 | |
| Stable release | 2019 |
|---|---|
| Type | 3D computer graphics |
| Website | www |
 | |
| Stable release | 2019 |
|---|---|
| Type | 3D computer graphics |
| Website | www |
HOOPS Visualize is designed to render graphics across both mobile and desktop platforms.
The program features a unified API that allows users to add interactive 3D visualization to both desktop and mobile applications.
HOOPS Visualize provides a hierarchical scene management engine capable of handling a range of graphics entities, together with a graphics pipeline and interaction handling algorithms. It includes clash detection, multi-plane sectioning, and large model visualization, along with many other features.
The HOOPS 3D Graphics System was originally developed in the mid-1980s in the CADIF Lab at Cornell University. Ithaca Software later formed to commercialize the technology. Subsequently, HOOPS was widely adopted for Computer-Aided Design (CAD), Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM ) and Computer-Aided Engineering (CAE) software.

Cornell University is a private and statutory Ivy League research university in Ithaca, New York. Founded in 1865 by Ezra Cornell and Andrew Dickson White, the university was intended to teach and make contributions in all fields of knowledge—from the classics to the sciences, and from the theoretical to the applied. These ideals, unconventional for the time, are captured in Cornell's founding principle, a popular 1868 Ezra Cornell quotation: "I would found an institution where any person can find instruction in any study."
In 1993, Autodesk, Inc. acquired Ithaca Software. [1] In 1996, HOOPS was spun out of Autodesk by Tech Soft 3D, Inc., [2] which continues to develop and sell the HOOPS 3D Graphics System under the name HOOPS Visualize. The software is made available free of charge to educational institutions.
AutoCAD is a commercial computer-aided design (CAD) and drafting software application. Developed and marketed by Autodesk, AutoCAD was first released in December 1989 as a desktop app running on microcomputers with internal graphics controllers. Before AutoCAD was introduced, most commercial CAD programs ran on mainframe computers or minicomputers, with each CAD operator (user) working at a separate graphics terminal. Since 2010, AutoCAD was released as a mobile- and web app as well, marketed as AutoCAD 360.

The graphical user interface is a form of user interface that allows users to interact with electronic devices through graphical icons and visual indicators such as secondary notation, instead of text-based user interfaces, typed command labels or text navigation. GUIs were introduced in reaction to the perceived steep learning curve of command-line interfaces (CLIs), which require commands to be typed on a computer keyboard.

Computer-aided design (CAD) is the use of computers to aid in the creation, modification, analysis, or optimization of a design. CAD software is used to increase the productivity of the designer, improve the quality of design, improve communications through documentation, and to create a database for manufacturing. CAD output is often in the form of electronic files for print, machining, or other manufacturing operations. The term CADD is also used.

A workstation is a special computer designed for technical or scientific applications. Intended primarily to be used by one person at a time, they are commonly connected to a local area network and run multi-user operating systems. The term workstation has also been used loosely to refer to everything from a mainframe computer terminal to a PC connected to a network, but the most common form refers to the group of hardware offered by several current and defunct companies such as Sun Microsystems, Silicon Graphics, Apollo Computer, DEC, HP, NeXT and IBM which opened the door for the 3D graphics animation revolution of the late 1990s.
Autodesk, Inc. is an American multinational software corporation that makes software services for the architecture, engineering, construction, manufacturing, media, education, and entertainment industries. Autodesk is headquartered in San Rafael, California, and features a gallery of its customers' work in its San Francisco building. The company has offices worldwide. Its U.S. locations are Northern California, Oregon, Colorado, Texas, Michigan, New England, New Hampshire and Massachusetts. Its Canada offices are located in Ontario, Quebec, and Alberta.
Autodesk 3ds Max, formerly 3D Studio and 3D Studio Max, is a professional 3D computer graphics program for making 3D animations, models, games and images. It is developed and produced by Autodesk Media and Entertainment. It has modeling capabilities and a flexible plugin architecture and must be used on the Microsoft Windows platform. It is frequently used by video game developers, many TV commercial studios, and architectural visualization studios. It is also used for movie effects and movie pre-visualization. For its modeling and animation tools, the latest version of 3ds Max also features shaders, dynamic simulation, particle systems, radiosity, normal map creation and rendering, global illumination, a customizable user interface, new icons, and its own scripting language.
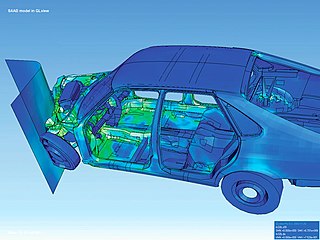
Visualization or visualisation is any technique for creating images, diagrams, or animations to communicate a message. Visualization through visual imagery has been an effective way to communicate both abstract and concrete ideas since the dawn of humanity. Examples from history include cave paintings, Egyptian hieroglyphs, Greek geometry, and Leonardo da Vinci's revolutionary methods of technical drawing for engineering and scientific purposes.
Autodesk Softimage, or simply Softimage is a discontinued 3D computer graphics application, for producing 3D computer graphics, 3D modeling, and computer animation. Now owned by Autodesk and formerly titled Softimage|XSI, the software has been predominantly used in the film, video game, and advertising industries for creating computer generated characters, objects, and environments.

STL is a file format native to the stereolithography CAD software created by 3D Systems. STL has several backronyms such as "Standard Triangle Language" and "Standard Tessellation Language". This file format is supported by many other software packages; it is widely used for rapid prototyping, 3D printing and computer-aided manufacturing. STL files describe only the surface geometry of a three-dimensional object without any representation of color, texture or other common CAD model attributes. The STL format specifies both ASCII and binary representations. Binary files are more common, since they are more compact.

Digital MockUp or DMU is a concept that allows the description of a product, usually in 3D, for its entire life cycle. Digital Mockup is enriched by all the activities that contribute to describing the product. The product design engineers, the manufacturing engineers, and the support engineers work together to create and manage the DMU. One of the objectives is to have an important knowledge of the future or the supported product to replace any physical prototypes with virtual ones, using 3D computer graphics techniques. As an extension it is also frequently referred to as Digital Prototyping or Virtual Prototyping. These two specific definitions refer to the production of a physical prototype, but they are part of the DMU concept. DMU allows engineers to design and configure complex products and validate their designs without ever needing to build a physical model.

Rhinoceros is a commercial 3D computer graphics and computer-aided design (CAD) application software developed by Robert McNeel & Associates, an American, privately held, employee-owned company founded in 1980. Rhinoceros geometry is based on the NURBS mathematical model, which focuses on producing mathematically precise representation of curves and freeform surfaces in computer graphics.

ARCHICAD is an architectural BIM CAD software for Macintosh and Windows developed by the Hungarian company Graphisoft. ARCHICAD offers computer aided solutions for handling all common aspects of aesthetics and engineering during the whole design process of the built environment — buildings, interiors, urban areas, etc.

3D computer graphics, or three-dimensional computer graphics, are graphics that use a three-dimensional representation of geometric data that is stored in the computer for the purposes of performing calculations and rendering 2D images. The resulting images may be stored for viewing later or displayed in real time.
Jock D. Mackinlay is an American information visualization expert and Vice President of Research and Design at Tableau Software. With Stuart K. Card, George G. Robertson and others he invented a number of Information Visualization techniques.

Creo is a family or suite of Computer-aided design (CAD) apps supporting product design for discrete manufacturers and is developed by PTC. The suite consists of apps, each delivering a distinct set of capabilities for a user role within product development.
Designers have used computers for calculations since their invention. Digital computers were used in power system analysis or optimization as early as proto-"Whirlwind" in 1949. Circuit design theory or power network methodology was algebraic, symbolic, and often vector-based.