Five ships of the Royal Navy have been named HMS Russell in honour of Edward Russell, 1st Earl of Orford.

The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by the English kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years War against the Kingdom of France. The modern Royal Navy traces its origins to the early 16th century; the oldest of the UK's armed services, it is known as the Senior Service.

Admiral of the Fleet Edward Russell, 1st Earl of Orford, PC was a Royal Navy officer. After serving as a junior officer at the Battle of Solebay during the Third Anglo-Dutch War, he served as a captain in the Mediterranean in operations against the Barbary pirates.
- HMS Russell (1692), an 80-gun second-rate ship of the line, rebuilt in 1735 and sunk in 1762 at Sheerness.
- HMS Russell (1764), launched in 1764, was a 74-gun third-rate ship of the line, sold in 1811.
- HMS Russell (1822), launched in 1822, was a 74-gun third-rate ship of the line, broken up in 1865.
- HMS Russell (1901), launched in 1901, was a Duncan-class battleship, sunk in 1916 by a mine off Malta
- HMS Russell (F97), launched in 1954, was a Blackwood-class or Type 14 second-rate anti-submarine frigate. Broken up in 1985.

HMS Russell was an 80-gun third rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, launched at Portsmouth Dockyard on 3 June 1692.
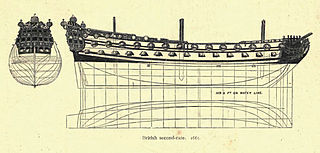
In the rating system of the British Royal Navy used to categorise sailing warships, a second-rate was a ship of the line which by the start of the 18th century mounted 90 to 98 guns on three gun decks; earlier 17th-century second rates had fewer guns and were originally two-deckers or had only partially armed third gun decks.

A ship of the line was a type of naval warship constructed from the 17th through to the mid-19th century to take part in the naval tactic known as the line of battle, in which two columns of opposing warships would manoeuvre to bring the greatest weight of broadside firepower to bear. Since these engagements were almost invariably won by the heaviest ships carrying the most powerful guns, the natural progression was to build sailing vessels that were the largest and most powerful of their time.

