Seven vessels of the British Royal Navy have borne the name HMS Amphion, after the Greek hero Amphion.
HMS Orion has been the name of several naval ships from different countries.

HMS Hurst Castle (K416) was a Castle-class corvette of the United Kingdom's Royal Navy. She was named after Hurst Castle at the western end of the Solent in Southern England.

HMS Cavalier is a retired C-class destroyer of the Royal Navy. She was laid down by J. Samuel White and Company at East Cowes on 28 March 1943, launched on 7 April 1944, and commissioned on 22 November 1944. She served in World War II and in various commissions in the Far East until she was decommissioned in 1972. After decommissioning she was preserved as a museum ship and currently resides at Chatham Historic Dockyard.

The S-class submarines of the Royal Navy were originally designed and built during the modernisation of the submarine force in the early 1930s to meet the need for smaller boats to patrol the restricted waters of the North Sea and the Mediterranean Sea, replacing the British H-class submarines. As part of the major naval construction for the Royal Navy during the Second World War, the S class became the single largest group of submarines ever built for the Royal Navy. A total of 62 were constructed over a period of 15 years, with fifty of the "improved" S class being launched between 1940 and 1945.
Three ships of the Royal Navy have been named HMS Swordfish after the fish.
The following ships of the Royal Navy were assigned the name Calypso, after Calypso, a sea nymph in Greek mythology:
Fifteen ships of the Royal Navy have borne the name HMS Ranger

The F class submarine was built for the Royal Navy as a coastal submarine based on the doubled hulled V class submarine with very few minor improvements. The only important improvement was the addition of a stern torpedo tube. The F class were ordered as a successor to the E class submarine, but only three were built out of the ten ordered.

HMS Scorcher was an S-class submarine of the Royal Navy, and part of the Third Group built of that class. She was built by Cammell Laird and launched on 18 December 1944. So far she has been the only ship of the Royal Navy to bear the name Scorcher. She was launched by Thomas Beacham, a Foreman Driller employed by Cammell Laird.

HMS Thule was a British submarine of the third group of the T class. She was built as P325 at Devonport Dockyard, and launched on 22 October 1942. So far she has been the only ship of the Royal Navy to bear the name Thule, after Thule, the mythological name for a northern island.

HMS Tantalus was a British submarine of the third group of the T class. She was built as P318 by Vickers Armstrong, Barrow, and launched on 24 February 1943. So far she has been the only ship of the Royal Navy to bear the name Tantalus, after the mythological Tantalus, son of Zeus.

HMS Taciturn was a British submarine of the third group of the T class. built by Vickers Armstrong, Barrow and Belliss and Morcom Ltd., and launched on 7 June 1944. So far she has been the only ship of the Royal Navy to bear the name Taciturn.

HMS Terrapin was a British submarine of the third group of the T class. She was built as P323 by Vickers Armstrong, Barrow and Belliss and Morcom Ltd, and launched on 31 August 1943. So far she has been the only ship of the Royal Navy to bear the name Terrapin, after the animal of that name. Apart from a brief period in home waters off the Scandinavian coast, Terrapin served in the Far East for much of her wartime career.

HMS Tactician was a British submarine of the third group of the T class. She was built as P314 by Vickers-Armstrongs, Barrow, and launched on 29 July 1942.
HNLMS Tijgerhaai (P336) was a Zwaardvisch-class submarine of the Royal Netherlands Navy during and after World War II. She was originally ordered as HMS Tarn (P326), a British T-class submarine, built by Vickers Armstrong, Barrow, but never saw service under that name. She would have been the only ship of the Royal Navy to bear the name Tarn.
A ship and two submarines of the Royal Navy have been named HMS Ursula:
Six ships of the Royal Navy have borne the name HMS Opossum, after the opossum:
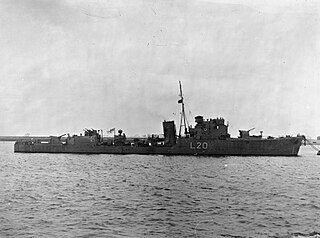
HMS Garth was a Type I Hunt-class destroyer of the Royal Navy built by John Brown & Company on the River Clyde, and launched on 28 December 1939. She was adopted by the Civil Community of Wokingham, Berkshire, as part of the Warship Week campaign in 1942.
James Joseph Colledge was a British naval historian, author of Ships of the Royal Navy, the standard work on the fighting ships of the British Royal Navy from the 15th century to the 20th century.

Ships of the Royal Navy is a naval history reference work by J. J. Colledge (1908–1997); it provides brief entries on all recorded ships in commission in the Royal Navy from the 15th century, giving location of constructions, date of launch, tonnage, specification and fate.

The International Standard Book Number (ISBN) is a numeric commercial book identifier which is intended to be unique. Publishers purchase ISBNs from an affiliate of the International ISBN Agency.















