In organic chemistry, a functional group is a substituent or moiety in a molecule that causes the molecule's characteristic chemical reactions. The same functional group will undergo the same or similar chemical reactions regardless of the rest of the molecule's composition. This enables systematic prediction of chemical reactions and behavior of chemical compounds and the design of chemical synthesis. The reactivity of a functional group can be modified by other functional groups nearby. Functional group interconversion can be used in retrosynthetic analysis to plan organic synthesis.

Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs) are fully or partly halogenated hydrocarbons that contain carbon (C), hydrogen (H), chlorine (Cl), and fluorine (F), produced as volatile derivatives of methane, ethane, and propane.
The haloalkanes are alkanes containing one or more halogen substituents. They are a subset of the general class of halocarbons, although the distinction is not often made. Haloalkanes are widely used commercially. They are used as flame retardants, fire extinguishants, refrigerants, propellants, solvents, and pharmaceuticals. Subsequent to the widespread use in commerce, many halocarbons have also been shown to be serious pollutants and toxins. For example, the chlorofluorocarbons have been shown to lead to ozone depletion. Methyl bromide is a controversial fumigant. Only haloalkanes that contain chlorine, bromine, and iodine are a threat to the ozone layer, but fluorinated volatile haloalkanes in theory may have activity as greenhouse gases. Methyl iodide, a naturally occurring substance, however, does not have ozone-depleting properties and the United States Environmental Protection Agency has designated the compound a non-ozone layer depleter. For more information, see Halomethane. Haloalkane or alkyl halides are the compounds which have the general formula "RX" where R is an alkyl or substituted alkyl group and X is a halogen.

Bromochlorodifluoromethane (BCF), also referred to by the code numbers Halon 1211 and Freon 12B1, is a haloalkane with the chemical formula CF2ClBr. It is used for fire suppression, especially for expensive equipment or items that could be damaged by the residue from other types of extinguishers. It is stored as a liquid under pressure and vaporizes when discharged to suppress fires. The use of halons, including Halon 1211, has decreased over time due to their adverse impact on the ozone layer. Alternatives have been developed to mitigate environmental concerns while still providing effective fire suppression capabilities.
Bromotrifluoromethane, commonly referred to by the code numbers Halon 1301, R13B1, Halon 13B1 or BTM, is an organic halide with the chemical formula CBrF3. It is used for gaseous fire suppression as a far less toxic alternative to bromochloromethane.

The organic compound 1,1,1-trichloroethane, also known as methyl chloroform and chlorothene, is a chloroalkane with the chemical formula CH3CCl3. It is an isomer of 1,1,2-trichloroethane. A colourless and sweet-smelling liquid, it was once produced industrially in large quantities for use as a solvent. It is regulated by the Montreal Protocol as an ozone-depleting substance and as such use has declined since 1996. Trichloroethane should not be confused with the similar-sounding trichloroethene which is also commonly used as a solvent.

Halomethane compounds are derivatives of methane with one or more of the hydrogen atoms replaced with halogen atoms. Halomethanes are both naturally occurring, especially in marine environments, and human-made, most notably as refrigerants, solvents, propellants, and fumigants. Many, including the chlorofluorocarbons, have attracted wide attention because they become active when exposed to ultraviolet light found at high altitudes and destroy the Earth's protective ozone layer.
Halocarbon compounds are chemical compounds in which one or more carbon atoms are linked by covalent bonds with one or more halogen atoms resulting in the formation of organofluorine compounds, organochlorine compounds, organobromine compounds, and organoiodine compounds. Chlorine halocarbons are the most common and are called organochlorides.
Trichloroethane (C2H3Cl3) may refer to either of two isomeric chemical compounds:
1,1-Dichloroethane is a chlorinated hydrocarbon. It is a colorless oily liquid with a chloroform-like odor. It is not easily soluble in water, but miscible with most organic solvents.
Methylhydrazines are hydrazines that have additional methyl groups. Heavily methylated versions exist as hydrazinium salts.
Bistriflimide, also known variously as bis(trifluoromethane)sulfonimide, bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide, bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imidate (and variations thereof), informally and somewhat inaccurately as triflimide or triflimidate, or by the abbreviations TFSI or NTf2, is a non-coordinating anion with the chemical formula [(CF3SO2)2N]−. Its salts are typically referred to as being metal triflimidates.
Triphos refers to two distinct organophosphorus compounds:

1,2-Dibromotetrafluoroethane (C2Br2F4) is a haloalkane. It is also known under codenames R-114B2 and Halon 2402. It is a colorless liquid with a boiling point of 47.2 °C. R-114B2 is occasionally used in fire suppression systems. It is highly volatile, passes through soil to air, and can be detected in the parts-per-quadrillion range.

Hafnium acetylacetonate, also known as Hf(acac)4, is a coordination compound with formula Hf(C5H7O2)4. This white solid is the main hafnium complex of acetylacetonate. The complex has a square antiprismatic geometry with eight nearly equivalent Hf-O bonds. The molecular symmetry is D2, i.e., the complex is chiral. It is prepared from hafnium tetrachloride and acetylacetone, and base. Zr(acac)4 is very similar in structure and properties.

1,1,1-Tribromoethane is a haloalkane with the chemical formula C2H3Br3.
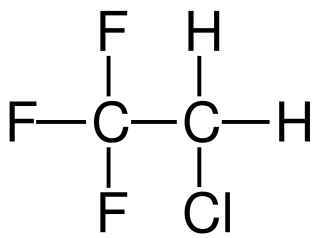
2-Chloro-1,1,1-trifluoroethane, also known as 1,1,1-trifluoro-2-chloroethane or Freon 133a, is an alkyl halide belonging to the category of hydrochlorofluorocarbons, having chemical formula F3C-CH2-Cl. Under standard conditions, it appears as a colorless gas, partially soluble in water. It is used as a refrigerant, as a solvent and as a reagent in organic synthesis.

Zirconium acetylacetonate is the coordination complex with the formula Zr(C5H7O2)4. It is a common acetylacetonate of zirconium. It is a white solid that exhibits high solubility in nonpolar organic solvents, but not simple hydrocarbons.
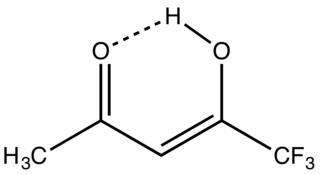
1,1,1-Trifluoroacetylacetone is the organofluorine compound with the formula CF3C(O)CH2C(O)CH3. It is a colorless liquid. Like other 1,3-diketones, it is used as a precursor to heterocycles, e.g. pyrazoles, and metal chelates. It is prepared by condensation of esters of trifluoroacetic acid with acetone.
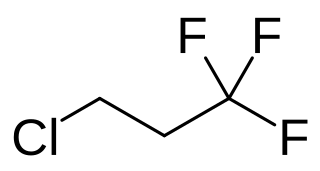
Chlorotrifluoropropane is a hydrochlorofluorocarbon with the chemical formula C3H4F3Cl). It is a volatile derivative propane. It appears as a colourless, odorless non-flammable liquid.












