
The gunnery officer of a warship was the officer responsible for operation and maintenance of the ship's guns and for safe storage of the ship's ammunition inventory.

The gunnery officer of a warship was the officer responsible for operation and maintenance of the ship's guns and for safe storage of the ship's ammunition inventory.
The gunnery officer was usually the line officer next in rank to the executive officer. [1] As shipboard guided missiles and torpedoes became more effective than naval artillery, guns were included within a weapons department replacing the older gunnery department. The weapons department is supervised by a weapons officer who may have a subordinate gunnery officer supervising the ship's guns.

The Board of Ordnance was a British government body. Established in the Tudor period, it had its headquarters in the Tower of London. Its primary responsibilities were 'to act as custodian of the lands, depots and forts required for the defence of the realm and its overseas possessions, and as the supplier of munitions and equipment to both the Army and the Navy'. The Board also maintained and directed the Artillery and Engineer corps, which it founded in the 18th century. By the 19th century, the Board of Ordnance was second in size only to HM Treasury among government departments. The Board lasted until 1855, at which point it was disbanded.
Gunnery sergeant (GySgt) is the seventh enlisted rank in the United States Marine Corps, above staff sergeant and below master sergeant and first sergeant, and is a senior non-commissioned officer (SNCO). It has a pay grade of E-7.

In military organizations, an artillery battery is a unit or multiple systems of artillery, mortar systems, rocket artillery, multiple rocket launchers, surface-to-surface missiles, ballistic missiles, cruise missiles, etc., so grouped to facilitate better battlefield communication and command and control, as well as to provide dispersion for its constituent gunnery crews and their systems. The term is also used in a naval context to describe groups of guns on warships.

The QF 4.5 inch gun has been the standard medium-calibre naval gun used by the Royal Navy as a medium-range weapon capable of use against surface, aircraft and shore targets since 1938. This article covers the early 45-calibre family of guns up to the 1970s. For the later unrelated 55-calibre Royal Navy gun, see 4.5 inch Mark 8 naval gun. Like all British nominally 4.5 inch naval guns, the QF Mk I has an actual calibre of 4.45 inches (113 mm).

The United States Navy Strike Fighter Tactics Instructor program, more popularly known as Top Gun, is a United States Navy training program that teaches air combat maneuvering tactics and techniques to selected naval aviators and naval flight officers, who return to their operating units as surrogate instructors.

A fire-control system (FCS) is a number of components working together, usually a gun data computer, a director and radar, which is designed to assist a ranged weapon system to target, track, and hit a target. It performs the same task as a human gunner firing a weapon, but attempts to do so faster and more accurately.

Naval artillery is artillery mounted on a warship, originally used only for naval warfare and then subsequently used for more specialized roles in surface warfare such as naval gunfire support (NGFS) and anti-aircraft warfare (AAW) engagements. The term generally refers to powder-launched projectile-firing weapons and excludes self-propelled projectiles such as torpedoes, rockets, and missiles and those simply dropped overboard such as depth charges and naval mines.

In ballistics, the elevation is the angle between the horizontal plane and the axial direction of the barrel of a gun, mortar or heavy artillery. Originally, elevation was a linear measure of how high the gunners had to physically lift the muzzle of a gun up from the gun carriage to compensate for projectile drop and hit targets at a certain distance.

A target ship is a vessel — typically an obsolete or captured warship — used as a seaborne target for naval gunnery practice or for weapons testing. Targets may be used with the intention of testing effectiveness of specific types of ammunition; or the target ship may be used for an extended period of routine target practice with specialized non-explosive ammunition. The potential consequences of a drifting wreck require careful preparation of the target ship to prevent pollution, or a floating or submerged collision risk for maritime navigation.
Master gunner is an appointment of the warrant officer rank in the British and United States armed forces.
148 (Meiktila) Commando Forward Observation Battery is a specialist Naval Gunfire Support Forward Observation (NGSFO) unit within 29 Commando Regiment Royal Artillery of UK Commando Force Royal Marines.

The Iowa-class battleships are the most heavily armed warships the United States Navy has ever put to sea, due to the continual development of their onboard weaponry. The first Iowa-class ship was laid down in June 1940; in their World War II configuration, each of the Iowa-class battleships had a main battery of 16-inch (406 mm) guns that could hit targets nearly 20 statute miles (32 km) away with a variety of artillery shells designed for anti-ship or bombardment work. The secondary battery of 5-inch (127 mm) guns could hit targets nearly 9 statute miles (14 km) away with solid projectiles or proximity fuzed shells, and was effective in an anti-aircraft role as well. Each of the four battleships carried a wide array of 20 mm and 40 mm anti-aircraft guns for defense against enemy aircraft.
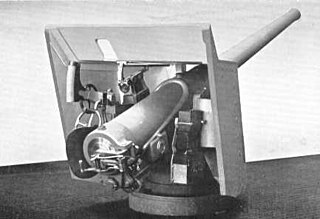
The QF 4.7-inch gun Mks I, II, III, and IV were a family of British quick-firing 4.724-inch (120 mm) naval and coast defence guns of the late 1880s and 1890s that served with the navies of various countries. They were also mounted on various wheeled carriages to provide the British Army with a long-range gun. They all had a barrel of 40 calibres length.

The QF 12-pounder 12-cwt gun (Quick-Firing) was a common, versatile 3-inch (76.2 mm) calibre naval gun introduced in 1894 and used until the middle of the 20th century. It was produced by Armstrong Whitworth, Elswick and used on Royal Navy warships, exported to allied countries, and used for land service. In British service "12-pounder" was the rounded value of the projectile weight, and "12 cwt (hundredweight)" was the weight of the barrel and breech, to differentiate it from other "12-pounder" guns.

The BL 9.2-inch Mk IX and Mk X guns were British breech loading 9.2-inch (234 mm) guns of 46.7 calibre, in service from 1899 to the 1950s as naval and coast defence guns. They had possibly the longest, most varied and successful service history of any British heavy ordnance.

The QF 4-inch gun Mks I, II, III were early British QF (quick-firing) naval guns originating in 1895. They all had barrels of 40 calibres length.

The BL 4-inch gun Mk VII was a British high-velocity naval gun introduced in 1908 as an anti-torpedo boat gun in large ships, and in the main armament of smaller ships. Of the 600 produced, 482 were still available in 1939 for use as coastal artillery and as a defensive weapon on Defensively Equipped Merchant Ships (DEMS) during the Second World War.

The Gunnery and Torpedo Division was the former Directorate of the Admiralty Naval Staff responsible for weapons policy making, development and assessing weapon requirements from 1918-1920.

The Gunnery Division was a Directorate of the Admiralty Naval Staff of the Royal Navy responsible for the tactical use of naval weapons and the training of naval personnel in relation to operational requirements. It was established in 1920 when the Gunnery and Torpedo Division was separated into an independent Gunnery Division and Torpedo Division. It existed until 1964 when the Department of Admiralty was abolished and replaced by a new Ministry of Defence.

The Naval Artillery and Torpedoes Division was a Directorate of the British Admiralty, Naval Staff that was created in June 1918 to decide weapons employment policy and also to develop weapon requirements. This division was also responsible for requirements for ship protection against weapons. It existed until 1920 when its responsibilities were divided into two new directorates, the Gunnery Division and the Torpedo Division.