Related Research Articles

Energy Star is a program run by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) that promotes energy efficiency. The program provides information on the energy consumption of products and devices using different standardized methods. The Energy Star label is found on more than 75 different certified product categories, homes, commercial buildings, and industrial plants. In the United States, the Energy Star label is also shown on the Energy Guide appliance label of qualifying products.

Green building refers to both a structure and the application of processes that are environmentally responsible and resource-efficient throughout a building's life-cycle: from planning to design, construction, operation, maintenance, renovation, and demolition. This requires close cooperation of the contractor, the architects, the engineers, and the client at all project stages. The Green Building practice expands and complements the classical building design concerns of economy, utility, durability, and comfort. Green building also refers to saving resources to the maximum extent, including energy saving, land saving, water saving, material saving, etc., during the whole life cycle of the building, protecting the environment and reducing pollution, providing people with healthy, comfortable and efficient use of space, and being in harmony with nature. Buildings that live in harmony; green building technology focuses on low consumption, high efficiency, economy, environmental protection, integration and optimization.’
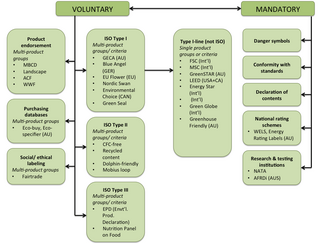
Ecolabels and Green Stickers are labeling systems for food and consumer products. The use of ecolabels is voluntary, whereas green stickers are mandated by law; for example, in North America major appliances and automobiles use Energy Star. They are a form of sustainability measurement directed at consumers, intended to make it easy to take environmental concerns into account when shopping. Some labels quantify pollution or energy consumption by way of index scores or units of measurement, while others assert compliance with a set of practices or minimum requirements for sustainability or reduction of harm to the environment. Many ecolabels are focused on minimising the negative ecological impacts of primary production or resource extraction in a given sector or commodity through a set of good practices that are captured in a sustainability standard. Through a verification process, usually referred to as "certification", a farm, forest, fishery, or mine can show that it complies with a standard and earn the right to sell its products as certified through the supply chain, often resulting in a consumer-facing ecolabel.
Green computing, green IT, or ICT sustainability, is the study and practice of environmentally sustainable computing or IT.

Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design (LEED) is a green building certification program used worldwide. Developed by the non-profit U.S. Green Building Council (USGBC), it includes a set of rating systems for the design, construction, operation, and maintenance of green buildings, homes, and neighborhoods, which aims to help building owners and operators be environmentally responsible and use resources efficiently.
Design for the environment (DfE) is a design approach to reduce the overall human health and environmental impact of a product, process or service, where impacts are considered across its life cycle. Different software tools have been developed to assist designers in finding optimized products or processes/services. DfE is also the original name of a United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) program, created in 1992, that works to prevent pollution, and the risk pollution presents to humans and the environment. The program provides information regarding safer chemical formulations for cleaning and other products. EPA renamed its program "Safer Choice" in 2015.
The Home Energy Rating is an American estimated measurement of a home's energy efficiency based on normalized modified end-use loads (nMEULs). In the United States, the Residential Energy Services Network (RESNET) is responsible for creation and maintenance of the RESNET Mortgage Industry National Home Energy Rating Standards (MINHERS), a proprietary system of standards, which includes standards language for the certification and quality assurance for RESNET Provider organizations. RESNET is an EPA recognized Home Certification Organization (HCO) that also help's create standards in compliance with the American National Standards Institute, namely ANSI 301, ANSI 310, ANSI 380, and ANSI 850. The Building Science Institute, Ltd. Co. (BSI) is another EPA recognized HCO that maintains the ANSI Standards to produce Energy Ratings and compliance with above-code programs such as the ENERGY STAR New Homes Program.

Green Seal is a non-profit environmental standard development and certification organization. Its flagship program is the certification of products and services. Certification is based on Green Seal standards, which contain performance, health, and sustainability criteria.
This article provides examples of green building programs in the United States. These programs span the public, private, and non-profit sectors, and all have the goal of increasing energy efficiency and the sustainability of the built environment.
Canada has implemented the "R-2000" in 1982 to promote better than building code construction to increase energy efficiency and promote sustainability. An optional feature of the R-2000 home program is the EnerGuide rating service. This service is available across Canada, allows home builders and home buyers to measure and rate the performance of their homes, and confirm that those specifications have been met. Some Canadian provinces are considering mandatory use of the service for all new homes.

The United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) was established in July 1970 when the White House and the United States Congress came together due to the public's demand for cleaner natural resources. The purpose of the EPA is to repair the damage done to the environment and to set up new criteria to allow Americans to make a clean environment a reality. The ultimate goal of the EPA is to protect human health and the environment.
The California Sustainability Alliance is an organization funded by the California IOUs, to facilitate discussions between various industries on the issues of resource sustainability. The Alliance was set up in 2008 to help California meet its goals in facing Climate change in the State, in relation to energy, resources, and the environment. Efforts are directed at increasing and accelerating sustainable measures and strategies. The Alliance specifically focuses on energy efficiency, climate action, “smart growth” principles, renewable energy development, water-use efficiency, waste management, and transportation management within California.
Environmentally sustainable design is the philosophy of designing physical objects, the built environment, and services to comply with the principles of ecological sustainability and also aimed at improving the health and comfort of occupants in a building. Sustainable design seeks to reduce negative impacts on the environment, the health and well-being of building occupants, thereby improving building performance. The basic objectives of sustainability are to reduce the consumption of non-renewable resources, minimize waste, and create healthy, productive environments.
Executive Order 13514 was an Executive Order, entitled Federal Leadership in Environmental, Energy, and Economic Performance, which U.S. President Barack Obama issued on October 5, 2009. EO 13514 was replaced by Executive Order 13693, titled Planning for Federal Sustainability in the Next Decade, issued by Obama on March 19, 2015. The Office of the Federal Environmental Executive, whose name was changed to the Office of Federal Sustainability by Executive Order 13693, is housed at the Council on Environmental Quality within the Executive Office of the President of the United States. Its role is to oversee policy, guidance, and implementation of the sustainability Executive Order.
Qatar Sustainability Assessment System (QSAS) is a green building certification system developed for the State of Qatar. The primary objective of Qatar Sustainability Assessment System [QSAS] is to create a sustainable built environment that minimizes ecological impact while addressing the specific regional needs and environment of Qatar.
Sustainable products are products who are either sustainability sourced, manufactured or processed that provide environmental, social and economic benefits while protecting public health and environment over their whole life cycle, from the extraction of raw materials until the final disposal.
Green Building Initiative (GBI) is a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization that owns and administers the Green Globes green building assessment and certification in the United States and Canada. It was established in 2004 and is headquartered in Portland, Oregon.
The Global Sustainability Assessment System (GSAS) [Originally QSAS] is the first performance-based system in the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) region, developed for assessing and rating buildings and infrastructure for their sustainability impacts. In 2016, FIFA officially endorsed GSAS as the sustainability assessment system for Qatar's eight stadiums set to host the 2022 FIFA World Cup. The primary objective of GSAS is to create a sustainable built environment that minimizes ecological impact and reduces resources consumption while addressing the local needs and environmental conditions specific to the region. GSAS adopts an integrated lifecycle approach for the assessment of the built environment including design, construction and operation phases.

The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency’s (EPA's) Safer Choice label, previously known as the Design for the Environment (DfE) label, helps consumers and commercial buyers identify and select products with safer chemical ingredients, without sacrificing quality or performance. When a product has the Safer Choice label, it means that every intentionally-added ingredient in the product has been evaluated by EPA scientists. Only the safest possible functional ingredients are allowed in products with the Safer Choice label.

Green building certification systems are a set of rating systems and tools that are used to assess a building or a construction project's performance from a sustainability and environmental perspective. Such ratings aim to improve the overall quality of buildings and infrastructures, integrate a life cycle approach in its design and construction, and promote the fulfillment of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals by the construction industry. Buildings that have been assessed and are deemed to meet a certain level of performance and quality, receive a certificate proving this achievement.
References
- 1 2 "Federal Leadership in High Performance and Sustainable Buildings Memorandum of Understanding | Whole Building Design Guide". Wbdg.org. Retrieved 2012-09-27.
- ↑ "Federal Leadership in Environmental, Energy, and Economic Performance" (PDF). Gpo.gov. Retrieved 2012-09-27.
- ↑ "Green Building Initiative testimony to the US House of Representatives Science, Space and Technology Committee Subcommittee on Investigations and Oversight" (PDF). Science.house.gov. Retrieved 2012-09-27.
- ↑ "Guiding Principles Compliance Assessment and Certification Program | The Green Building Initiative". GBI. Retrieved 2012-09-27.
- ↑ [ dead link ]