Related Research Articles

Menopause, also known as the climacteric, is the time when menstrual periods permanently stop, marking the end of reproduction. It typically occurs between the ages of 45 and 55, although the exact timing can vary. Menopause is usually a natural change related to a decrease in circulating blood estrogen levels. It can occur earlier in those who smoke tobacco. Other causes include surgery that removes both ovaries, some types of chemotherapy, or anything that leads to a decrease in hormone levels. At the physiological level, menopause happens because of a decrease in the ovaries' production of the hormones estrogen and progesterone. While typically not needed, a diagnosis of menopause can be confirmed by measuring hormone levels in the blood or urine. Menopause is the opposite of menarche, the time when a girl's periods start.
Oophorectomy, historically also called ovariotomy, is the surgical removal of an ovary or ovaries. The surgery is also called ovariectomy, but this term is mostly used in reference to non-human animals, e.g. the surgical removal of ovaries from laboratory animals. Removal of the ovaries of females is the biological equivalent of castration of males; the term castration is only occasionally used in the medical literature to refer to oophorectomy of women. In veterinary medicine, the removal of ovaries and uterus is called ovariohysterectomy (spaying) and is a form of sterilization.
Hot flashes, also known as hot flushes, are a form of flushing, often caused by the changing hormone levels that are characteristic of menopause. They are typically experienced as a feeling of intense heat with sweating and rapid heartbeat, and may typically last from two to 30 minutes for each occurrence.
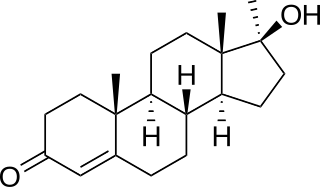
Methyltestosterone, sold under the brand names Android, Metandren, and Testred among others, is an androgen and anabolic steroid (AAS) medication which is used in the treatment of low testosterone levels in men, delayed puberty in boys, at low doses as a component of menopausal hormone therapy for menopausal symptoms like hot flashes, osteoporosis, and low sexual desire in women, and to treat breast cancer in women. It is taken by mouth or held in the cheek or under the tongue.

Selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs), also known as estrogen receptor agonists/antagonists (ERAAs), are a class of drugs that act on estrogen receptors (ERs). Compared to pure ER agonists–antagonists, SERMs are more tissue-specific, allowing them to selectively inhibit or stimulate estrogen-like action in various tissues.
Bioidentical hormone replacement therapy (BHRT), also known as bioidentical hormone therapy (BHT) or natural hormone therapy, is the use of hormones that are identical on a molecular level with endogenous hormones in hormone replacement therapy. It may also be combined with blood and saliva testing of hormone levels, and the use of pharmacy compounding to obtain hormones in an effort to reach a targeted level of hormones in the body. A number of claims by some proponents of BHT have not been confirmed through scientific testing. Specific hormones used in BHT include estrone, estradiol, progesterone, testosterone, dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA), and estriol.
Breast pain is the symptom of discomfort in either one or both breasts. Pain in both breasts is often described as breast tenderness, is usually associated with the menstrual period and is not serious. Pain that involves only one part of a breast is more concerning, particularly if a hard mass or nipple discharge is also present.

An estrogen patch, or oestrogen patch, is a transdermal delivery system for estrogens such as estradiol and ethinylestradiol which can be used in menopausal hormone therapy, feminizing hormone therapy for transgender women, hormonal birth control, and other uses. Transdermal preparations of estrogen are metabolized differently than oral preparations. Transdermal estrogens avoid the first pass through the liver and thus potentially reduce the risk of blood clotting and stroke.

Estropipate, also known as piperazine estrone sulfate and sold under the brand names Harmogen, Improvera, Ogen, Ortho-Est, and Sulestrex among others, is an estrogen medication which is used mainly in menopausal hormone therapy in the treatment of menopausal symptoms. It is a salt of estrone sulfate and piperazine, and is transformed into estrone and estradiol in the body. It is taken by mouth.
Medically unexplained physical symptoms are symptoms for which a treating physician or other healthcare providers have found no medical cause, or whose cause remains contested. In its strictest sense, the term simply means that the cause for the symptoms is unknown or disputed—there is no scientific consensus. Not all medically unexplained symptoms are influenced by identifiable psychological factors. However, in practice, most physicians and authors who use the term consider that the symptoms most likely arise from psychological causes. Typically, the possibility that MUPS are caused by prescription drugs or other drugs is ignored. It is estimated that between 15% and 30% of all primary care consultations are for medically unexplained symptoms. A large Canadian community survey revealed that the most common medically unexplained symptoms are musculoskeletal pain, ear, nose, and throat symptoms, abdominal pain and gastrointestinal symptoms, fatigue, and dizziness. The term MUPS can also be used to refer to syndromes whose etiology remains contested, including chronic fatigue syndrome, fibromyalgia, multiple chemical sensitivity and Gulf War illness.
A functional symptom is a medical symptom with no known physical cause. In other words, there is no structural or pathologically defined disease to explain the symptom. The use of the term 'functional symptom' does not assume psychogenesis, only that the body is not functioning as expected. Functional symptoms are increasingly viewed within a framework in which 'biological, psychological, interpersonal and healthcare factors' should all be considered to be relevant for determining the aetiology and treatment plans.
Hormone replacement therapy (HRT), also known as menopausal hormone therapy or postmenopausal hormone therapy, is a form of hormone therapy used to treat symptoms associated with female menopause. Effects of menopause can include symptoms such as hot flashes, accelerated skin aging, vaginal dryness, decreased muscle mass, and complications such as osteoporosis, sexual dysfunction, and vaginal atrophy. They are mostly caused by low levels of female sex hormones that occur during menopause.
Somatic symptom disorder, also known as somatoform disorder or somatization disorder, is defined by one or more chronic physical symptoms that coincide with excessive and maladaptive thoughts, emotions, and behaviors connected to those symptoms. The symptoms are not deliberately produced or feigned, and they may or may not coexist with a known medical ailment.
Menerba, also known as Menopause Formula 101 (MF-101), is a botanical drug candidate that acts as a selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) which is being studied for its potential to relieve hot flashes associated with menopause. Menerba, an estrogen receptor beta (ERβ) agonist (ERBA), is part of a new class of receptor subtype-selective estrogens, which is selective in transcriptional regulation to one of the two known estrogen receptor (ER) subtypes. Menerba consists of 22 herbs that have been used historically in traditional Chinese medicine.
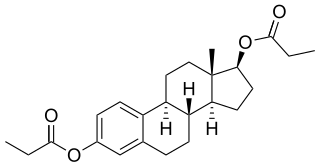
Estradiol dipropionate (EDP), sold under the brand names Agofollin, Di-Ovocylin, and Progynon DP among others, is an estrogen medication which has been used in hormone therapy for menopausal symptoms and low estrogen levels in women and in the treatment of gynecological disorders. It has also been used in feminizing hormone therapy for transgender women and in the treatment of prostate cancer in men. Although widely used in the past, estradiol dipropionate has largely been discontinued and is mostly no longer available today. It appears to remain in use only in Japan, Macedonia, and Australia. Estradiol dipropionate is given by injection into muscle at intervals ranging from once or twice a week to once every week and a half to two weeks.
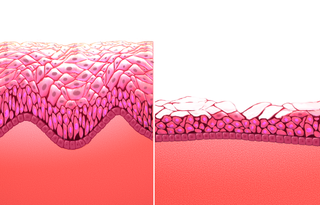
Atrophic vaginitis is inflammation of the vagina as a result of tissue thinning due to low estrogen levels. Symptoms may include pain with sex, vaginal itchiness or dryness, and an urge to urinate or burning with urination. It generally does not resolve without ongoing treatment. Complications may include urinary tract infections. Atrophic vaginitis as well as vulvovaginal atrophy, bladder and urethral dysfunctions are a group of conditions that constitute genitourinary syndrome of menopause (GSM). Diagnosis is typically based on symptoms.

Myra Sally Hunter is Professor of Clinical Health Psychology at the Institute of Psychiatry, Psychology and Neuroscience, King's College, London, and a Clinical and Health Psychologist at the South London and Maudsley NHS Foundation Trust.

Prasterone enanthate, also known as dehydroepiandrosterone enanthate (DHEA-E) and sold in combination with estradiol valerate under the brand name Gynodian Depot among others, is a weak androgen, estrogen, and neurosteroid medication which is used as a component of menopausal hormone therapy to treat menopausal symptoms in women. It is available only as an injectable preparation in combination with estradiol valerate. The medication is given by injection into muscle typically once every 4 weeks.

Fezolinetant, sold under the brand name Veozah among others, is a medication used for the treatment of hot flashes (vasomotor symptoms) due to menopause. It is a small-molecule, orally active, selective neurokinin-3 (NK3) receptor antagonist which is under development by for the treatment of sex hormone-related disorders. It is taken by mouth. It is developed by Astellas Pharma which acquired it from Ogeda (formerly Euroscreen) in April 2017.

Estrone (E1), sold under the brand names Estragyn, Kestrin, and Theelin among many others, is an estrogen medication and naturally occurring steroid hormone which has been used in menopausal hormone therapy and for other indications. It has been provided as an aqueous suspension or oil solution given by injection into muscle and as a vaginal cream applied inside of the vagina. It can also be taken by mouth as estradiol/estrone/estriol and in the form of prodrugs like estropipate and conjugated estrogens.
References
- ↑ Burbos, Nikolaos; Morris, Edward P (2011). "Menopausal symptoms". BMJ Clinical Evidence. BMJ Publishing Group. ISSN 1752-8526. PMC 3275139 . PMID 21696644.
A numerical index that scores 21 menopausal symptoms in three domains: psychological, somatic, and vasomotor. Each symptom is rated from 0 to 3 where 0 = no symptoms and 3 = extreme symptoms.