Related Research Articles

The federal city of Bonn (German pronunciation: [bɔn] is a city on the banks of the Rhine located in the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia, with a population of over 300,000. About 24 km south-southeast of Cologne, Bonn is in the southernmost part of the Rhine-Ruhr region, Germany's largest metropolitan area, with over 11 million inhabitants. It is a university city, was the birthplace of Ludwig van Beethoven and was the capital of West Germany from 1949 to 1990. Bonn was the seat of government of reunited Germany from 1990 to 1999.

The Augustusburg and Falkenlust Palaces form a historical building complex in Brühl, North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. The buildings are connected by the spacious gardens and trees of the Schlosspark. Built in the early 18th century, the palaces and adjoining gardens are considered masterpieces of early rococo architecture and have been listed as a UNESCO cultural World Heritage Site since 1984. Augustusburg Palace and its parks also serve as a venue for the Brühl Palace Concerts.

The Nymphenburg Palace is a Baroque palace situated in Munich's western district Neuhausen-Nymphenburg, in Bavaria, southern Germany. Combined with the adjacent Nymphenburg Palace Park it constitutes one of the premier royal palaces of Europe. Its frontal width of 632 m (2,073 ft) even surpasses Versailles Palace. The Nymphenburg served as the main summer residence for the former rulers of Bavaria of the House of Wittelsbach.

Heidelberg Castle is a ruin in Germany and landmark of Heidelberg. The castle ruins are among the most important Renaissance structures north of the Alps.

Peter Joseph Lenné was a Prussian gardener and landscape architect. As director general of the Royal Prussian palaces and parks in Potsdam and Berlin, his work shaped the development of 19th-century German garden design in the Neoclassical style. Laid out according to the principles of the English landscape garden, his parks are now World Heritage Sites.

Archduke Maximilian Francis of Austria was Elector of Cologne and Grand Master of the Teutonic Knights. He was the youngest child of Holy Roman Empress Maria Theresa and Holy Roman Emperor Francis I. He was the last fully functioning Elector of Cologne and the second employer and patron of the young Ludwig van Beethoven.
François de Cuvilliés, sometimes referred to as the Elder, was a Belgian-born Bavarian decorative designer and architect. He was instrumental in bringing the Rococo style to the Wittelsbach court at Munich and to Central Europe in general.

Schwetzingen Palace is a schloss in the German state of Baden-Württemberg. Schwetzingen was the summer residence of the Electors Palatine Charles III Philip and Charles IV Theodore. It is situated in Schwetzingen, roughly equidistant from the electors' seats at Heidelberg and Mannheim, and is most notable for its spacious and ornate gardens. Other than these exceptionally well preserved gardens and the palace proper, the compound also features the Schlosstheater Schwetzingen, the principal venue for the annual Schwetzingen Festival.

Nicolas de Pigage was a French builder.

Elisabeth Auguste of Sulzbach was the eldest granddaughter of the Elector of the Palatinate Charles III Philip, and by her marriage to Elector Palatine Charles IV Theodore, Electress Palatine and later Electress of Bavaria.
Francesco Rabaliatti was a German architect and Court Builder to the Prince-elector Karl Theodor.

Schloss Köpenick is a Baroque water palace of the Hohenzollern electors of Brandenburg which stands on an island in the Dahme River surrounded by an English-style park and gives its name to Köpenick, a district of Berlin.

Bergpark Wilhelmshöhe is a landscape park in Kassel, Germany. The area of the park is 2.4 square kilometres, making it the largest European hillside park, and second largest park on a hill slope in the world. Construction of the Bergpark, or "mountain park", began in 1689 at the behest of the Landgraves of Hesse-Kassel and took about 150 years. The park is open to the public today. Since 2013, it has been a UNESCO World Heritage Site because of its monumental Baroque architecture and its unique fountains and water features.

Poppelsdorf Palace is a Baroque building in the Poppelsdorf district of Bonn, western Germany, which is now part of the University of Bonn.

Pillnitz Palace is a restored Baroque schloss at the eastern end of the city of Dresden in the German state of Saxony. It is located on the bank of the River Elbe in the former village of Pillnitz. It was the summer residence of many electors and kings of Saxony; it is also known for the Declaration of Pillnitz in 1791.

Schloss Türnich is a schloss located in Türnich, now part of Kerpen, North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. The present main building was built from 1757 to 1766 in Baroque style, with an adjacent English landscape park. It has belonged to the Hoensbroech family since 1850. A richly decorated chapel was added in 1895.
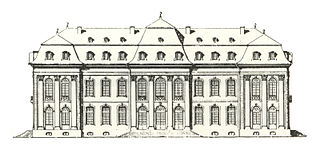
Schloss Philippsfreude was a rococo Schloss in Wittlich in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. It served as a hunting lodge and summer palace for the Prince-Electors of Trier. It was destroyed by French revolutionary troops in 1797. Today, nothing is left anymore.

Michael Leveilly was a French architect who was active essentially in Germany.
Johann Heinrich Jakob Roth was a German master builder of the 18th century.

Klassische Philharmonie Bonn is a German touring symphony orchestra, based in Bonn, North Rhine-Westphalia. It was founded by Heribert Beissel in 1986, derived from the Chur Cölnisches Orchester that he had founded in 1959 to perform music played originally at the Bonn court of the Electors of Cologne. Beissel conducted the orchestra until his death in 2021. They have regularly played a concert series Wiener Klassik at more than ten concert halls in Germany, and also toured in Europe, the U.S. and Japan.
References
- ↑ Baudez, Basile (2021-12-21). Inessential Colors: Architecture on Paper in Early Modern Europe. Princeton University Press. p. 128. ISBN 978-0-691-21356-9.
- ↑ "Guillaume d'Hauberat: Staatliche Schlösser und Gärten Baden-Württemberg". www.schloss-mannheim.de. Retrieved 2023-04-06.