Related Research Articles
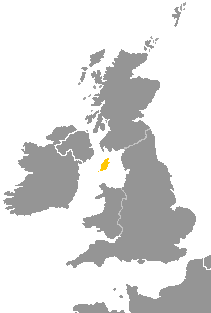
Manx, also known as Manx Gaelic, is a Gaelic language of the insular Celtic branch of the Celtic language family, itself a branch of the Indo-European language family. Manx is the historical language of the Manx people.

Scottish Gaelic, also known as Scots Gaelic and Gaelic, is a Goidelic language native to the Gaels of Scotland. As a Goidelic language, Scottish Gaelic, as well as both Irish and Manx, developed out of Old Irish. It became a distinct spoken language sometime in the 13th century in the Middle Irish period, although a common literary language was shared by the Gaels of both Ireland and Scotland until well into the 17th century. Most of modern Scotland was once Gaelic-speaking, as evidenced especially by Gaelic-language place names.
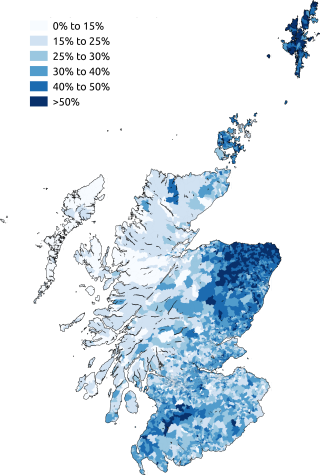
Scots is an Anglic language variety in the West Germanic language family, spoken in Scotland and parts of Ulster in the north of Ireland. Most commonly spoken in the Scottish Lowlands, Northern Isles and northern Ulster, it is sometimes called Lowland Scots or Broad Scots to distinguish it from Scottish Gaelic, the Goidelic Celtic language that was historically restricted to most of the Scottish Highlands, the Hebrides and Galloway after the 16th century. Modern Scots is a sister language of Modern English, as the two diverged independently from the same source: Early Middle English (1150–1300).

Conradh na Gaeilge is a social and cultural organisation which promotes the Irish language in Ireland and worldwide. The organisation was founded in 1893 with Douglas Hyde as its first president, when it emerged as the successor of several 19th century groups such as the Gaelic Union. The organisation would be the spearhead of the Gaelic revival and Gaeilgeoir activism. Originally the organisation intended to be apolitical, but many of its participants became involved in the republican movement and the struggle for Irish statehood.
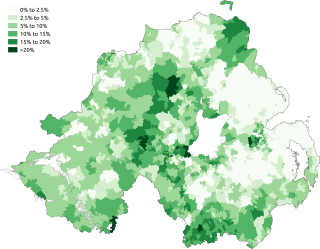
The Irish language is an official language in Northern Ireland. The Irish language is the second most spoken language in Northern Ireland. The dialect spoken there is known as Ulster Irish. Protection for the Irish language in Northern Ireland stems largely from the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages.
William Gillies (1865–1932) was a Scottish patriot and a socialist. He helped to form the Scots National League, which joined with other bodies to form the National Party of Scotland, which in turn evolved into the Scottish National Party (SNP).

Ruaraidh Erskine of Marr was a Scottish nationalist political activist, writer and Scottish Gaelic language campaigner.

Canadian Gaelic or Cape Breton Gaelic, often known in Canadian English simply as Gaelic, is a collective term for the dialects of Scottish Gaelic spoken in Atlantic Canada.
Gaelicisation, or Gaelicization, is the act or process of making something Gaelic, or gaining characteristics of the Gaels, a sub-branch of celticisation. The Gaels are an ethno-linguistic group, traditionally viewed as having spread from Ireland to Scotland and the Isle of Man.

Gaelic-medium education is a form of education in Scotland that allows pupils to be taught primarily through the medium of Scottish Gaelic, with English being taught as the secondary language.

Irish, also known as Gaelic, is a Goidelic language of the Insular Celtic branch of the Celtic language family, which is a part of the Indo-European language family. Irish is indigenous to the island of Ireland and was the population's first language until the 19th century, when English gradually became dominant, particularly in the last decades of the century. Irish is still spoken as a first language in a small number of areas of certain counties such as Cork, Donegal, Galway, and Kerry, as well as smaller areas of counties Mayo, Meath, and Waterford. It is also spoken by a larger group of habitual but non-traditional speakers, mostly in urban areas where the majority are second-language speakers. Daily users in Ireland outside the education system number around 73,000 (1.5%), and the total number of persons who claimed they could speak Irish in April 2016 was 1,761,420, representing 39.8% of respondents.

Dalelia or Dalilea is hamlet on the north shore of Loch Shiel in Acharacle district of Argyll, Scottish Highlands and is in the Scottish council area of Highland. Kinlochmoidart is to the north. The alternate Gaelic name "Dàil an Leigh" has been suggested but this is believed to be a folk etymology for Dàil Eileadh.
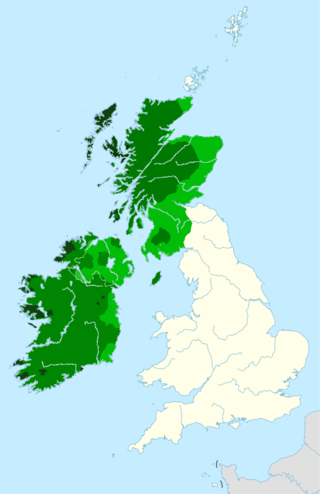
The Gaels are an ethnolinguistic group native to Ireland, Scotland and the Isle of Man in the British Isles. They are associated with the Gaelic languages: a branch of the Celtic languages comprising Irish, Manx and Scottish Gaelic.
Scottish Gaelic literature refers to literature composed in the Scottish Gaelic language and in the Gàidhealtachd communities where it is and has been spoken. Scottish Gaelic is a member of the Goidelic branch of Celtic languages, along with Irish and Manx.
Ewen MacLachlan (1775–1822) was a Scottish scholar and poet. He is noted for his translations of ancient classical literature into Gaelic, for his own Gaelic verse, and for his contribution to Gaelic dictionaries.
The Irish language originated in Ireland and has historically been the dominant language of the Irish people. They took it with them to a number of other countries, and in Scotland and the Isle of Man it gave rise to Scottish Gaelic and Manx, respectively.
Gairm was a Scottish Gaelic quarterly magazine founded in 1951 by Derick Thomson, and Finlay J. MacDonald. Its first issue was published in Autumn 1952. MacDonald served as an editor until 1964; Thomson remained present for decades until it ceased publication in 2004, producing just over 200 issues in total. According to Alan Campbell, the magazine was a "one-man show;" he explained that Thomson "sustained something very valuable for a long period of time." Although it had a relatively low circulation, it was influential on Gaelic literature as it was the longest-running Gaelic literary magazine of the 20th century, in circulation for more than twice as long as its predecessor, Guth na Bliadhna. Gairm attempted to encompass a variety of perspectives and themes, and "disseminated a lot of work that we weren't aware of" in the words of Martin MacDonald. As well as being familiar to most literate Gaels, the magazine attracted almost all influential Gaelic writers who were active, including Sorley MacLean, Iain Crichton Smith, George Campbell Hay, and Dòmhnall MacAmhlaigh.

CLÀR is a Scottish Gaelic publisher. Established in 1996, the company is run on a voluntary, independent basis and based in Inverness, Scotland. It was the publisher for the Ùr-sgeul project, specialising in new Gaelic fiction.
References
- ↑ F.G. Thomson.
- ↑ Gibson, John G. (2017). Gaelic Cape Breton Step-Dancing: An Historical and Ethnographic Perspective. McGill-Queen's Press - MQUP. ISBN 9780773550612 . Retrieved 9 July 2017.
- 1 2 Hutchinson, Roger (2011). A Waxing Moon: The Modern Gaelic Revival. Random House. ISBN 9781780573106 . Retrieved 9 July 2017.
- ↑ O'Leary, Philip (20 July 2005). The Prose Literature of the Gaelic Revival, 1881-1921: Ideology and Innovation. Penn State Press. ISBN 978-0271025964 . Retrieved 9 July 2017.
- ↑ Walsh, Brendan; Lalor, John (2015). "New languages of possibility: early experiments in education as dissent". History of Education. 44 (5): 595–617. doi:10.1080/0046760X.2015.1050609. S2CID 142414388.