
Graphic design is a profession, academic discipline and applied art whose activity consists in projecting visual communications intended to transmit specific messages to social groups, with specific objectives. Graphic design is an interdisciplinary branch of design and of the fine arts. Its practice involves creativity, innovation and lateral thinking using manual or digital tools, where it is usual to use text and graphics to communicate visually.

Television (TV) is a telecommunication medium for transmitting moving images and sound. The term can refer to a television set, or the medium of television transmission. Television is a mass medium for advertising, entertainment, news, and sports.

Daguerreotype was the first publicly available photographic process; it was widely used during the 1840s and 1850s. "Daguerreotype" also refers to an image created through this process.

A toaster is a small electric appliance that uses radiant heat to brown sliced bread into toast.

A refracting telescope is a type of optical telescope that uses a lens as its objective to form an image. The refracting telescope design was originally used in spyglasses and astronomical telescopes but is also used for long-focus camera lenses. Although large refracting telescopes were very popular in the second half of the 19th century, for most research purposes, the refracting telescope has been superseded by the reflecting telescope, which allows larger apertures. A refractor's magnification is calculated by dividing the focal length of the objective lens by that of the eyepiece.

A button is a fastener that joins two pieces of fabric together by slipping through a loop or by sliding through a buttonhole.

A camera lucida is an optical device used as a drawing aid by artists and microscopists.

Pepper's ghost is an illusion technique used in the theatre, cinema, amusement parks, museums, television, and concerts. The illusion is performed by reflecting an image of an object off-stage so that it appears to be in front of the audience.
Bill Brandt was a British photographer and photojournalist. Born in Germany, Brandt moved to England, where he became known for his images of British society for such magazines as Lilliput and Picture Post; later he made distorted nudes, portraits of famous artists and landscapes. He is widely considered to be one of the most important British photographers of the 20th century.

Cornelis Jacobszoon Drebbel was a Dutch engineer and inventor. He was the builder of the first operational submarine in 1620 and an innovator who contributed to the development of measurement and control systems, optics and chemistry.

A Schmidt camera, also referred to as the Schmidt telescope, is a catadioptric astrophotographic telescope designed to provide wide fields of view with limited aberrations. The design was invented by Bernhard Schmidt in 1930.

A micrograph or photomicrograph is a photograph or digital image taken through a microscope or similar device to show a magnified image of an object. This is opposed to a macrograph or photomacrograph, an image which is also taken on a microscope but is only slightly magnified, usually less than 10 times. Micrography is the practice or art of using microscopes to make photographs.

A catadioptric optical system is one where refraction and reflection are combined in an optical system, usually via lenses (dioptrics) and curved mirrors (catoptrics). Catadioptric combinations are used in focusing systems such as searchlights, headlamps, early lighthouse focusing systems, optical telescopes, microscopes, and telephoto lenses. Other optical systems that use lenses and mirrors are also referred to as "catadioptric", such as surveillance catadioptric sensors.

The Maksutov is a catadioptric telescope design that combines a spherical mirror with a weakly negative meniscus lens in a design that takes advantage of all the surfaces being nearly "spherically symmetrical". The negative lens is usually full diameter and placed at the entrance pupil of the telescope. The design corrects the problems of off-axis aberrations such as coma found in reflecting telescopes while also correcting chromatic aberration. It was patented in 1941 by Russian optician Dmitri Dmitrievich Maksutov. Maksutov based his design on the idea behind the Schmidt camera of using the spherical errors of a negative lens to correct the opposite errors in a spherical primary mirror. The design is most commonly seen in a Cassegrain variation, with an integrated secondary, that can use all-spherical elements, thereby simplifying fabrication. Maksutov telescopes have been sold on the amateur market since the 1950s.

Cornelius Varley, FRSA was a British water-colour painter and optical instrument-maker. He invented the graphic telescope and the graphic microscope.
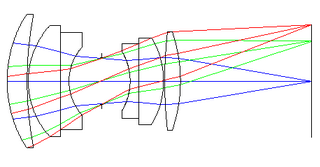
The double Gauss lens is a compound lens used mostly in camera lenses that reduces optical aberrations over a large focal plane.

A telescope is a device used to observe distant objects by their emission, absorption, or reflection of electromagnetic radiation. Originally it was an optical instrument using lenses, curved mirrors, or a combination of both to observe distant objects – an optical telescope. Nowadays, the word "telescope" is defined as wide range of instruments capable of detecting different regions of the electromagnetic spectrum, and in some cases other types of detectors.

A meniscus corrector is a negative meniscus lens that is used to correct spherical aberration in image-forming optical systems such as catadioptric telescopes. It works by having the equal but opposite spherical aberration of the objective it is designed to correct.
Andrew Pritchard FRSE was an English naturalist and natural history dealer who made significant improvements to microscopy and studied microscopic organisms. His belief that God and nature were one led him to the Unitarians, a religious movement to which he and his family devoted much energy. He became a leading member of Newington Green Unitarian Church in north London, and worked to build a school there.
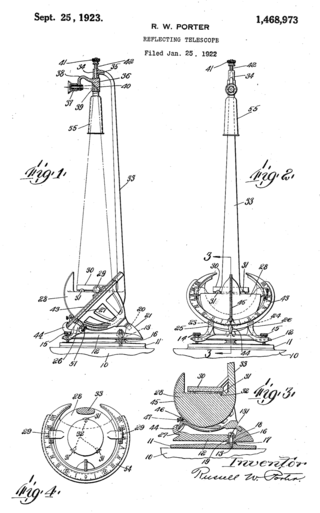
The Porter Garden Telescope was an innovative ornamental telescope for the garden designed by Russell W. Porter and commercialized by Jones & Lamson Machine Company at the beginning of the 1920s in the United States.

















