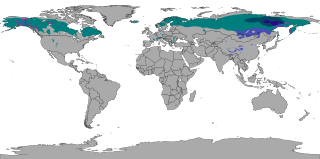
The subarctic climate is a continental climate with long, cold winters, and short, warm to cool summers. It is found on large landmasses, often away from the moderating effects of an ocean, generally at latitudes from 50°N to 70°N, poleward of the humid continental climates. Subarctic or boreal climates are the source regions for the cold air that affects temperate latitudes to the south in winter. These climates represent Köppen climate classification Dfc, Dwc, Dsc, Dfd, Dwd and Dsd.

Prairies are ecosystems considered part of the temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands biome by ecologists, based on similar temperate climates, moderate rainfall, and a composition of grasses, herbs, and shrubs, rather than trees, as the dominant vegetation type. Temperate grassland regions include the Pampas of Argentina, Brazil and Uruguay, and the steppe of Ukraine, Russia, and Kazakhstan. Lands typically referred to as "prairie" tend to be in North America. The term encompasses the area referred to as the Interior Lowlands of Canada, the United States, and Mexico, which includes all of the Great Plains as well as the wetter, hillier land to the east.

A grassland is an area where the vegetation is dominated by grasses (Poaceae). However, sedge (Cyperaceae) and rush (Juncaceae) can also be found along with variable proportions of legumes, like clover, and other herbs. Grasslands occur naturally on all continents except Antarctica and are found in most ecoregions of the Earth. Furthermore, grasslands are one of the largest biomes on Earth and dominate the landscape worldwide. There are different types of grasslands: natural grasslands, semi-natural grasslands, and agricultural grasslands. They cover 31–69% of the Earth's land area.
Alberta is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. Located in Western Canada, the province has an area of 661,190 km2 (255,290 sq mi) and is bounded to the south by the United States state of Montana along 49° north for 298 km (185 mi); to the east at 110° west by the province of Saskatchewan for 1,223 km (760 mi); and at 60° north the Northwest Territories for 644 km (400 mi). The southern half of the province borders British Columbia along the Continental Divide of the Americas on the peaks of the Rocky Mountains, while the northern half borders British Columbia along the 120th meridian west. Along with Saskatchewan it is one of only two landlocked provinces or territories.

Rangelands are grasslands, shrublands, woodlands, wetlands, and deserts that are grazed by domestic livestock or wild animals. Types of rangelands include tallgrass and shortgrass prairies, desert grasslands and shrublands, woodlands, savannas, chaparrals, steppes, and tundras. Rangelands do not include forests lacking grazable understory vegetation, barren desert, farmland, or land covered by solid rock, concrete and/or glaciers.

The tallgrass prairie is an ecosystem native to central North America. Historically, natural and anthropogenic fire, as well as grazing by large mammals provided periodic disturbances to these ecosystems, limiting the encroachment of trees, recycling soil nutrients, and facilitating seed dispersal and germination. Prior to widespread use of the steel plow, which enabled large scale conversion to agricultural land use, tallgrass prairies extended throughout the American Midwest and smaller portions of southern central Canada, from the transitional ecotones out of eastern North American forests, west to a climatic threshold based on precipitation and soils, to the southern reaches of the Flint Hills in Oklahoma, to a transition into forest in Manitoba.

The Driftless Area, also known as Bluff Country and the Paleozoic Plateau, is a topographical and cultural region in the Midwestern United States that comprises southwestern Wisconsin, southeastern Minnesota, northeastern Iowa, and the extreme northwestern corner of Illinois. The Driftless Area is a USDA Level III Ecoregion: Ecoregion 52. The Driftless Area takes up a large portion of the Upper Midwest forest–savanna transition. The Blufflands refers to the eastern section of the Driftless area in Minnesota, due to the steep bluffs and cliffs around the river valleys. The western half is known as the Rochester Plateau, which is flatter than the Blufflands. The Coulee Region refers to the southwestern part of the Driftless Area in Wisconsin. It is named for its numerous ravines.

Great River Bluffs State Park is a state park of Minnesota, United States, on the Mississippi River southeast of Winona. Originally known as O. L. Kipp State Park, it was renamed in the late 1990s to describe better its resources. The park preserves steep-sided bluffs rising 500 feet (150 m) above the river and the narrow valleys between them, which support rare and fragile plant communities. Two of the bluffs have received further protection under the Minnesota Scientific and Natural Areas program, which are known as King's and Queen's Bluff Scientific and Natural Area.

Pawnee National Grassland is a United States National Grassland located in northeastern Colorado on the Colorado Eastern Plains. The grassland is located in the South Platte River basin in remote northern and extreme northeastern Weld County between Greeley and Sterling. It comprises two parcels totaling 193,060 acres (78,130 ha) largely between State Highway 14 and the Wyoming border. The larger eastern parcel lies adjacent to the borders of both Nebraska and Wyoming. It is administered in conjunction with the Arapaho-Roosevelt National Forest from the U.S. Forest Service office in Fort Collins, with a local ranger district office in Greeley.

Aspen parkland refers to a very large area of transitional biome between prairie and boreal forest in two sections, namely the Peace River Country of northwestern Alberta crossing the border into British Columbia, and a much larger area stretching from central Alberta, all across central Saskatchewan to south central Manitoba and continuing into small parts of the US states of Minnesota and North Dakota. Aspen parkland consists of groves of aspen, poplar and spruce, interspersed with areas of prairie grasslands, also intersected by large stream and river valleys lined with aspen-spruce forests and dense shrubbery. This is the largest boreal-grassland transition zone in the world and is a zone of constant competition and tension as prairie and woodlands struggle to overtake each other within the parkland.

A water-meadow is an area of grassland subject to controlled irrigation to increase agricultural productivity. Water-meadows were mainly used in Europe from the 16th to the early 20th centuries. Working water-meadows have now largely disappeared, but the field patterns and water channels of derelict water-meadows remain common in areas where they were used, such as parts of Northern Italy, Switzerland and England. Derelict water-meadows are often of importance as wetland wildlife habitats.

Bear Rocks is a widely recognized symbol of West Virginia wilderness and among the most frequently photographed places in the state. It is a well-known landmark on the eastern edge of the plateau that includes the Dolly Sods Wilderness. It sits in a high-elevation heathland punctuated with wind-carved sandstone outcrops and is home to more than a dozen rare plant and animal species. Situated on the crest of the Allegheny Front, Bear Rocks afford vistas over the South Branch Potomac River. Visibility can extend eastward to the Shenandoah National Park in Virginia.

The Western Gulf coastal grasslands are a subtropical grassland ecoregion of the southern United States and northeastern Mexico. It is known in Louisiana as the "Cajun Prairie", Texas as "Coastal Prairie," and as the Tamaulipan pastizal in Mexico.

Cimarron National Grassland is a National Grassland located in Morton County, Kansas, United States, with a very small part extending eastward into Stevens County. Cimarron National Grassland is located near Comanche National Grassland which is across the border in Colorado. The grassland is administered by the Forest Service together with the Pike and San Isabel National Forests and the Comanche National Grassland, from common headquarters located in Pueblo, Colorado. There are local ranger district offices in Elkhart, Kansas. The grassland is the largest area of public land in the state of Kansas.

California coastal prairie, also known as northern coastal grassland, is a grassland plant community of California and Oregon in the temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands biome. This ecosystem is found along the Pacific Coast, from as far south as Los Angeles in Southern California to southern Oregon. It typically stretches as far inland as 100 km, and occurs at altitudes of 350 m or lower.

The Konza Prairie Biological Station is a 8,616-acre (3,487 ha) protected area of native tallgrass prairie in the Flint Hills of northeastern Kansas. "Konza" is an alternative name for the Kansa or Kaw Indians who inhabited this area until the mid-19th century. The Konza Prairie is owned by The Nature Conservancy and Kansas State University.
Yellow River State Forest, (YRSF), is mostly forested land owned by the Iowa Department of Natural Resources. It is located in the southeastern corner of Allamakee County, the most northeasterly of Iowa's counties. It is adjacent to the Upper Mississippi River National Wildlife and Fish Refuge and is just north of Effigy Mounds National Monument in the bluff region of the Upper Mississippi River.

Fults Hill Prairie State Natural Area, also known as the Fults Hill Prairie Nature Preserve, is an State Park and nature reserve on 997 acres (403 ha) in Monroe County, Illinois, United States. A key feature of the preserve is a 532-acre (215 ha) hill prairie located on the east bluff of the Mississippi River overlooking the American Bottom near Fults, Illinois. The Fults Hill Prairie has been listed as a National Natural Landmark.

The eastern woodlands of the United States covered large portions of the southeast side of the continent until the early 20th century. These were in a fire ecology of open grassland and forests with low ground cover of herbs and grasses.

South Chilcotin Mountains Provincial Park is a provincial park in British Columbia, Canada, located on Highway 40 northwest of Lillooet, British Columbia. The park, which is 56,796 ha. in size, was established on April 18, 2001, and It was created out of a portion of the Spruce Lake Protected Area. The park is located on three Indigenous Nations: The Tsilhqot’in, St’at’imc, and Secwepemc.





















