Related Research Articles

The Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD), known informally as the Biodiversity Convention, is a multilateral treaty. The Convention has three main goals: the conservation of biological diversity ; the sustainable use of its components; and the fair and equitable sharing of benefits arising from genetic resources. Its objective is to develop national strategies for the conservation and sustainable use of biological diversity, and it is often seen as the key document regarding sustainable development.

Electronic mail is a method of exchanging messages ("mail") between people using electronic devices. Email was thus conceived as the electronic (digital) version of, or counterpart to, mail, at a time when "mail" meant only physical mail. Email later became a ubiquitous communication medium, to the point that in current use, an email address is often treated as a basic and necessary part of many processes in business, commerce, government, education, entertainment, and other spheres of daily life in most countries.

The history of the Internet has its origin in information theory and the efforts of scientists and engineers to build and interconnect computer networks. The Internet Protocol Suite, the set of rules used to communicate between networks and devices on the Internet, arose from research and development in the United States and involved international collaboration, particularly with researchers in the United Kingdom and France.

The Internet is the global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate between networks and devices. It is a network of networks that consists of private, public, academic, business, and government networks of local to global scope, linked by a broad array of electronic, wireless, and optical networking technologies. The Internet carries a vast range of information resources and services, such as the inter-linked hypertext documents and applications of the World Wide Web (WWW), electronic mail, telephony, and file sharing.

A local area network (LAN) is a computer network that interconnects computers within a limited area such as a residence, school, laboratory, university campus or office building. By contrast, a wide area network (WAN) not only covers a larger geographic distance, but also generally involves leased telecommunication circuits.

Short Message/Messaging Service, commonly abbreviated as SMS, is a text messaging service component of most telephone, Internet and mobile device systems. It uses standardized communication protocols that let mobile devices exchange short text messages. An intermediary service can facilitate a text-to-voice conversion to be sent to landlines.
Automatic Link Establishment, commonly known as ALE, is the worldwide de facto standard for digitally initiating and sustaining HF radio communications. ALE is a feature in an HF communications radio transceiver system that enables the radio station to make contact, or initiate a circuit, between itself and another HF radio station or network of stations. The purpose is to provide a reliable rapid method of calling and connecting during constantly changing HF ionospheric propagation, reception interference, and shared spectrum use of busy or congested HF channels.
Interoperability is a characteristic of a product or system to work with other products or systems. While the term was initially defined for information technology or systems engineering services to allow for information exchange, a broader definition takes into account social, political, and organizational factors that impact system-to-system performance.

Iran's telecommunications industry is almost entirely state-owned, dominated by the Telecommunication Company of Iran (TCI). Fixed-line penetration in 2004 was relatively well-developed by regional standards, standing at 22 lines per 100 people, higher than Egypt with 14 and Saudi Arabia with 15, although behind the UAE with 27. Iran had more than 1 mobile phone per inhabitant by 2012.
Direct Connect (DC) is a peer-to-peer file sharing protocol. Direct Connect clients connect to a central hub and can download files directly from one another. Advanced Direct Connect can be considered a successor protocol.
The Organization for the Advancement of Structured Information Standards is a nonprofit consortium that works on the development, convergence, and adoption of open standards for cybersecurity, blockchain, Internet of things (IoT), emergency management, cloud computing, legal data exchange, energy, content technologies, and other areas.

Internet access is the ability of individuals and organizations to connect to the Internet using computer terminals, computers, and other devices; and to access services such as email and the World Wide Web. Internet access is sold by Internet service providers (ISPs) delivering connectivity at a wide range of data transfer rates via various networking technologies. Many organizations, including a growing number of municipal entities, also provide cost-free wireless access and landlines.

Robert Elliot Kahn is an American electrical engineer, who, along with Vint Cerf, first proposed the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and the Internet Protocol (IP), the fundamental communication protocols at the heart of the Internet.
An anonymous P2P communication system is a peer-to-peer distributed application in which the nodes, which are used to share resources, or participants are anonymous or pseudonymous. Anonymity of participants is usually achieved by special routing overlay networks that hide the physical location of each node from other participants.
Delay-tolerant networking (DTN) is an approach to computer network architecture that seeks to address the technical issues in heterogeneous networks that may lack continuous network connectivity. Examples of such networks are those operating in mobile or extreme terrestrial environments, or planned networks in space.
Peer-to-peer file sharing is the distribution and sharing of digital media using peer-to-peer (P2P) networking technology. P2P file sharing allows users to access media files such as books, music, movies, and games using a P2P software program that searches for other connected computers on a P2P network to locate the desired content. The nodes (peers) of such networks are end-user computers and distribution servers.
A Patient Safety Organization (PSO) is a group, institution, or association that improves medical care by reducing medical errors. Common functions of patient safety organizations are data collection and analysis, reporting, education, funding, and advocacy. A PSO differs from a Federally designed Patient Safety Organization (PSO), which provides health care providers in the U.S. privilege and confidentiality protections for efforts to improve patient safety and the quality of patient care delivery

Food safety in China is a concern relating to agriculture in the world's most populated country. China's principal crops are rice, corn, wheat, soybeans, and cotton in addition to apples and other fruits and vegetables. China's principal livestock products include pork, beef, dairy, and eggs. The Chinese government oversees agricultural production as well as the manufacture of food packaging, containers, chemical additives, drug production, and business regulation. In recent years, the Chinese government attempted to consolidate food safety regulation with the creation of the State Food and Drug Administration of China in 2003; officials have also been under increasing public and international pressure to solve food safety problems. Chinese Vice Premier Li Keqiang said, "Food is essential, and safety should be a top priority. Food safety is closely related to people's lives and health and economic development and social harmony," at a State Council meeting in Beijing.
MTConnect is a manufacturing technical standard to retrieve process information from numerically controlled machine tools. As explained by a member of the team that developed it, "This standard specifies the open-source, royalty-free communications protocol based on XML and HTTP Internet technology for real-time data sharing between shopfloor equipment such as machine tools and computer systems. MTConnect provides a common vocabulary with standardized definitions for the meaning of data that machine tools generate, making the data interpretable by software applications." A simple, real-world example of how this tool is used to improve shop management is given by the same author.
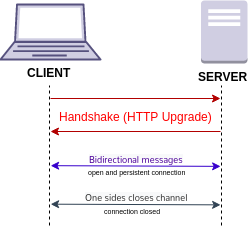
WebSocket is a computer communications protocol, providing full-duplex communication channels over a single TCP connection. The WebSocket protocol was standardized by the IETF as RFC 6455 in 2011. The current API specification allowing web applications to use this protocol is known as WebSockets. It is a living standard maintained by the WHATWG and a successor to The WebSocket API from the W3C.
References
- ↑ "GISIN – Global Invasive Species Information Network (gisin) – Home". Archived from the original on 2017-09-26. Retrieved 2008-06-09.
- ↑ "Draft of proposed GISIN data-sharing protocol". Archived from the original on 2011-07-27. Retrieved 2008-06-25.