Related Research Articles

Astrobiology is a scientific field within the life and environmental sciences that studies the origins, early evolution, distribution, and future of life in the universe by investigating its deterministic conditions and contingent events. As a discipline, astrobiology is founded on the premise that life may exist beyond Earth.

The following outline is provided as an overview and topical guide to space science:

Astronomy is a natural science that studies celestial objects and phenomena. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and evolution. Objects of interest include planets, moons, stars, nebulae, galaxies, meteoroid, asteroid, and comets. Relevant phenomena include supernova explosions, gamma ray bursts, quasars, blazars, pulsars, and cosmic microwave background radiation. More generally, astronomy studies everything that originates beyond Earth's atmosphere. Cosmology is a branch of astronomy that studies the universe as a whole.

The European Organisation for Astronomical Research in the Southern Hemisphere, commonly referred to as the European Southern Observatory (ESO), is an intergovernmental research organisation made up of 16 member states for ground-based astronomy. Created in 1962, ESO has provided astronomers with state-of-the-art research facilities and access to the southern sky. The organisation employs over 750 staff members and receives annual member state contributions of approximately €162 million. Its observatories are located in northern Chile.

A volcanologist, or volcano scientist, is a geologist who focuses on understanding the formation and eruptive activity of volcanoes. Volcanologists frequently visit volcanoes, sometimes active ones, to observe and monitor volcanic eruptions, collect eruptive products including tephra, rock and lava samples. One major focus of inquiry in recent times is the prediction of eruptions to alleviate the impact on surrounding populations and monitor natural hazards associated with volcanic activity. Geologists who research volcanic materials that make up the solid Earth are referred to as igneous petrologists.

The Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) is a major NASA space research laboratory located approximately 6.5 miles (10.5 km) northeast of Washington, D.C. in Greenbelt, Maryland, United States. Established on May 1, 1959 as NASA's first space flight center, GSFC employs approximately 10,000 civil servants and contractors. Named in recognition of American rocket propulsion pioneer Robert H. Goddard, it is one of ten major NASA field centers. GSFC is partially within the former Goddard census-designated place; it has a Greenbelt mailing address.

Michel Gustave Édouard Mayor is a Swiss astrophysicist and professor emeritus at the University of Geneva's Department of Astronomy. He formally retired in 2007, but remains active as a researcher at the Observatory of Geneva. He is co-laureate of the 2019 Nobel Prize in Physics along with Jim Peebles and Didier Queloz, and the winner of the 2010 Viktor Ambartsumian International Prize and the 2015 Kyoto Prize.

Didier Patrick Queloz is a Swiss astronomer. He is the Jacksonian Professor of Natural Philosophy at the University of Cambridge, where he is also a fellow of Trinity College, Cambridge, as well as a professor at the University of Geneva. Together with Michel Mayor in 1995, he discovered 51 Pegasi b, the first extrasolar planet orbiting a Sun-like star, 51 Pegasi. For this discovery, he shared the 2019 Nobel Prize in Physics with Mayor and Jim Peebles. In 2021, he was announced as the founding director of the Center for the Origin and Prevalence of Life at ETH Zurich.
A mantle is a layer inside a planetary body bounded below by a core and above by a crust. Mantles are made of rock or ices, and are generally the largest and most massive layer of the planetary body. Mantles are characteristic of planetary bodies that have undergone differentiation by density. All terrestrial planets, a number of asteroids, and some planetary moons have mantles.

Institut de Radioastronomie Millimetrique (IRAM) is an international research institute and Europe's leading center for radio astronomy at millimeter wavelengths. Its mission is to explore the universe, study its origins and its evolution with two of the most advanced radio facilities in the world:
The Lamont–Doherty Earth Observatory (LDEO) is the scientific research center of the Columbia Climate School, and a unit of The Earth Institute at Columbia University. It focuses on climate and earth sciences and is located on a 189-acre campus in Palisades, New York, 18 miles (29 km) north of Manhattan on the Hudson River.
The Earth Institute is a research institute at Columbia University that was established in 1995. Its stated mission is to address complex issues facing the planet and its inhabitants, with a focus on sustainable development. With an interdisciplinary approach, this includes research in climate change, geology, global health, economics, management, agriculture, ecosystems, urbanization, energy, hazards, and water. The Earth Institute's activities are guided by the idea that science and technological tools that already exist could be applied to greatly improve conditions for the world's poor, while preserving the natural systems that support life on Earth.
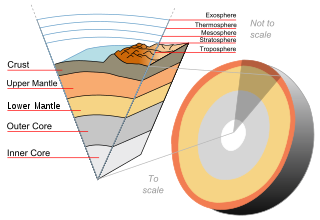
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Earth science:
Joseph Fourier University was a French university situated in the city of Grenoble and focused on the fields of sciences, technologies and health. It is now part of the Université Grenoble Alpes.

The Université Grenoble Alpes is a public research university in Grenoble, France. Founded in 1339, it is the third largest university in France with about 60,000 students and over 3,000 researchers.

The Russian Space Research Institute is the leading organization of the Russian Academy of Sciences on space exploration to benefit fundamental science. It was formerly known as the Space Research Institute of the USSR Academy of Sciences. It is usually known by the shorter name Space Research Institute and especially by the initialism IKI.
The Carnegie Institution of Washington, known also for public purposes as the Carnegie Institution for Science (CIS), is an organization in the United States established to fund and perform scientific research. The institution is headquartered in Washington, D.C. As of June 30, 2020, the Institution's endowment was valued at $926.9 million. In 2018 the expenses for scientific programs and administration were $96.6 million. Eric Isaacs is president of the institution.

Sir Alexander Norman Halliday is a British geochemist and academic who is the Founding Dean of the Columbia Climate School, and Director of the Earth Institute at Columbia University. He joined the Earth Institute in April 2018, after spending more than a decade at the Department of Earth Sciences at the University of Oxford, during which time he was dean of science and engineering. He is also a professor of Earth and Environmental Sciences at Columbia University.

BRGM is France's public reference institution in Earth Science applications for the management of surface and subsurface resources and risks. It is the French Geological Survey.

The Stockholm Resilience Centre (SRC), is a research centre on resilience and sustainability science at Stockholm University. It is a joint initiative between Stockholm University and the Beijer Institute of Ecological Economics at the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences.
References
- ↑ "Original research structures" . Retrieved 26 November 2019.
- ↑ "Grenoble observatory of sciences of the universe" . Retrieved 26 November 2019.
- ↑ "governmental decree" . Retrieved 29 June 2016.
- ↑ "Members Units" . Retrieved 26 November 2019.
- ↑ "Permanent exhibition".
45°11′39″N5°45′42″E / 45.1942°N 5.7616°E
