A prefecture is an administrative jurisdiction or subdivision in any of various countries and within some international church structures, and in antiquity a Roman district governed by an appointed prefect.
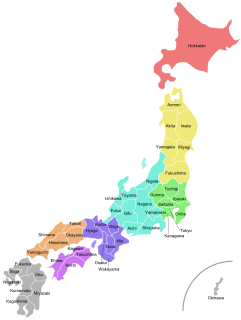
Japan is divided into 47 prefectures, forming the first level of jurisdiction and administrative division. They consist of 43 prefectures proper, two urban prefectures, one "circuit" or "territory" and one "metropolis". The Meiji Fuhanken sanchisei administration created the first prefectures from 1868 to replace the urban and rural administrators in the parts of the country previously controlled directly by the shogunate and a few territories of rebels/shogunate loyalists who had not submitted to the new government such as Aizu/Wakamatsu. In 1871, all remaining feudal domains (han) were also transformed into prefectures, so that prefectures subdivided the whole country. In several waves of territorial consolidation, today's 47 prefectures were formed by the turn of the century. In many instances, these are contiguous with the ancient ritsuryō provinces of Japan.
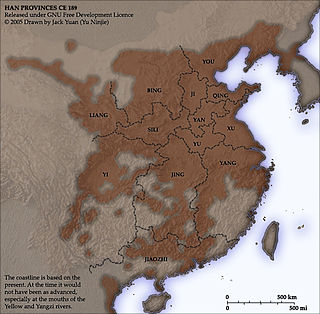
Due to China's large population and area, the administrative divisions of China have consisted of several levels since ancient times. The constitution of China provides for three de jure levels of government. Currently, however, there are five practical levels of local government: the provincial, prefecture, county, township, and village.

The Chūgoku region, also known as the San'in-San'yō region, is the westernmost region of Honshū, the largest island of Japan. It consists of the prefectures of Hiroshima, Okayama, Shimane, Tottori, and Yamaguchi. In 2010, it had a population of 7,563,428.
A subprefecture is an administrative division of a country that is below prefecture or province.

Yanbian is an autonomous prefecture in northeastern Jilin Province, China. Yanbian is bordered to the north by Heilongjiang, on the west by Baishan and Jilin City, on the south by North Hamgyong Province of North Korea, and on the east by Primorsky Krai of Russia. Yanbian is designated as the Korean autonomous prefecture due to the large number of ethnic Koreans living in the region. The prefectural capital is Yanji, and the total area is 42,700 square kilometres (16,500 sq mi).

A prefectural-level municipality, prefectural-level city or prefectural city; formerly known as province-administrated city from 1949 to 1983, is an administrative division of the People's Republic of China (PRC), ranking below a province and above a county in China's administrative structure. Prefectural level cities form the second level of the administrative structure. Administrative chiefs (mayors) of prefectural level cities generally have the same rank as a division chief of a national ministry. Since the 1980s, most former prefectures have been renamed into prefectural level cities.
A sub-prefectural municipality, sub-prefectural city, or vice-prefectural municipality, is an unofficial designation for a type of administrative division of China. A sub-prefectural city is officially considered to be a county-level city, but it has more power de facto because the cadres assigned to its government are one half-level higher in rank than those of an "ordinary" county-level city—though still lower than those of a prefecture-level city.

Ili or Ili Kazakh Autonomous Prefecture in northernmost Xinjiang is the only Kazakh autonomous prefecture in China.

Prefectures, formally a kind of prefecture-level divisions as a term in the context of China, are used to refer to several unrelated political divisions in both ancient and modern China. There are 334 prefecture-level divisions in China. They include 7 prefectures, 294 prefecture-level cities, 30 autonomous prefectures and 3 leagues. Other than provincial level divisions, prefectural level divisions are not mentioned in the Chinese constitution.
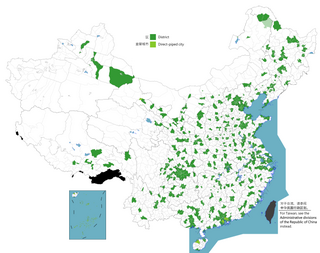
The term district, in the context of China, is used to refer to several unrelated political divisions in both ancient and modern China.
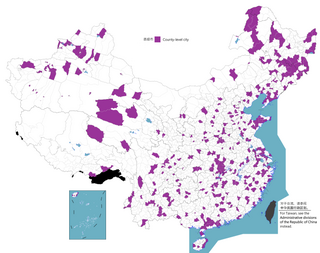
A county-level municipality, county-level city, or county city is a county-level administrative division of mainland China. County-level cities are usually governed by prefecture-level divisions, but a few are governed directly by province-level divisions. Formerly known as prefecture-controlled city.

Shigatse, officially known as Xigazê, is a prefecture-level city of the Tibet Autonomous Region of China, with an area of 182,000 km2 (70,271 sq mi). It is located within the historical Tsang province of Tibet.

Ngawa Tibetan and Qiang Autonomous Prefecture, also known as Aba, is an autonomous prefecture of northwestern Sichuan, bordering Gansu to the north and northeast and Qinghai to the northwest. Its seat is in Barkam, and it has an area of 83,201 km2 (32,124 sq mi). The population was 919,987 in late 2013.

Diqing Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture is an autonomous prefecture in northwestern Yunnan province, China. It has an area of 23,870 km2 (9,220 sq mi). Its capital, which is also the largest city in the prefecture, is Shangri-La City.
Autonomous prefectures are one type of autonomous administrative divisions of China, existing at the prefectural level, with either ethnic minorities forming over 50% of the population or being the historic home of significant minorities. All autonomous prefectures are mostly dominated, in population, by the Han Chinese. The official name of an autonomous prefecture includes the most dominant minority in that region, sometimes two, rarely three. For example, a Kazakh prefecture may be called Kazak Zizhizhou. Like all other prefectural level divisions, autonomous prefectures are divided into county level divisions. There is one exception: Ili Kazak Autonomous Prefecture contains two prefectures of its own. Under the Constitution of the People's Republic of China, autonomous prefectures cannot be abolished.