
A propeller is a device with a rotating hub and radiating blades that are set at a pitch to form a helical spiral which, when rotated, exerts linear thrust upon a working fluid such as water or air. Propellers are used to pump fluid through a pipe or duct, or to create thrust to propel a boat through water or an aircraft through air. The blades are shaped so that their rotational motion through the fluid causes a pressure difference between the two surfaces of the blade by Bernoulli's principle which exerts force on the fluid. Most marine propellers are screw propellers with helical blades rotating on a propeller shaft with an approximately horizontal axis.

Landing is the last part of a flight, where a flying animal, aircraft, or spacecraft returns to the ground. When the flying object returns to water, the process is called alighting, although it is commonly called "landing", "touchdown" or "splashdown" as well. A normal aircraft flight would include several parts of flight including taxi, takeoff, climb, cruise, descent and landing.

Aircraft engine controls provide a means for the pilot to control and monitor the operation of the aircraft's powerplant. This article describes controls used with a basic internal-combustion engine driving a propeller. Some optional or more advanced configurations are described at the end of the article. Jet turbine engines use different operating principles and have their own sets of controls and sensors.
Blade pitch or simply pitch refers to the angle of a blade in a fluid. The term has applications in aeronautics, shipping, and other fields.

In aeronautics, a variable-pitch propeller is a type of propeller (airscrew) with blades that can be rotated around their long axis to change the blade pitch. A controllable-pitch propeller is one where the pitch is controlled manually by the pilot. Alternatively, a constant-speed propeller is one where the pilot sets the desired engine speed (RPM), and the blade pitch is controlled automatically without the pilot's intervention so that the rotational speed remains constant. The device which controls the propeller pitch and thus speed is called a propeller governor or constant speed unit.

A quadcopter, also called quadrocopter, or quadrotor is a type of helicopter or multicopter that has four rotors.

P-factor, also known as asymmetric blade effect and asymmetric disc effect, is an aerodynamic phenomenon experienced by a moving propeller, wherein the propeller's center of thrust moves off-center when the aircraft is at a high angle of attack. This shift in the location of the center of thrust will exert a yawing moment on the aircraft, causing it to yaw slightly to one side. A rudder input is required to counteract the yawing tendency.

In aeronautics, an aircraft propeller, also called an airscrew, converts rotary motion from an engine or other power source into a swirling slipstream which pushes the propeller forwards or backwards. It comprises a rotating power-driven hub, to which are attached several radial airfoil-section blades such that the whole assembly rotates about a longitudinal axis. The blade pitch may be fixed, manually variable to a few set positions, or of the automatically variable "constant-speed" type.

A helicopter is a type of rotorcraft in which lift and thrust are supplied by horizontally spinning rotors. This allows the helicopter to take off and land vertically, to hover, and to fly forward, backward and laterally. These attributes allow helicopters to be used in congested or isolated areas where fixed-wing aircraft and many forms of short take-off and landing (STOL) or short take-off and vertical landing (STOVL) aircraft cannot perform without a runway.
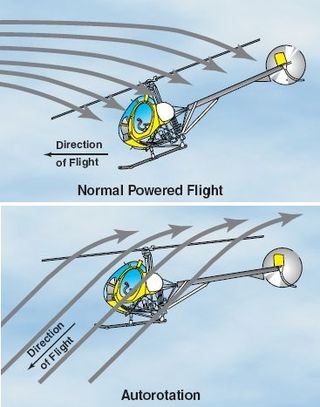
Autorotation is a state of flight in which the main rotor system of a helicopter or other rotary-wing aircraft turns by the action of air moving up through the rotor, as with an autogyro, rather than engine power driving the rotor. The term autorotation dates to a period of early helicopter development between 1915 and 1920, and refers to the rotors turning without the engine. It is analogous to the gliding flight of a fixed-wing aircraft. Some trees have seeds that have evolved wing-like structures that enable the seed to spin to the ground in autorotation, which helps the seeds to disseminate over a wider area.

The Bölkow Bo 46 was a West German experimental helicopter built to test the Derschmidt rotor system that aimed to allow much higher speeds than traditional helicopter designs. Wind tunnel testing showed promise, but the Bo 46 demonstrated a number of problems and added complexity that led to the concept being abandoned. The Bo 46 was one of a number of new designs exploring high-speed helicopter flight that were built in the early 1960s.

Unlike a standard one-piece boat or aircraft propeller, a modular propeller is made up of using a number of replaceable parts, typically:

The Lamco Eurocub is a Hungarian ultralight aircraft with fixed conventional landing gear, manufactured by Danex Engineering Kft. It is used primarily for flight training, touring and personal flying.
Electravia - Helices E-Props is a French aviation manufacturer based in Vaumeilh, specializing in the non-certified light aviation sector. At one time it produced electric propulsion systems and now designs and manufactures carbon fibre propellers for light aircraft.

The Colomban MC-30 Luciole is an ultra-lightweight plans-built single-seat low-wing tail-dragger monoplane, designed by the French aeronautical engineer Michel Colomban, creator of the tiny single-seat Colomban Cri-cri twin-engined aircraft and the MC-100 Ban-Bi two-seat aircraft.

Ivoprop Corporation, founded in 1984 by Ivo Zdarsky, is an American manufacturer of composite propellers for homebuilt and ultralight aircraft, as well as airboats. The company's headquarters are in Long Beach, California.

The V-Prop is an automatic self-powering electronic variable-pitch propeller developed by Silence Aircraft, the manufacturers of the Silence Twister single-seat elliptical-winged kitplane.
Thomas William Moy (1823–1910) was an English engineer and patent agent best known for his Aerial Steamer of 1875.
The Coax-P is a contra-rotating propeller developed by NeuraJet of Senftenbach, Austria and Sun Flightcraft of Innsbruck, Austria for the Rotax 503 and Rotax 582 aircraft engines for use on ultralight aircraft.















