
The Rolls-Royce Merlin is a British liquid-cooled V-12 piston aero engine of 27-litres capacity. Rolls-Royce designed the engine and first ran it in 1933 as a private venture. Initially known as the PV-12, it was later called Merlin following the company convention of naming its four-stroke piston aero engines after birds of prey.

The Bristol Pegasus is a British nine-cylinder, single-row, air-cooled radial aero engine. Designed by Roy Fedden of the Bristol Aeroplane Company, it was used to power both civil and military aircraft of the 1930s and 1940s. Developed from the earlier Mercury and Jupiter engines, later variants could produce 1,000 horsepower from its capacity of 1,750 cubic inches by use of a geared supercharger.

The Bristol Mercury is a British nine-cylinder, air-cooled, single-row, piston radial engine. Designed by Roy Fedden of the Bristol Aeroplane Company it was used to power both civil and military aircraft of the 1930s and 1940s. Developed from the earlier Jupiter engine, later variants could produce 800 horsepower (600 kW) from its capacity of 1,500 cubic inches by use of a geared supercharger.
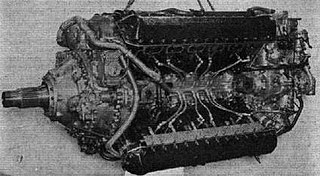
The Rolls-Royce Vulture was a British aero engine developed shortly before World War II that was designed and built by Rolls-Royce Limited. The Vulture used the unusual "X-24" configuration, whereby four cylinder blocks derived from the Rolls-Royce Peregrine were joined by a common crankshaft supported by a single crankcase. The engine was originally designed to produce around 1,750 horsepower (1,300 kW) but problems with the Vulture design meant that the engines were derated to around 1,450 to 1,550 hp in service by limiting the maximum rpm.

The Rolls-Royce Griffon is a British 37-litre capacity, 60-degree V-12, liquid-cooled aero engine designed and built by Rolls-Royce Limited. In keeping with company convention, the Griffon was named after a bird of prey, in this case the griffon vulture.

The Rolls-Royce Peregrine was a 21-litre (1,300 cu in), 885-horsepower (660 kW) liquid-cooled V-12 aero engine designed and built by the British manufacturer Rolls-Royce in the late 1930s. It was essentially the ultimate development of the company's Kestrel engine, which had seen widespread use in military aircraft of the pre-war period.

The Rolls-Royce Kestrel is a 21.25 litre V-12 aircraft engine from Rolls-Royce. It was their first cast-block engine, and used as the pattern for most of their future piston-engine designs. Used during the interwar period, it was fitted to a number of British fighters and bombers of the era, including the Hawker Fury and Hawker Hart family, and the Handley Page Heyford. The Kestrel engine was also sold to international air force customers, in this role it used to power prototypes of the German Messerschmitt Bf 109 and the Junkers Ju 87 "Stuka" dive-bomber, as the Junkers Jumo 210 engines were not ready to be fitted. Several examples of the Kestrel engine remain airworthy today.
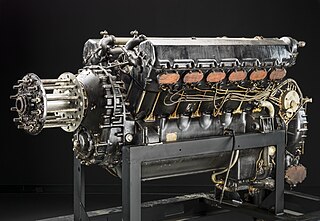
The Rolls-Royce Buzzard was a British piston aero engine of 36.7 litres capacity that produced about 800 horsepower (600 kW). Designed and built by Rolls-Royce Limited it is a V12 engine of 6 in (150 mm) bore and 6.6 in (170 mm) stroke. Only 100 were made. A further development was the Rolls-Royce R engine. The Buzzard was developed by scaling-up the Rolls-Royce Kestrel Engine.

The Rolls-Royce R is a British aero engine that was designed and built specifically for air racing purposes by Rolls-Royce Limited. Nineteen R engines were assembled in a limited production run between 1929 and 1931. Developed from the Rolls-Royce Buzzard, it was a 37-litre capacity, supercharged V-12 capable of producing just under 2,800 horsepower (2,090 kW), and weighed 1,640 pounds (770 kg). Intensive factory testing revealed mechanical failures which were remedied by redesigning the components, greatly improving reliability.

The Rolls-Royce Eagle was the first aircraft engine to be developed by Rolls-Royce Limited. Introduced in 1915 to meet British military requirements during World War I, it was used to power the Handley Page Type O bombers and a number of other military aircraft.

The Rolls-Royce Eagle Mk XXII is a British 24-cylinder, sleeve valve, H-block aero engine of 46 litre displacement. It was designed and built in the early-1940s by Rolls-Royce Limited and first ran in 1944. It was liquid-cooled, of flat H configuration with two crankshafts and was capable of 3,200 horsepower at 18 psi boost.

The Rolls-Royce Crecy was a British experimental two-stroke, 90-degree, V12, liquid-cooled aero-engine of 1,593.4 cu.in capacity, featuring sleeve valves and direct petrol injection. Initially intended for a high-speed "sprint" interceptor fighter, the Crecy was later seen as an economical high-altitude long-range powerplant. Developed between 1941 and 1946, it was among the most advanced two-stroke aero-engines ever built. The engine never reached flight trials and the project was cancelled in December 1945, overtaken by the progress of jet engine development.

The Rolls-Royce Falcon is an aero engine developed in 1915. It was a smaller version of the Rolls-Royce Eagle, a liquid-cooled V-12 of 867 cu in capacity. Fitted to many British World War I-era aircraft, production ceased in 1927. The Falcon was designed by R.W. Harvey-Bailey.

The Rolls-Royce Condor aircraft piston engine was a larger version of the Rolls-Royce Eagle developing up to 675 horsepower. The engine first ran in 1918 and a total of 327 engines were recorded as being built.

The Armstrong Siddeley Jaguar is an aircraft engine developed by Armstrong Siddeley. The Jaguar was a petrol-fuelled air-cooled 14-cylinder two-row radial engine design. The Jaguar III was first used in 1923, followed in 1925 by the Jaguar IV and in 1927 by the Jaguar VI. In 1925 the Jaguar became the first production aero engine incorporating a geared supercharger.

The Rolls-Royce Exe, or Boreas, was a 24-cylinder air-cooled X block sleeve valve aircraft engine intended primarily for the new Fairey Fleet Air Arm aircraft, particularly the Fairey Barracuda. The Exe was relatively powerful for its era, producing about 1,100 hp (820 kW). This is notable given the relatively small 1,300 cubic inches (22 L) displacement, the Merlin requiring 1,600 cubic inches (27 L) for approximately the same power level. The X-24 layout made this quite a compact engine.

The Supermarine Type 224 was an inverted gull-wing monoplane fighter aircraft designed by R.J. Mitchell at Supermarine in response to Air Ministry Specification F.7/30, which sought a fighter for introduction to succeed the Gloster Gauntlet. It was powered by the Rolls-Royce Goshawk engine, which used an experimental evaporative cooling system, and problems with this system, combined with its disappointing performance, led to it being rejected, a contract for production aircraft eventually going to the Gloster Gladiator. It is nevertheless notable because R.J. Mitchell learnt lessons from its failure that were to contribute greatly to his success with the Supermarine Spitfire.

The Gloster SS.35 Gnatsnapper was a British naval biplane fighter design of the late 1920s. Two prototypes were built but the type did not enter production.

The Westland F.7/30 was a British fighter prototype. A single prototype was built in 1934, but the type was not put in production because its performance fell far below the RAF's requirements. The Gloster Gladiator won the F.7/30 competition.
The Rolls-Royce Eagle XVI was a British experimental 16 cylinder aero engine designed and developed by Rolls-Royce Limited in 1925. The engine was test run but did not fly, the project, together with the planned larger variant, the Eagle XX, was cancelled in favour of the Rolls-Royce Kestrel, that was being developed concurrently.




















