| Look up goshawk in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
Goshawk is a name applied to several species of birds of prey. Goshawk may also refer to:
Goshawk may refer to several species of birds of prey, mainly in the genus Accipiter:
| Look up goshawk in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
Goshawk is a name applied to several species of birds of prey. Goshawk may also refer to:
Goshawk may refer to several species of birds of prey, mainly in the genus Accipiter:

The Curtiss F11C Goshawk was a 1930s United States naval biplane fighter aircraft that saw limited success but was part of a long line of Curtiss Hawk airplanes built by the Curtiss Aeroplane and Motor Company for the American military.

The Curtiss BF2C Goshawk was a United States 1930s naval biplane aircraft that saw limited success and was part of a long line of Hawk Series airplanes made by the Curtiss Aeroplane and Motor Company for the American military, and for export as the Model 68 Hawk III.
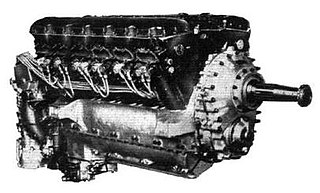
The Rolls-Royce Goshawk was a development of the Rolls-Royce Kestrel that used evaporative or steam cooling. In line with Rolls-Royce convention of naming piston engines after birds of prey, it was named after the goshawk.
Five ships and a shore establishment of the Royal Navy have borne the name HMS Goshawk, after the bird of prey, the goshawk. A sixth ship was renamed before being launched:
Several ships of the United States Navy have been named USS Goshawk, after the goshawk, a large, short-winged hawk.
USS Goshawk (AM-79), was a Goshawk class minesweeper built in 1919 as the steel-hulled fishing trawler M/V Penobscot by the Foundation (Marine) Co., Savannah, Georgia, for Mr. W. F. Henningsen, Seattle, Washington.
Goshawk Squadron is a 1971 black comedy novel by Derek Robinson which tells of the adventures of a squadron of SE5a pilots from January 1918 to the time of the German spring offensive of March 1918.

Terence Hanbury "Tim" White was an English author best known for his Arthurian novels, The Once and Future King, first published together in 1958. One of his most memorable is the first of the series, The Sword in the Stone, published as a stand-alone book in 1938.
The Gay Goshawk is Child ballad number 96.
| This disambiguation page lists articles associated with the title Goshawk. If an internal link led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the intended article. |
Sea Hawk or Seahawk may refer to:

Curtiss Aeroplane and Motor Company was an American aircraft manufacturer formed in 1916 by Glenn Hammond Curtiss. After significant commercial success in the 'teens and 20s, it merged with the Wright Aeronautical in 1929 to form Curtiss-Wright Corporation.

The Naval Aircraft Factory (NAF) was established by the United States Navy in 1918 in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. It was created to help solve aircraft supply issues which faced the Navy Department upon the entry of the U.S. into World War I. The US Army’s requirements for an enormous quantity of airplanes created a decided lack of interest among aircraft manufacturers in the Navy's requirements for a comparatively small quantity of aircraft. The Navy Department concluded that it was necessary to build a Navy-owned aircraft factory in order to assure a part of its aircraft supply; to obtain cost data for the department’s guidance in its dealings with private manufacturers; and to have under its own control a factory capable of producing experimental designs.

The McDonnell Douglas T-45 Goshawk is a highly modified version of the British BAE Systems Hawk land-based training jet aircraft. Manufactured by McDonnell Douglas and British Aerospace, the T-45 is used by the United States Navy as an aircraft carrier-capable trainer.

The Curtiss F9C Sparrowhawk is a light 1930s biplane fighter aircraft that was carried by the United States Navy airships USS Akron and Macon. It is an example of a parasite fighter, a small airplane designed to be deployed from a larger aircraft such as an airship or bomber.

The Curtiss SBC Helldiver was a two-seat scout bomber and dive bomber built by the Curtiss-Wright Corporation. It was the last military biplane procured by the United States Navy. Delivered in 1937, it became obsolete even before World War II and was kept well away from combat with Axis fighters.
The 1911 Curtiss Model D was an early United States pusher aircraft with the engine and propeller behind the pilot's seat. It was among the very first aircraft in the world to be built in any quantity — all of which were produced by Curtiss during an era of trial-and-error development and equally important parallel technical development in internal combustion engine technologies.

The Curtiss F7C Seahawk was a carrier-capable biplane fighter aircraft of the United States Navy Marine Corps in the late 1920s and early 1930s.

The Naval Aircraft Factory TS-1 was an early biplane fighter aircraft of the United States Navy, serving from 1922 to 1929.

The Burgess Company was a U.S. airplane manufacturer between 1910 and 1918.

The Curtiss Models F made up a family of early flying boats developed in the United States in the years leading up to World War I. Widely produced, Model Fs saw service with the United States Navy under the designations C-2 through C-5, later reclassified to AB-2 through AB-5. Several examples were exported to Russia, and the type was built under license in Italy.

The Curtiss Fledgling, known internally to Curtiss as the Model 48 and Model 51 was a trainer aircraft developed for the United States Navy in the late 1920s and known in that service as the N2C.

Carrier-based aircraft, sometimes known as carrier-capable aircraft or carrier-borne aircraft, are naval aircraft designed for operations from aircraft carriers. They must be able to launch in a short distance and be sturdy enough to withstand the abrupt forces of launching from and recovering on a pitching deck. In addition, their wings are generally able to fold up, easing operations in tight quarters.
Sparrowhawk is a name applied to several bird species.
Fighter Squadron 6 or VF-6 was an aviation unit of the United States Navy. Originally established as Combat Squadron 4 on 23 September 1921, it was redesignated VF-2 on 1 July 1922, redesignated VF-2B on 19 March 1923, redesignated VF-6B on 1 January 1927, redesignated VF-6 on 1 July 1927, redesignated VB-2B on 1 July 1928, redesignated VF-6B on 1 July 1930, redesignated VF-3 on 1 July 1937, redesignated VF-6 on 15 July 1943 and disestablished on 29 October 1945.