Related Research Articles

Computing is any goal-oriented activity requiring, benefiting from, or creating computing machinery. It includes the study and experimentation of algorithmic processes, and the development of both hardware and software. Computing has scientific, engineering, mathematical, technological, and social aspects. Major computing disciplines include computer engineering, computer science, cybersecurity, data science, information systems, information technology, and software engineering.

Computer science is the study of computation, information, and automation. Computer science spans theoretical disciplines to applied disciplines.

MATLAB is a proprietary multi-paradigm programming language and numeric computing environment developed by MathWorks. MATLAB allows matrix manipulations, plotting of functions and data, implementation of algorithms, creation of user interfaces, and interfacing with programs written in other languages.

Numerical analysis is the study of algorithms that use numerical approximation for the problems of mathematical analysis. It is the study of numerical methods that attempt to find approximate solutions of problems rather than the exact ones. Numerical analysis finds application in all fields of engineering and the physical sciences, and in the 21st century also the life and social sciences like economics, medicine, business and even the arts. Current growth in computing power has enabled the use of more complex numerical analysis, providing detailed and realistic mathematical models in science and engineering. Examples of numerical analysis include: ordinary differential equations as found in celestial mechanics, numerical linear algebra in data analysis, and stochastic differential equations and Markov chains for simulating living cells in medicine and biology.
Software engineering is an engineering approach to software development. A practitioner, called a software engineer, applies the engineering design process to develop software.

The Z notation is a formal specification language used for describing and modelling computing systems. It is targeted at the clear specification of computer programs and computer-based systems in general.

The history of computing is longer than the history of computing hardware and modern computing technology and includes the history of methods intended for pen and paper or for chalk and slate, with or without the aid of tables.
Computational science, also known as scientific computing, technical computing or scientific computation (SC), is a division of science, and more specifically the Computer Sciences, which uses advanced computing capabilities to understand and solve complex physical problems. While this discussion typically extenuates into Visual Computation, this research field of study will typically include the following research categorizations.
The general algebraic modeling system (GAMS) is a high-level modeling system for mathematical optimization. GAMS is designed for modeling and solving linear, nonlinear, and mixed-integer optimization problems. The system is tailored for complex, large-scale modeling applications and allows the user to build large maintainable models that can be adapted to new situations. The system is available for use on various computer platforms. Models are portable from one platform to another.
Financial modeling is the task of building an abstract representation of a real world financial situation. This is a mathematical model designed to represent the performance of a financial asset or portfolio of a business, project, or any other investment.

SageMath is a computer algebra system (CAS) with features covering many aspects of mathematics, including algebra, combinatorics, graph theory, group theory, differentiable manifolds, numerical analysis, number theory, calculus and statistics.

Computational mathematics is the study of the interaction between mathematics and calculations done by a computer.

The Interdisciplinary Center for Scientific Computing is a scientific research institute of the Heidelberg University, Germany. It centralizes scientific activity and promotes research and work in scientific computing. Founded in 1987 by the Heidelberg University and the state of Baden-Württemberg, IWR participates in joint project and cooperations with industry in Germany as well as abroad. As a research institute with about 380 staff, IWR is considered one of the world's largest research centers for scientific computing.
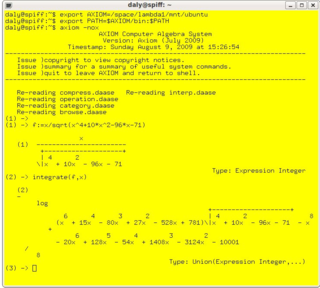
In mathematics and computer science, computer algebra, also called symbolic computation or algebraic computation, is a scientific area that refers to the study and development of algorithms and software for manipulating mathematical expressions and other mathematical objects. Although computer algebra could be considered a subfield of scientific computing, they are generally considered as distinct fields because scientific computing is usually based on numerical computation with approximate floating point numbers, while symbolic computation emphasizes exact computation with expressions containing variables that have no given value and are manipulated as symbols.
Special functions are particular mathematical functions that have more or less established names and notations due to their importance in mathematical analysis, functional analysis, geometry, physics, or other applications.
This glossary of computer science is a list of definitions of terms and concepts used in computer science, its sub-disciplines, and related fields, including terms relevant to software, data science, and computer programming.

Micah Altman is an American social scientist who conducts research in social science informatics. Since 2012, he has worked as the head research scientist in the MIT Libraries, first as director of the Program on Information Science (2012-2018) and subsequently as director of research for the libraries' Center for Research on Equitable and Open Scholarship. Altman previously worked at Harvard University. He is known for his work on redistricting, scholarly communication, privacy and open science. Altman is a co-founder of Public Mapping Project, which develops DistrictBuilder, an open-source software.
References
- ↑ Altman, Micah; Gill, Jeff; McDonald, Michael P. (2004), Numerical Issues in Statistical Computing for the Social Scientist, Wiley Series in Probability and Statistics, vol. 508, John Wiley & Sons, p. 92, ISBN 9780471475743
- ↑ Skiena, Steven S. (1998), The Algorithm Design Manual, Springer, p. 429, ISBN 9780387948607
- ↑ Krommer, Arnold R.; Ueberhuber, Christoph W. (1998), Computational Integration, SIAM, p. 68, ISBN 9780898713749
- ↑ Kincaid, David; Cheney, Ward (2002), Numerical Analysis: Mathematics of Scientific Computing, Pure and applied undergraduate texts, vol. 2 (3rd ed.), American Mathematical Society, p. 732, ISBN 9780821847886
- ↑ Johnson, Richard W. (2016), Handbook of Fluid Dynamics (2nd ed.), CRC Press, p. 33-18, ISBN 9781439849576