
The economy of Denmark is a modern mixed economy with comfortable living standards, a high level of government services and transfers, and a high dependence on foreign trade. The economy is dominated by the service sector with 80% of all jobs, whereas about 11% of all employees work in manufacturing and 2% in agriculture. The nominal gross national income per capita was the seventh-highest in the world at $58,439 in 2020. Correcting for purchasing power, per capita income was Int$57,781 or 10th-highest globally. The Income distribution is relatively equal, but inequality has somewhat increased during the last decades. This increase was attributed to both a larger spread in gross incomes and various economic policy measures. In 2017, Denmark had the seventh-lowest Gini coefficient of the then 28 European Union countries. With 5,822,763 inhabitants, Denmark has the 36th largest national economy in the world measured by nominal gross domestic product (GDP), and the 51st largest in the world measured by purchasing power parity (PPP).

Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the market value of all the final goods and services produced in a specific time period by countries. GDP (nominal) per capita does not, however, reflect differences in the cost of living and the inflation rates of the countries; therefore, using a basis of GDP per capita at purchasing power parity (PPP) may be more useful when comparing living standards between nations, while nominal GDP is more useful comparing national economies on the international market. Total GDP can also be broken down into the contribution of each industry or sector of the economy. The ratio of GDP to the total population of the region is the per capita GDP and the same is called Mean Standard of Living.

The economy of Luxembourg is largely dependent on the banking, steel, and industrial sectors. Luxembourgers enjoy the highest per capita gross domestic product in the world.

The economy of Malta is a highly industrialised, service-based economy. It is classified as an advanced economy by the International Monetary Fund and is considered a high-income country by the World Bank and an innovation-driven economy by the World Economic Forum. It is a member of the European Union and of the eurozone, having formally adopted the euro on 1 January 2008.
The economy of Romania is a high-income economy with a skilled labour force, ranked 10th in the European Union by total nominal GDP and 7th largest when adjusted by purchasing power parity.

The economy of Slovenia is a developed economy, and the country enjoys a high level of prosperity and stability as well as above-average GDP per capita by purchasing power parity at 83% of the EU28 average in 2015. Nominal GDP in 2018 is 42.534 billion EUR, nominal GDP per capita (GDP/pc) in 2018 is EUR 21,267. The highest GDP/pc is in central Slovenia, where the capital city Ljubljana is located. It is part of the Western Slovenia statistical region, which has a higher GDP/pc than eastern Slovenia.

The economy of Austria is a developed social market economy, with the country being one of the fourteen richest in the world in terms of GDP per capita. Until the 1980s, many of Austria's largest industry firms were nationalised. In recent years, privatisation has reduced state holdings to a level comparable to other European economies. Labour movements are particularly strong in Austria, and they have a large influence on labour politics. Next to a highly developed industry, international tourism is the most important part of the national economy.

Eurostat is a Directorate-General of the European Commission located in the Kirchberg quarter of Luxembourg City, Luxembourg. Eurostat’s main responsibilities are to provide statistical information to the institutions of the European Union (EU) and to promote the harmonisation of statistical methods across its member states and candidates for accession as well as EFTA countries. The organisations in the different countries that cooperate with Eurostat are summarised under the concept of the European Statistical System.
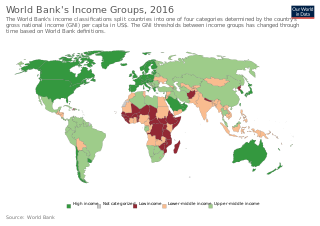
The gross national income (GNI), previously known as gross national product (GNP), is the total domestic and foreign output claimed by residents of a country, consisting of gross domestic product (GDP), plus factor incomes earned by foreign residents, minus income earned in the domestic economy by nonresidents. Comparing GNI to GDP shows the degree to which a nation's GDP represents domestic or international activity. GNI has gradually replaced GNP in international statistics. While being conceptually identical, it is calculated differently. GNI is the basis of calculation of the largest part of contributions to the budget of the European Union. In February 2017, Ireland's GDP became so distorted from the base erosion and profit shifting ("BEPS") tax planning tools of U.S. multinationals, that the Central Bank of Ireland replaced Irish GDP with a new metric, Irish Modified GNI. In 2017, Irish GDP was 162% of Irish Modified GNI.

National accounts or national account systems (NAS) are the implementation of complete and consistent accounting techniques for measuring the economic activity of a nation. These include detailed underlying measures that rely on double-entry accounting. By design, such accounting makes the totals on both sides of an account equal even though they each measure different characteristics, for example production and the income from it. As a method, the subject is termed national accounting or, more generally, social accounting. Stated otherwise, national accounts as systems may be distinguished from the economic data associated with those systems. While sharing many common principles with business accounting, national accounts are based on economic concepts. One conceptual construct for representing flows of all economic transactions that take place in an economy is a social accounting matrix with accounts in each respective row-column entry.

Consumption of fixed capital (CFC) is a term used in business accounts, tax assessments and national accounts for depreciation of fixed assets. CFC is used in preference to "depreciation" to emphasize that fixed capital is used up in the process of generating new output, and because unlike depreciation it is not valued at historic cost but at current market value ; CFC may also include other expenses incurred in using or installing fixed assets beyond actual depreciation charges. Normally the term applies only to producing enterprises, but sometimes it applies also to real estate assets.

The economy of the European Union is the joint economy of the member states of the European Union (EU). It is the second largest economy in the world in nominal terms, after the United States, and the third one in purchasing power parity (PPP) terms, after China and the United States. The European Union's GDP was estimated to be around $17.1 trillion (nominal) in 2020, representing around 1/6 of the global economy.

Insular Italy is one of the five official statistical regions of Italy used by the National Institute of Statistics (ISTAT), a first level NUTS region and a European Parliament constituency. Insular Italy encompasses two of the country's 20 regions: Sardinia and Sicily.

The value product (VP) is an economic concept formulated by Karl Marx in his critique of political economy during the 1860s, and used in Marxian social accounting theory for capitalist economies. Its annual monetary value is approximately equal to the netted sum of six flows of income generated by production:
Compensation of employees (CE) is a statistical term used in national accounts, balance of payments statistics and sometimes in corporate accounts as well. It refers basically to the total gross (pre-tax) wages paid by employers to employees for work done in an accounting period, such as a quarter or a year.
Operating surplus is an accounting concept used in national accounts statistics and in corporate and government accounts. It is the balancing item of the Generation of Income Account in the UNSNA. It may be used in macro-economics as a proxy for total pre-tax profit income, although entrepreneurial income may provide a better measure of business profits. According to the 2008 SNA, it is the measure of the surplus accruing from production before deducting property income, e.g., land rent and interest.

South Italy is one of the five official statistical regions of Italy used by the National Institute of Statistics (ISTAT), a first level NUTS region and a European Parliament constituency. South Italy encompasses six of the country's 20 regions:
Gross national income at market prices in the European Union of 27 Member States (GNI) amounted to EUR 44.778 per inhabitant in 2020.

The annual United Kingdom National Accounts records and describes economic activity in the United Kingdom and as such is used by government, banks, academics and industries to formulate the economic and social policies and monitor the economic progress of the United Kingdom. It also allows international comparisons to be made. The Blue Book is published by the UK Office for National Statistics alongside the United Kingdom Balance of Payments – The Pink Book.














