Related Research Articles
Enhanced 911, E-911 or E911 is a system used in North America to automatically provide the caller's location to 911 dispatchers. 911 is the universal emergency telephone number in the region. In the European Union, a similar system exists known as E112 and known as eCall when called by a vehicle.

Most public switched telephone networks have a single emergency telephone number that allows a caller to contact local emergency services for assistance. The emergency number differs from country to country; it is typically a three-digit number so that it can be easily remembered and dialed quickly. Some countries have a different emergency number for each of the different emergency services; these often differ only by the last digit.
A toll-free telephone number or freephone number is a telephone number that is billed for all arriving calls instead of incurring charges to the originating telephone subscriber. For the calling party, a call to a toll-free number from a landline is free of charge.
111 is the emergency telephone number in New Zealand. It was first implemented in Masterton and Carterton on 29 September 1958, and was progressively rolled out nationwide with the last exchanges converting in 1988.

The director telephone system was a development of the Strowger or step-by-step (SXS) switching system used in London and five other large cities in the UK from the 1920s to the 1970s.
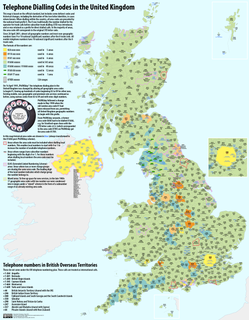
Telephone numbers in the United Kingdom are administered by the Office of Communications (Ofcom). For this purpose, Ofcom established a telephone numbering plan, known as the National Telephone Numbering Plan, which is the system for assigning telephone numbers to subscriber stations.
The Australian telephone numbering plan describes the allocation of phone numbers in Australia. It has changed many times, the most recent major reorganisation by the Australian Communications and Media Authority taking place between 1994 and 1998.
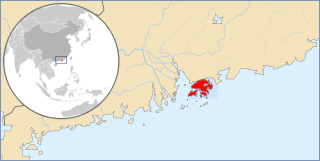
Telephone numbers in Hong Kong are mostly eight-digit. Fixed land line numbers start with 2 or 3, mobile (cellular) phone numbers with 5, 6, 7 or 9, pager numbers with 7 and forwarding service with 8. Since the end of 1989, there have been no area codes within Hong Kong.
The term opt-out refers to several methods by which individuals can avoid receiving unsolicited product or service information. This option is usually associated with direct marketing campaigns such as e-mail marketing or direct mail. A list of those who have opted out is called a Robinson list.
Direct inward dialing (DID), also called direct dial-in (DDI) in Europe and Oceania, is a telecommunication service offered by telephone companies to subscribers who operate a private branch exchange (PBX) system. The feature provides service for multiple telephone numbers over one or more analog or digital physical circuits to the PBX, and transmits the dialed telephone number to the PBX so that a PBX extension is directly accessible for an outside caller, possibly by-passing an auto-attendant.
ACCOLC was a procedure in the United Kingdom for restricting mobile telephone usage in the event of emergencies. It is similar to the GTPS for landlines.

Telephone numbers in Singapore, also known as the National Numbering Plan, are regulated by the Info-communications Media Development Authority (IMDA). Due to the small geographical size of Singapore, there are no area or trunk codes; all numbers belong to one numbering area, and thus come in the same 8-digit format. Numbers are categorised based on the first digit, thus providing ten possible categories, of which six are currently in use and the remaining four reserved for future usage.

000 Emergency, also known as Triple Zero or Triple 0, and sometimes stylised Triple Zero (000), is the primary national emergency telephone number in Australia. The Emergency Call Service is operated by Telstra, and overseen by the Australian Communications and Media Authority (ACMA), and is intended only for use in life-threatening or time-critical emergencies.

106 Text Emergency Call, commonly known as simply 106, is the Australian national emergency telephone number to be used in life-threatening or time critical situations for those with a speech and / or hearing impairment who use telecommunications device for the deaf. It is run by the emergency telephone operator for the National Relay Service (NRS); formerly the Australian Communications Exchange (ACE), a non-profit organisation that provided the relay services component for the NRS. 106 can only be used by people with a TTY / textphone, or a computer with terminal software and a modem. 106 calls are given priority over other calls handled by the National Relay Service. 106 is a free-to-call number.
The Telephone Preference Service (TPS) is a UK register of domestic telephone numbers whose users have indicated that they do not wish to receive sales and marketing telephone calls. Registration is free of charge. The service is paid for by the direct marketing industry. There is a similar service for corporate users, the Corporate Telephone Preference Service (CTPS). Similar do not call lists are implemented in other countries.

The New Zealand telephone numbering plan describes the allocation of telephone numbers in New Zealand and the Pitcairn Islands.
Area code 710 is a special area code in the North American Numbering Plan (NANP). It was reserved for the federal government of the United States in 1983. As of December 2006, it had only one working telephone number, 710-627-4387 (710-NCS-GETS) for the Government Emergency Telecommunications Service (GETS) in the National Communications System (NCS). Previously it was an area code in the AT&T Teletypewriter Exchange (TWX) for the northeastern part of the United States.

A telephone number is a sequence of digits assigned to a fixed-line telephone subscriber station connected to a telephone line or to a wireless electronic telephony device, such as a radio telephone or a mobile telephone, or to other devices for data transmission via the public switched telephone network (PSTN) or other public and private networks.
MTPAS is a British procedure for prioritising access to the mobile telephone networks for privileged persons. It replaced ACCOLC in 2009.
A call detail record (CDR) is a data record produced by a telephone exchange or other telecommunications equipment that documents the details of a telephone call or other telecommunications transactions that passes through that facility or device. The record contains various attributes of the call, such as time, duration, completion status, source number, and destination number. It is the automated equivalent of the paper toll tickets that were written and timed by operators for long-distance calls in a manual telephone exchange.
References
- 1 2 "Resilient communications". GOV.UK. Retrieved 2020-01-11.
- ↑ Privileged Access Schemes: MTPAS, FTPAS and Airwave
- ↑ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2006-07-18. Retrieved 2005-07-08.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ↑ https://www.gov.uk/resilient-communications