
Kidney failure, also known as renal failure or end-stage renal disease (ESRD), is a medical condition in which the kidneys can no longer adequately filter waste products from the blood, functioning at less than 15% of normal levels. Kidney failure is classified as either acute kidney failure, which develops rapidly and may resolve; and chronic kidney failure, which develops slowly and can often be irreversible. Symptoms may include leg swelling, feeling tired, vomiting, loss of appetite, and confusion. Complications of acute and chronic failure include uremia, hyperkalemia, and volume overload. Complications of chronic failure also include heart disease, high blood pressure, and anaemia.

Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a type of long-term kidney disease, in which either there is a gradual loss of kidney function which occurs over a period of months to years, or an abnormal kidney structure. Initially generally no symptoms are seen, but later symptoms may include leg swelling, feeling tired, vomiting, loss of appetite, and confusion. Complications can relate to hormonal dysfunction of the kidneys and include high blood pressure, bone disease, and anemia. Additionally CKD patients have markedly increased cardiovascular complications with increased risks of death and hospitalization. CKD can lead to kidney failure requiring kidney dialysis or kidney transplantation.
Hypoxia-inducible factors (HIFs) are transcription factors that respond to decreases in available oxygen in the cellular environment, or hypoxia. They also respond to instances of pseudohypoxia, such as thiamine deficiency. Both hypoxia and pseudohypoxia leads to impairment of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) production by the mitochondria.

Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha, also known as HIF-1-alpha, is a subunit of a heterodimeric transcription factor hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1) that is encoded by the HIF1A gene. The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2019 was awarded for the discovery of HIF.

Procollagen-proline dioxygenase, commonly known as prolyl hydroxylase, is a member of the class of enzymes known as alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent hydroxylases. These enzymes catalyze the incorporation of oxygen into organic substrates through a mechanism that requires alpha-Ketoglutaric acid, Fe2+, and ascorbate. This particular enzyme catalyzes the formation of (2S, 4R)-4-hydroxyproline, a compound that represents the most prevalent post-translational modification in the human proteome.

Hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase 2 (HIF-PH2), or prolyl hydroxylase domain-containing protein 2 (PHD2), is an enzyme encoded by the EGLN1 gene. It is also known as Egl nine homolog 1. PHD2 is a α-ketoglutarate/2-oxoglutarate-dependent hydroxylase, a superfamily non-haem iron-containing proteins. In humans, PHD2 is one of the three isoforms of hypoxia-inducible factor-proline dioxygenase, which is also known as HIF prolyl-hydroxylase.

Robert Provenzano is an American nephrologist. He is also an Associate Clinical Professor of Medicine at Wayne State University School of Medicine.
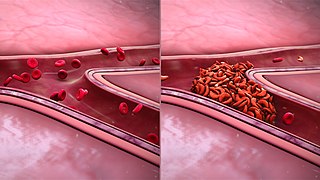
Sickle cell nephropathy is a type of kidney disease associated with sickle cell disease which causes kidney complications as a result of sickling of red blood cells in the small blood vessels. The hypertonic and relatively hypoxic environment of the renal medulla, coupled with the slow blood flow in the vasa recta, favors sickling of red blood cells, with resultant local infarction. Functional tubule defects in patients with sickle cell disease are likely the result of partial ischemic injury to the renal tubules.
Cardiorenal syndrome (CRS) is an umbrella term used in the medical field that defines disorders of the heart and kidneys whereby "acute or chronic dysfunction in one organ may induce acute or chronic dysfunction of the other". When one of these organs fails, the other may subsequently fail. The heart and the kidneys are involved in maintaining hemodynamic stability and organ perfusion through an intricate network. Patients who have renal failure first may be hard to determine if heart failure is concurrent. These two organs communicate with one another through a variety of pathways in an interdependent relationship. In a 2004 report from the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute, CRS was defined as a condition where treatment of congestive heart failure is limited by decline in kidney function. This definition has since been challenged repeatedly but there still remains little consensus over a universally accepted definition for CRS. At a consensus conference of the Acute Dialysis Quality Initiative (ADQI), the CRS was classified into five subtypes primarily based upon the organ that initiated the insult as well as the acuity of disease.
Aluminium toxicity in people on dialysis is a problem for people on haemodialysis. Aluminium is often found in unfiltered water used to prepare dialysate. The dialysis process does not efficiently remove excess aluminium from the body, so it may build up over time. Aluminium is a potentially toxic metal, and aluminium poisoning may lead to mainly three disorders: aluminium-induced bone disease, microcytic anemia and neurological dysfunction (encephalopathy). Such conditions are more prominently observed in people with chronic kidney failure and especially in people on haemodialysis.
Hypoxia-inducible factor-proline dioxygenase (EC 1.14.11.29, HIF hydroxylase) is an enzyme with systematic name hypoxia-inducible factor-L-proline, 2-oxoglutarate:oxygen oxidoreductase (4-hydroxylating). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Sucroferric oxyhydroxide, sold under the brand name Velphoro, is a non-calcium, iron-based phosphate binder used for the control of serum phosphorus levels in adults with chronic kidney disease (CKD) on hemodialysis (HD) or peritoneal dialysis (PD). It is used in form of chewable tablets.
CSL Vifor is a global specialty pharmaceuticals company in the treatment areas of iron deficiency, dialysis, nephrology & rare disease. It is headquartered in Switzerland and consists of CSL Vifor, Vifor Fresenius Medical Care Renal Pharma (VFMCRP) and Sanifit Therapeutics.

Vadadustat, sold under the brand name Vafseo, is a medication used for the treatment of symptomatic anemia associated with chronic kidney disease. Vadadustat is a hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor.

Roxadustat, sold under the brand name Evrenzo, is an anti-anemia medication. Roxadustat is a HIF prolyl-hydroxylase inhibitor that increases endogenous production of erythropoietin and stimulates production of hemoglobin and red blood cells. It was investigated in clinical trials for the treatment of anemia caused by chronic kidney disease (CKD). It is taken by mouth. The drug was developed by FibroGen, in partnership with AstraZeneca.

Daprodustat, sold under the brand name Duvroq among others, is a medication that is used for the treatment of anemia due to chronic kidney disease. It is a hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor. It is taken by mouth.
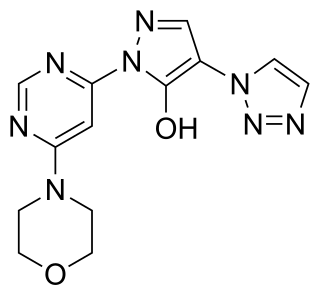
Molidustat is a drug which acts as an HIF prolyl-hydroxylase inhibitor and thereby increases endogenous production of erythropoietin, which stimulates production of hemoglobin and red blood cells. It is in Phase III clinical trials for the treatment of anemia caused by chronic kidney disease. Due to its potential applications in athletic doping, it has also been incorporated into screens for performance-enhancing drugs.
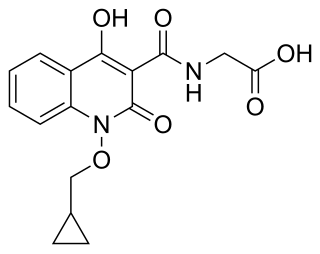
Desidustat is a drug for the treatment of anemia of chronic kidney disease. This drug with the brand name Oxemia is discovered and developed by Zydus Life Sciences. Desidustat reduces the requirement of recombinant erythropoietin (EPO) in anemia, and decreases EPO-resistance, by reducing IL-6, IL-1β, and anti-EPO antibodies. The subject expert committee of CDSCO has recommended the grant of permission for manufacturing and marketing of Desidustat 25 mg and 50 mg tablets in India, based on some conditions related to package insert, phase 4 protocols, prescription details, and GCP. Clinical trials on desidustat have been done in India and Australia. In a Phase 2, randomized, double-blind, 6-week, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging, safety and efficacy study, a mean hemoglobin increase of 1.57, 2.22, and 2.92 g/dL in desidustat 100, 150, and 200 mg arms, respectively, was observed. The Phase 3 clinical trials were conducted in chronic kidney disease patients which were not on dialysis as well as on dialysis. Desidustat is developed for the treatment of anemia as an oral tablet, where currently injections of erythropoietin and its analogues are drugs of choice. Desidustat is a HIF prolyl-hydroxylase inhibitor. In preclinical studies, effects of desidustat was assessed in normal and nephrectomized rats, and in chemotherapy-induced anemia. Desidustat demonstrated hematinic potential by combined effects on endogenous erythropoietin release and efficient iron utilization. Desidustat can also be useful in treatment of anemia of inflammation since it causes efficient erythropoiesis and hepcidin downregulation. Desidustat has been shown to have significant effect in the treatment of complement-mediated diseases. Complement activation-induced membrane attack complex (MAC) formation and Factor B activity were also reduced by desidustat treatment. Owing to this mechanism, desidustat can be an effective therapy against membranous nephropathy and retinal degeneration, since it specifically inhibited alternative complement system, without affecting the lectin-, or classical complement pathway. In January 2020, Zydus entered into licensing agreement with China Medical System (CMS) Holdings for development and commercialization of desidustat in Greater China. Under the license agreement, CMS will pay Zydus an initial upfront payment, regulatory milestones, sales milestones and royalties on net sales of the product. CMS will be responsible for development, registration and commercialization of desidustat in Greater China. National Medical Products Administration of China (NMPA) accepted the new drug application for desidustat on 23 April 2024. It has been observed that desidustat protects against acute and chronic kidney injury by reducing inflammatory cytokines like IL-6 and oxidative stress. A clinical trial to evaluate the efficacy and safety of desidustat tablet for the management of COVID-19 patients is ongoing in Mexico, wherein desidustat has shown to prevent acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) by inhibiting IL-6. Zydus has also received approval from the US FDA to initiate clinical trials of desidustat in chemotherapy Induced anemia (CIA). Desidustat was successfully introduced as an alternative treatment in patient of endogenous erythropoietin (EPO)-induced pure red cell aplasia (PRCA) due to anti-EPO antibodies. This led to a substantial and sustained improvement in hemoglobin levels, emphasizing the crucial role of desidustat intervention in EPO-induced PRCA cases. Zydus Lifesciences and Sun Pharmaceuticals have entered an agreement in October 2023 to co-market Desidustat. Sun Pharma will sell the drug as Rytstat, while Zydus will continue to sell it as Oxemia. Zydus Lifesciences is launching a proof-of-concept Phase 2a clinical trial to evaluate the safety and efficacy of desidustat in people with sickle cell disease (SCD). The study is the result of a collaboration with the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR)

Belzutifan, sold under the brand name Welireg, is an anti-cancer medication used for the treatment of von Hippel–Lindau disease-associated renal cell carcinoma. It is taken by mouth. Belzutifan is an hypoxia-inducible factor-2 alpha (HIF-2α) inhibitor.

Enarodustat is a drug used for the treatment of anemia, especially when associated with chronic kidney disease (CKD). Enarodustat functions as a inhibitor of hypoxia inducible factor-proly hydroxylase (HIF-PH).














