Related Research Articles
Zephaniah is the name of several people in the Hebrew Bible; the most prominent being the prophet who prophesied in the days of Josiah, king of Judah and is attributed a book bearing his name among the Twelve Minor Prophets. His name is commonly transliterated Sophonias in Bibles translated from the Vulgate or Septuagint. The name might mean "Yah has concealed", "[he whom] Yah has hidden", or "Yah lies in wait".

Anathoth is the name of one of the Levitical cities given to "the children of Aaron" in the tribe of Benjamin. Residents were called Antothites or Anetothites.
Seraiah or Sraya is the name of several people mentioned in the Hebrew Bible, and a name with other non-biblical uses.
The Rechabites are a biblical clan, the descendants of Rechab through Jehonadab.

Mount Ephraim, or alternatively Mount of Ephraim, was the historical name for the central mountainous district of Israel once occupied by the Tribe of Ephraim, extending from Bethel to the plain of Jezreel. In Joshua's time, approximately sometime between the 18th century BCE and the 13th century BCE, these hills were densely wooded. They were intersected by well-watered, fertile valleys, referred to in Jeremiah 50:19.

Jeremiah, also called Jeremias or the "weeping prophet", was one of the major prophets of the Hebrew Bible. According to Jewish tradition, Jeremiah authored the Book of Jeremiah, the Books of Kings and the Book of Lamentations, with the assistance and under the editorship of Baruch ben Neriah, his scribe and disciple.

Easton is a city in, and the county seat of, Northampton County, Pennsylvania, United States. The city's population was 28,127 as of the 2020 census. Easton is located at the confluence of the Lehigh River, a 109-mile-long (175 km) river that joins the Delaware River in Easton and serves as the city's eastern geographic boundary with Phillipsburg, New Jersey.

Calvary or Golgotha was a site immediately outside Jerusalem's walls where, according to Christianity's four canonical gospels, Jesus was crucified.

Sheena Shirley Easton is a Scottish singer and actress. She came into the public eye in an episode of the first British musical reality television series The Big Time: Pop Singer, which recorded her attempts to gain a record deal and her eventual signing with the EMI label. Easton's first two singles, "Modern Girl" and "9 to 5", both entered the Top 10 of the UK Singles Chart simultaneously. She became one of the most successful British female recording artists of the 1980s.
Easton is an inner city area of the city of Bristol in the United Kingdom. Informally the area is considered to stretch east of Bristol city centre and the M32 motorway, centred on Lawrence Hill. Its southern and eastern borders are less defined, merging into St Philip's Marsh and Eastville. The area includes the Lawrence Hill and Barton Hill estates.

The 75th Avenue station is a local station on the IND Queens Boulevard Line of the New York City Subway. Located at the intersection of 75th Avenue and Queens Boulevard in Forest Hills, Queens, it is served by the F train at all times, the E train at all times except weekday rush hours and middays, and the <F> train during rush hours in the reverse peak direction.


Herod's Gate is one of the seven open Gates of the Old City of Jerusalem. It connects the Muslim Quarter inside of the old city to the eponymic Palestinian neighbourhood of Bab az-Zahra, situated just outside. It is a short distance to the east of the Damascus Gate. Its elevation is 755 meters above sea level.
Bezetha, also called by Josephus the New City, was a suburb of Jerusalem, north and north-west of the Temple, built opposite the tower Antonia and extending as far as Herod's Gate westward and beyond. Originally, this part of the city was outside the area enclosed by the second wall, but during the reign of Agrippa I, had been enclosed by the newer third wall. In Josephus' time, the hill on which Bezetha was built could be distinguished by its elevation in relation to the tower of Antonia, which was built beyond the intermediate valley below, between Bezetha and the north side of the Temple Mount. Topographical maps still show the contours in elevation.

The Siege of Jerusalem was the final event of the Judahite revolts against Babylon, in which Nebuchadnezzar II, king of the Neo-Babylonian Empire, besieged Jerusalem, the capital city of the Kingdom of Judah. Jerusalem fell after a 30-month siege, following which the Babylonians systematically destroyed the city and Solomon's Temple. The Kingdom of Judah was dissolved and many of its inhabitants were exiled to Babylon.
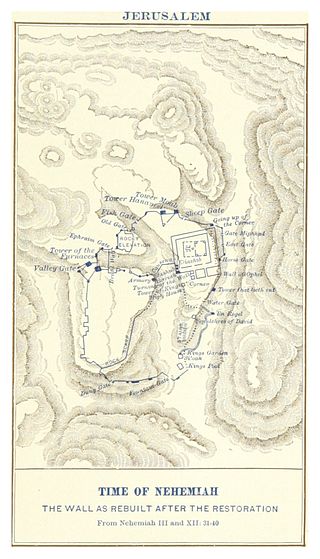
The Tower of Hananeel is a tower in the walls of Jerusalem, adjoining the Tower of Meah to the east connecting to the "sheep gate". It is mentioned in Nehemiah 3:1 and Nehemiah 12:39. It is located on the northern wall section of the old city, near the northeastern corner, a point of the city always requiring special fortification and later the sites successively of the Hasmonean Baris and of the Antonia Fortress.

Jeremiah 31 is the thirty-first chapter of the Book of Jeremiah in the Hebrew Bible or the Old Testament of the Christian Bible. It is numbered as Jeremiah 38 in the Septuagint. The book contains prophecies attributed to the prophet Jeremiah, and is one of the Books of the Prophets (Nevi'im). This chapter is notable for the passage about the "New Covenant" (31:31-34) of God with His restored people and the quoting of 31:15 in the “Massacre of the Innocents" narrative. The Jerusalem Bible refers to chapters 30 and 31 as "the Book of Consolation", and Lutheran theologian Ernst Hengstenberg calls these two chapters "the triumphal hymn of Israel’s salvation".
References
This article includes a list of references, related reading, or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it lacks inline citations .(December 2007) |
- Theologisch-homiletisches Bibelwerk (1857), Johann Peter Lange
 This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain : Easton, Matthew George (1897). Easton's Bible Dictionary (New and revised ed.). T. Nelson and Sons.
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain : Easton, Matthew George (1897). Easton's Bible Dictionary (New and revised ed.). T. Nelson and Sons.{{cite encyclopedia}}: Missing or empty|title=(help)