Related Research Articles
A file archiver is a computer program that combines a number of files together into one archive file, or a series of archive files, for easier transportation or storage. File archivers may employ lossless data compression in their archive formats to reduce the size of the archive.
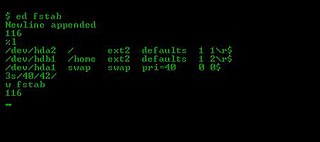
ed is a line editor for Unix and Unix-like operating systems. It was one of the first parts of the Unix operating system that was developed, in August 1969. It remains part of the POSIX and Open Group standards for Unix-based operating systems, alongside the more sophisticated full-screen editor vi.

Multics is an influential early time-sharing operating system based on the concept of a single-level memory. Nathan Gregory writes that Multics "has influenced all modern operating systems since, from microcomputers to mainframes."

A Unix shell is a command-line interpreter or shell that provides a command line user interface for Unix-like operating systems. The shell is both an interactive command language and a scripting language, and is used by the operating system to control the execution of the system using shell scripts.

The PDP-7 is an 18-bit minicomputer produced by Digital Equipment Corporation as part of the PDP series. Introduced in 1964, shipped since 1965, it was the first to use their Flip-Chip technology. With a cost of US$72,000, it was cheap but powerful by the standards of the time. The PDP-7 is the third of Digital's 18-bit machines, with essentially the same instruction set architecture as the PDP-4 and the PDP-9.

The GE 645 mainframe computer was a development of the GE 635 for use in the Multics project. This was the first computer that implemented a configurable hardware protected memory system. It was designed to satisfy the requirements of Project MAC to develop a platform that would host their proposed next generation time-sharing operating system (Multics) and to meet the requirements of a theorized computer utility. The system was the first truly symmetric multiprocessing machine to use virtual memory, it was also among the first machines to implement what is now known as a translation lookaside buffer, the foundational patent for which was granted to John Couleur and Edward Glaser.
TYPSET is an early document editor that was used with the 1964-released RUNOFF program, one of the earliest text formatting programs to see significant use.
In computing, a symbolic link is a file whose purpose is to point to a file or directory by specifying a path thereto.

In Unix-like and some other operating systems, the pwd command writes the full pathname of the current working directory to the standard output.

The Compatible Time-Sharing System (CTSS) was the first general purpose time-sharing operating system. Compatible Time Sharing referred to time sharing which was compatible with batch processing; it could offer both time sharing and batch processing concurrently.
In computing, echo is a command that outputs the strings that are passed to it as arguments. It is a command available in various operating system shells and typically used in shell scripts and batch files to output status text to the screen or a computer file, or as a source part of a pipeline.
In computing, a shell is a computer program that exposes an operating system's services to a human user or other programs. In general, operating system shells use either a command-line interface (CLI) or graphical user interface (GUI), depending on a computer's role and particular operation. It is named a shell because it is the outermost layer around the operating system.

Louis Pouzin is a French computer scientist. He designed a pioneering packet communications network, CYCLADES that was the first to implement the end-to-end principle, which became fundamental to the design of the Internet.
RUNCOM is a CTSS macro command (script) processor.

Unix is a family of multitasking, multi-user computer operating systems that derive from the original AT&T Unix, whose development started in 1969 at the Bell Labs research center by Ken Thompson, Dennis Ritchie, and others.
In computing, a script is a relatively short and simple set of instructions that typically automate an otherwise manual process. The act of writing a script is called scripting. Scripting language or script language describes a programming language that it is used for scripting.
Tom Van Vleck is an American computer software engineer.
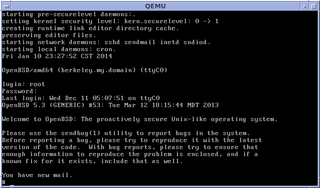
Many computer systems display a message of the day or welcome message when a user first connects to them, logs in to them, or starts them. It is a way of sending a common message to all users, and may include information about system changes, system availability, and so on. More recently, systems have displayed personalized messages of the day.

A command-line interface (CLI) is a means of interacting with a computer program by inputting lines of text called command-lines. Command-line interfaces emerged in the mid-1960s, on computer terminals, as an interactive and more user-friendly alternative to the non-interactive interface available with punched cards.
The history of email entails an evolving set of technologies and standards that culminated in the email systems in use today.
References
- 1 2 Shevinsky, Elissa (2015). Lean Out: The Struggle for Gender Equality in Tech and Start-up Culture. OR Books. ISBN 978-1939293862.
- 1 2 3 "The Origin of the Shell". www.multicians.org. Retrieved 2017-04-12.
- ↑ Metz, Cade (3 January 2013). "Say Bonjour to the Internet's Long-Lost French Uncle". WIRED. Retrieved 31 July 2017.
- ↑ "Unix Shells". Archived from the original on 2017-12-21. Retrieved 2017-08-21.
- ↑ Pat Crisman; Glenda Schroeder; Louis Pouzin. "Programming Staff Note 39, 'Proposed Minimum System Documentation'" (PDF).
- ↑ "The History of Electronic Mail". www.multicians.org. Retrieved 21 August 2017.
- 1 2 Van Vleck, T. (January 2012). "Electronic Mail and Text Messaging in CTSS, 1965-1973". IEEE Annals of the History of Computing. 34 (1): 4–6. doi:10.1109/MAHC.2012.6. S2CID 201795798.
- ↑ Boryczka, Urszula; Probierz, Barbara; Kozak, Jan (2016). "Automatic Categorization of Email into Folders by Ant Colony Decision Tree and Social Networks". Intelligent Decision Technologies 2016. Smart Innovation, Systems and Technologies. Vol. 57. pp. 71–81. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-39627-9_7. ISBN 978-3-319-39626-2.
