facial Recognition Technology (FERET) database. The goal of the FERET program was to advance the field of face recognition technology by establishing a common database of facial imagery for researchers to use and setting a performance baseline for face-recognition algorithms.
Videotelephony as a concept began to materialize shortly after the telephone was patented in 1876, and its history is closely connected to that of the telephone.

Pixel Camera is a camera phone application developed by Google for the Android operating system on Google Pixel devices. Development with zoom lenses for the application began in 2011 at the Google X research incubator led by Marc Levoy, which was developing image fusion technology for Google Glass. It was publicly released for Android 4.4+ on the Google Play on April 16, 2014. The app was initially released as Google Camera and supported on all devices running Android 4.4 KitKat and higher. However, in October 2023, coinciding with the release of the Pixel 8 series, it was renamed to Pixel Camera and became officially supported only on Google Pixel devices.
Michael Burton FBA is an English psychologist and professor at the Department of Psychology at University of York.
Association in psychology refers to a mental connection between concepts, events, or mental states that usually stems from specific experiences. Associations are seen throughout several schools of thought in psychology including behaviorism, associationism, psychoanalysis, social psychology, and structuralism. The idea stems from Plato and Aristotle, especially with regard to the succession of memories, and it was carried on by philosophers such as John Locke, David Hume, David Hartley, and James Mill. It finds its place in modern psychology in such areas as memory, learning, and the study of neural pathways.













