
HMS Assurance was a 32-gun fourth-rate of the English Navy, built by Peter Pett I at Deptford Dockyard and launched in 1646. She was in the Parliamentary force during the English Civil War, then the Commonwealth Navy and was incorporated into the Royal Navy after the Restoration in 1660. During her time in the Commonwealth Navy she partook in the Battles of Dover, Portland, Gabbard and Texel. She foundered in a gale at Woolwich in 1660 and was salved. After the Restoration she partook in the Battle of Lowestoffe, the Four Days Fight and the Texel (1673). She was reduced to a Fifth Rate in 1690 before being sold in 1698.

HMS Adventure was a 34-gun fourth-rate of the English Navy, built by Peter Pett II at Woolwich Dockyard and launched in 1646. With the outbreak of the English Civil War she served on the Parliamentary side until 1649. She was incorporated into the Commonwealth Navy in 1650. She partook in the Battle off Dover in 1652, the Battle of Portland and the Battle of Gabbard in 1653. Adventure was employed on Bulstrode Whitelocke's embassy to Sweden, 1653–1654. After the Restoration she was incorporated into the Royal Navy. She was present at the Battle of Lowestoft (1665) and the Battle of Solebay (1672). She also participated in the Golden Horse and Two Lions actions in 1681. She was in the Battle of Barfleur in 1692. She captured several ships in the later part of her career, before being captured by the French in 1709.
Nonsuch was a 32-gun fourth-rate of the English Navy, built by Peter Pett I at Deptford Dockyard and launched in 1646. She was in the Parliamentary force during the English Civil War, then the Commonwealth Navy and was incorporated into the Royal Navy after the Restoration in 1660. During her time in the Commonwealth Navy she partook in the Battles of Krntish Knock, Portland and Gabbard. She was wreck at Gibraltar in 1664.
Sapphire was a 38-gun fourth-rate of the Commonwealth of England. After commissioning she was actively involved in the First Anglo-Dutch War participating in most major fleet actions. During the Second Anglo-Dutch War she was only in the first two engagements then spent her time in Irish Waters and the Mediterranean. She was run ashore due to a pending attack by suspected Algerian pirates on Sicily in March 1670.
HMS President was a 34-gun fourth-rate of the English Navy, built by Peter Pett I at Deptford Dockyard and launched in 1650. She was incorporated into the Commonwealth Navy in 1650. She partook in the Battle off Dover and Kentish Knock in 1652, the Battle of Portland, the Gabbard and Scheveningen in 1653. She was renamed Bonaventure in 1660. After the Restoration she was incorporated into the Royal Navy. She was present at the Battle of Lowestoft (1665), the Four Days Battle and the Oxfordness in 1666. She was rebuilt in 1666. She was present at the Battle of Martinique in 1667, Battle of Solebay (1672), Battle of Schooneveld and Texel in 1673, the Battle of Beachy Head in 1690, the Battle of Barfleur 1692.
HMS Reserve was one of six 40-gun fourth-rate frigates, built for the Commonwealth of England under the 1650 Programme, after the Restoration of the monarchy in 1660 she was incorporated into the navy of the Kingdom of England. She partook in no major Fleet actions during the First Anglo-Dutch War. After the Restoration during the Second Anglo-Dutch War she partook in the Battle of Lowestoft, the Four Days' Battle and the St James Day Battle. She spent the bulk of her service either in the Mediterranean or at Newfoundland. She foundered off Yarmouth in November 1703.
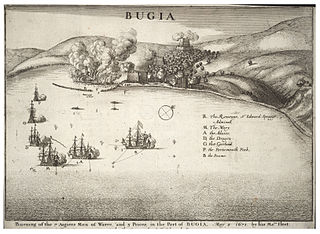
Advice was one of six 40-gun fourth-rate frigates, built for the Commonwealth of England under the 1650 Programme, she would be transferred to the navy of the Kingdom of England upon the Restoration of the monarchy in May 1660. During her time with the Commonwealth Navy she would fight in two major fleet engagements of the First Anglo-Dutch War, this being the Battle of Portland and the Battle of the Gabbard. After the Restoration she would be involved in the Second Anglo-Dutch War specifically the Battle of Lowestoft and the St James Day Battle. She would also be present at the attack on the Vile or better known as Holmes Bonfire. She would see action against the Algerines at the Battle of Bugia. During the Third Anglo-Dutch War she would do battle at the Battle of Solebay, The Battle of Schooneveld and the Battle of Texel. She would also do battle against the French at the Battle of Bantry Bay. She would see service in both the West and East Indies before being rebuilt at Woolwich.
The Pelican was one of six 40-gun fourth-rate frigates, built for the Commonwealth of England under the 1650 Programme. After commissioning she partook in the First Anglo-Dutch War being present at the Battles of Kentish Knock, Portland, the Gabbard and Scheveningen. She was accidentally burnt at Portsmouth in early 1656.

HMS Centurion was one of six 40-gun fourth-rate frigates, built for the Commonwealth of England under the 1650 Programme, she would be transferred to the navy of the Kingdom of England upon the Restoration of the monarchy in May 1660. When commissioned she partook in the First Anglo-Dutch War. After the first war ended she was in the Mediterranean fighting the Algerines at the Battle of Santa Cruz. She fought the battles of Dover, Portland, the Gabbard, and Scheveningen. During the Second Anglo-Dutch War she partook in the battles of Lowestoft and Orfordness. Following the second war she spent her time either in North America or the Mediterranean. She was wrecked in a storm in December 1689.

Foresight was a 40-gun fourth-rate of the Commonwealth of England, after the Restoration of the monarchy in 1660 she was incorporated into the Navy of the Kingdom of England. During her time in the Commonwealth Navy she partook in the First Anglo-Dutch war being present in the battles of Dungeness, Kentish Knock, Portland, The Gabbard and Scheveningen. She was also present at the Battle of Santa Cruz and the bombardment of Porto Farina, In the Second Anglo-Dutch War she was involved in the Battle of Vagen and the St James Day Fight. During the Third Anglo-Dutch War she participated in the battles of Schooneveld and Texel. For the remainder of her career she was in the West Indies, the Mediterranean and North American waters. She was wrecked south of Cuba in July 1698.
HMS Assistance was one of six 40-gun fourth-rate frigates, built for the Commonwealth of England under the 1650 Programme, after the Restoration of the monarchy in 1660 she was incorporated into the navy of the Kingdom of England. During her time in the Commonwealth Navy she partook in the First Anglo-Dutch war being present in the battles of Kentish Knock, Portland and The Gabbard. In the Mediterranean she was present at the Battle of Santa Cruz and the bombardment of Porto Farina, In the Second Anglo-Dutch War she was involved in the Battle of Lowestoft, Battle of Vagen and the St James Day Fight. She did not participate in fleet actions after this. She spent the rest of her service life undergoing several rebuilds and plying the waters as a cruiser protecting British trade and projecting British sovereignty. After nearly 95 years of Service she was sunk as a break water at Sheerness at the end of 1745.
Laurel was a 48-gun fourth-rate of the navy of the Commonwealth of England. She participated in almost all major Fleet Actions of the First Anglo-Dutch War. She was an active participant in the battles of Kentish Knock, Dungeness, Portland, The Gabbard and Scheveningen. She went to the west Indies with Admiral William Penn. She was wrecked in May 1657.
HMS Portsmouth was a 34-gun fourth-rate of the English Navy, built by Thomas Eastwood at Portsmouth Dockyard and launched in 1649. She was incorporated into the Commonwealth Navy in 1650. She partook in the Battle off Dover and Kentish Knock in 1652, the Gabbard and Scheveningen in 1653. After the Restoration she was incorporated into the Royal Navy. She was present at the Battle of Lowestoft (1665) and the Four Days Battle. She was present at the Texel in 1673, the Battle of Bantry Bay in 1689. She was captured by the French in August 1689 and blown up.
Guinea was a 38-gun fourth rate vessel of the Kingdom of England, Her initial commission was as a Royalist vessel during the English Civil War named Charles. She was captured then commissioned into the Parliamentary Naval Force as Guinea. During the First Anglo-Dutch War she partook in the Battle of Kentish Knock, the Battle of Portland and the Battle of The Gabbard. During the Second Anglo-Dutch War she participated in the Battle of Lowestoft, the Battle of Vagen and the St James Day Fight. She was sold on 27 November 1667.
Marmaduke was a 40-gun fourth rate vessel of the Kingdom of England, Her initial commission was as a Royalist vessel during the English Civil War named Revenge. She defected to the Parliamentarians then commissioned as Marmaduke. During the First Anglo-Dutch War she partook in the Battle of The Gabbard. During the Second Anglo-Dutch War she participated in the Four Days' Fight. She was scuttled during the Dutch raid on the Medway and sold in 1669.
Amity was a 36-gun fourth rate vessel of the Commonwealth of England. She was purchased by Parliament on 18 January 1650 and renamed. She was commissioned into the Parliamentary Naval Force as Amity. During the First Anglo-Dutch War she partook in the Battle of Portland and the Battle of The Gabbard. She was incorporated into the English Navy after the Restoration in May 1660. During the Second Anglo-Dutch War she participated in the Battle of Lowestoft, the Four Days' Battle and the St James Day Fight. She was sold on 27 November 1667.
Convertine was a 36-gun fourth rate vessel captured from the Portuguese by the Commonwealth of England. She was commissioned into the Parliamentary Naval Force as Convertine. During the First Anglo-Dutch War she partook in the Battle of Dungeness, Battle of Portland and the Battle of the Gabbard. During the Second Anglo-Dutch War she participated in the Battle of Lowestoft and the Four Days' Battle. She was captured during the Four Days' Battle.
Gift was a 38-gun fourth rate vessel captured from the French by the Commonwealth of England, She was captured on 4 September 1652 as the 36-gun Le Don de Gieu. She was commissioned into the Parliamentary Naval Force as Gift. During the First Anglo-Dutch War she partook in the Battle of Portland, the Battle of the Gabbard and the Battle of Scheveningen. She spent time fishery patrols and escorting convoys. She was converted to a fireship in 1666 and expended at the St James Fight on 25 July 1666.
The English ship Merlin was a 14-gun sixth rate vessel built under the 1651 Programme at Chatham Dockyard for the Commonwealth of England in 1651/52. She sailed with Robert Blakes Fleet during her career in the Commonwealth Navy. She partook in the Battles of Portland, the Gabbard, Scheveningen and Porto Fina. She was incorporated into the Royal Navy as HMS Merlin in May 1660. She continued her duties in trade protection and convoy escort. She was taken by the Dutch off Cadiz, Spain defending her convoy in October 1665.
The English ship Martin was a 14-gun sixth rate vessel built under the 1651 Programme at Portsmouth Dockyard for the Commonwealth of England in 1651/52. Her service in the Commonwealth Navy was very active. She participated in the Battles of Dover, Portland and the Gabbard. She was with Robert Blake at Porto Farina. She was the main vessel at the Capture of Jamaica in 1655. With the Restoration she became HMS Martin. During the Second Anglo-Dutch War she was in the initial battle of Lowestoft then the Battle of Vagen. She was sold in February 1667.



