| C119 | |
|---|---|
| ILO Convention | |
| Date of adoption | June 25, 1963 |
| Date in force | April 21, 1965 |
| Classification | Physical Hazards, Noise and Vibration |
| Subject | Occupational Safety and Health |
| Previous | Equality of Treatment (Social Security) Convention, 1962 |
| Next | Hygiene (Commerce and Offices) Convention, 1964 |
Guarding of Machinery Convention, 1963 is an International Labour Organization Convention.
It was established in 1963, with the preamble stating:
Having decided upon the adoption of certain proposals with regard to the prohibition of the sale, hire and use of inadequately guarded machinery,...
As of 2013, the convention has been ratified by 52 states.

The European Convention on Human Rights is an international convention to protect human rights and political freedoms in Europe. Drafted in 1950 by the then newly formed Council of Europe, the convention entered into force on 3 September 1953. All Council of Europe member states are party to the Convention and new members are expected to ratify the convention at the earliest opportunity.

The International Maritime Organization is a specialised agency of the United Nations responsible for regulating shipping. The IMO was established following agreement at a UN conference held in Geneva in 1948 and the IMO came into existence ten years later, meeting for the first time in 1959. Headquartered in London, United Kingdom, the IMO currently has 174 member states and three associate members.

The Constitution of the United States is the supreme law of the United States of America. This founding document, originally comprising seven articles, delineates the national frame of government. Its first three articles embody the doctrine of the separation of powers, whereby the federal government is divided into three branches: the legislative, consisting of the bicameral Congress ; the executive, consisting of the president and subordinate officers ; and the judicial, consisting of the Supreme Court and other federal courts. Article IV, Article V and Article VI embody concepts of federalism, describing the rights and responsibilities of state governments, the states in relationship to the federal government, and the shared process of constitutional amendment. Article VII establishes the procedure subsequently used by the 13 States to ratify it. It is regarded as the oldest written and codified national constitution in force.

The Vienna Convention on Diplomatic Relations of 1961 is an international treaty that defines a framework for diplomatic relations between independent countries. It specifies the privileges of a diplomatic mission that enable diplomats to perform their function without fear of coercion or harassment by the host country. This forms the legal basis for diplomatic immunity. Its articles are considered a cornerstone of modern international relations. As of June 2020, it has been ratified by 193 states.

A constitutional convention is a gathering for the purpose of writing a new constitution or revising an existing constitution. Members of a constitutional convention are often, though not necessarily or entirely, elected by popular vote. However, a wholly popularly-elected constitutional convention can also be referred to as a constituent assembly.

The Vienna Convention on the Law of Treaties (VCLT) is an international agreement regulating treaties between states. Known as the "treaty on treaties", it establishes comprehensive rules, procedures, and guidelines for how treaties are defined, drafted, amended, interpreted, and generally operated. An international treaty is a written agreement between international law subjects reflecting their consent to the creation, alteration, or termination of their rights and obligations. The VCLT is considered a codification of customary international law and state practice concerning treaties.

The Hague Conventions of 1899 and 1907 are a series of international treaties and declarations negotiated at two international peace conferences at The Hague in the Netherlands. Along with the Geneva Conventions, the Hague Conventions were among the first formal statements of the laws of war and war crimes in the body of secular international law. A third conference was planned for 1914 and later rescheduled for 1915, but it did not take place because of the start of World War I.

The Corwin Amendment is a proposed amendment to the United States Constitution that would shield "domestic institutions" of the states from the federal constitutional amendment process and from abolition or interference by Congress. Although the Corwin Amendment does not explicitly use the word slavery, it was designed specifically to protect slavery from federal power. Congress proposed the Corwin Amendment on March 2, 1861, shortly before the outbreak of the American Civil War. It has not been ratified by the requisite number of states.
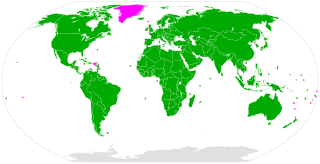
The Convention concerning the Prohibition and Immediate Action for the Elimination of the Worst Forms of Child Labour, known in short as the Worst Forms of Child Labour Convention, was adopted by the International Labour Organization (ILO) in 1999 as ILO Convention No 182. It is one of eight ILO fundamental conventions.
The Vienna Convention on Civil Liability for Nuclear Damage is a 1963 treaty that governs issues of liability in cases of nuclear accident. It was concluded at Vienna on 21 May 1963 and entered into force on 12 November 1977. The convention has been amended by a 1997 protocol, in force since 4 October 2003. The depository is the International Atomic Energy Agency.
United States v. Sprague, 282 U.S. 716 (1931), was a United States Supreme Court case that dealt with the Fifth Article of the US Constitution. The defendants had been indicted under the National Prohibition Act and were attempting to quash their indictments, arguing that the Eighteenth Amendment had not been properly ratified. Their reasoning was that the Congress of the United States had chosen to ratify it by usage of state legislatures instead of constitutional conventions.
Minimum Wage-Fixing Machinery Convention, 1928 is an International Labour Organization Convention.
The Right to Organise and Collective Bargaining Convention (1949) No 98 is an International Labour Organization Convention. It is one of eight ILO fundamental conventions.
Safety Provisions (Building) Convention, 1937 is an International Labour Organization Convention.
Minimum Wage Fixing Machinery (Agriculture) Convention, 1951 is an International Labour Organization Convention.
Minimum Wage Fixing Convention 1970 is a Convention by the International Labour Organization established in 1970. The preamble stated:
Noting the terms of the Minimum Wage-Fixing Machinery Convention, 1928, and the Equal Remuneration Convention, 1951, which have been widely ratified, as well as of the Minimum Wage Fixing Machinery (Agriculture) Convention, 1951, and
Considering that these Convention have played a valuable part in protecting disadvantaged groups of wage earners, and
Considering that the time has come to adopt a further instrument complementing these Conventions and providing protection for wage earners against unduly low wages, which, while of general application, pays special regard to the needs of developing countries, and
Having decided upon the adoption of certain proposals with regard to minimum wage fixing machinery and related problems, with special reference to developing countries,..
Prevention of Accidents (Seafarers) Convention, 1970 is an International Labour Organization Convention.
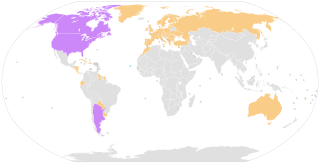
The Hague Convention on parental responsibility and protection of children, or Hague Convention 1996, officially Convention of 19 October 1996 on Jurisdiction, Applicable Law, Recognition, Enforcement and Co-operation in respect of Parental Responsibility and Measures for the Protection of Children or Hague Convention 1996 is a convention of the Hague Conference on Private International Law. It covers civil measures of protection concerning children, ranging from orders concerning parental responsibility and contact to public measures of protection or care, and from matters of representation to the protection of children's property. It is therefore much broader in scope than two earlier conventions of the HCCH on the subject.

The drafting of the Constitution of the United States began on May 25, 1787, when the Constitutional Convention met for the first time with a quorum at the Pennsylvania State House in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania to revise the Articles of Confederation. It ended on September 17, 1787, the day the Constitution drafted by the convention's delegates to replace the Articles was adopted and signed. The ratification process for the Constitution began that day, and ended when the final state, Rhode Island, ratified it on May 29, 1790.
The right to sit refers to laws or policies granting workers the right to be granted suitable seating at the workplace. Jurisdictions that have enshrined "right to sit" laws or policies include the United Kingdom, Jamaica, South Africa, Tanzania, Lesotho, Malaysia, Israel, Ireland, the Indian states of Tamil Nadu and Kerala, the Canadian province of Newfoundland and Labrador, and the British overseas territory of Montserrat. Almost all states of the United States and Australia, as well as the majority of Canadian provinces passed right to sit legislation for women workers between 1881 and 1917. US states with current right to sit legislation include California, Florida, Massachusetts, Montana, New Jersey, New Mexico, New York, West Virginia, and Wisconsin. A right to sit provision is included in the International Labour Organization's Hygiene Convention, 1964; the convention being ratified by 51 countries as of 2014. Local jurisdictions with right to sit laws include Portland, Oregon, St. Louis, Missouri and London's Royal Borough of Kensington and Chelsea. Some jurisdictions, such as Alabama, Connecticut, Kentucky, Quebec, and Washington, D.C. have revoked their right to sit laws. Many right to sit laws originally contained gendered language specifying women workers only. Some jurisdictions maintain gendered laws, but many jurisdictions have amended their right to sit laws to be gender neutral.