Six ships of the Royal Navy have borne the name HMS Griper:

The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by the English kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years War against the Kingdom of France. The modern Royal Navy traces its origins to the early 16th century; the oldest of the UK's armed services, it is known as the Senior Service.
- HMS Griper (1797) was a gunvessel launched in 1797 and sold in 1802.
- HMS Griper (1804) was a 12-gun gun-brig launched in 1804 and wrecked in 1807.
- HMS Griper (1813) was a 12-gun gun-brig launched in 1813. She was used as a 2-gun discovery sloop in the Arctic from 1824, transferred to the Coastguard in 1836, used as a target from 1856 and was finally broken up in 1868.
- HMS Griper (1855) was an Albacore-class wooden screw gunboat launched in 1855 and broken up in 1869.
- HMS Griper (1879) was an iron screw gunboat launched in 1879. She was used for harbour service from 1905 and renamed YC 373. She was made a base ship in 1923 and was renamed HMS Flora, and then HMS Afrikander in 1933. She was sold in 1937.
- HMS Griper (W112) was an Assurance-class class rescue tug launched in 1942. She was sold to the Singapore Harbour Board in 1946 and renamed Surabaja in 1962.

A brig is a sailing vessel with two square-rigged masts. During the Age of Sail, brigs were seen as fast and maneuverable and were used as both naval warships and merchant vessels. They were especially popular in the 18th and early 19th centuries. Brigs fell out of use with the arrival of the steam ship because they required a relatively large crew for their small size and were difficult to sail into the wind. Their rigging differs from that of a brigantine which has a gaff-rigged mainsail, while a brig has a square mainsail with an additional gaff-rigged spanker behind the mainsail.

HMS Griper was a Bold-class gun-brig of the British Royal Navy, built in 1813 by Mark Williams and John Davidson at Hythe. She participated in the 1819 expedition to the Arctic led by William Parry, made a voyage to Greenland and Norway in 1823, and took part in Parry's third expedition in 1824 as a support ship. Her crew in 1819, 1823, or 1824, qualified for the "Arctic Medal", which the Admiralty issued in 1857. She was eventually broken up in 1868.
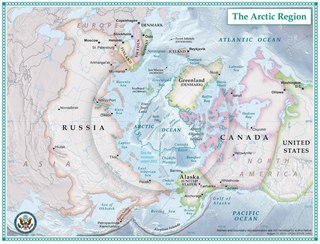
The Arctic is a polar region located at the northernmost part of Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean, adjacent seas, and parts of Alaska, Finland, Greenland (Denmark), Iceland, Northern Canada, Norway, Russia and Sweden. Land within the Arctic region has seasonally varying snow and ice cover, with predominantly treeless permafrost -containing tundra. Arctic seas contain seasonal sea ice in many places.
| This article includes a list of ships with the same or similar names. If an internal link for a specific ship led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the intended ship article, if one exists. |