Related Research Articles
Earned value management (EVM), earned value project management, or earned value performance management (EVPM) is a project management technique for measuring project performance and progress in an objective manner.
Project management is the process of leading the work of a team to achieve goals and meet success criteria at a specified time. The primary challenge of project management is to achieve all of the project goals within the given constraints. This information is usually described in project documentation, created at the beginning of the development process. The primary constraints are scope, time, quality and budget. The secondary challenge is to optimize the allocation of necessary inputs and apply them to meet pre-defined objectives.

A work-breakdown structure (WBS) in project management and systems engineering, is a deliverable-oriented breakdown of a project into smaller components. A work breakdown structure is a key project deliverable that organizes the team's work into manageable sections. The Project Management Body of Knowledge defines the work-breakdown structure "A hierarchical decomposition of the total scope of work to be carried out by the project team to accomplish the project objectives and create the required deliverables."
Contemporary business and science treat a project as any undertaking, carried out individually or collaboratively and possibly involving research or design, that is carefully planned to achieve a particular aim.

The critical path method (CPM), or critical path analysis (CPA), is an algorithm for scheduling a set of project activities. It is commonly used in conjunction with the program evaluation and review technique (PERT). A critical path is determined by identifying the longest stretch of dependent activities and measuring the time required to complete them from start to finish.
Project management software (PMS) has the capacity to help plan, organize, and manage resource tools and develop resource estimates. Depending on the sophistication of the software, it can manage estimation and planning, scheduling, cost control and budget management, resource allocation, collaboration software, communication, decision-making, quality management, time management and documentation or administration systems. Today, numerous PC and browser-based project management software and contract management software solutions exist, and are finding applications in almost every type of business.

The program (or project) evaluation and review technique (PERT) is a statistical tool used in project management, which was designed to analyze and represent the tasks involved in completing a given project.
In project management, a schedule is a listing of a project's milestones, activities, and deliverables, usually with intended start and finish dates. Those items are often estimated by other information included in the project schedule of resource allocation, budget, task duration, and linkages of dependencies and scheduled events. A schedule is commonly used in the project planning and project portfolio management parts of project management. Elements on a schedule may be closely related to the work breakdown structure (WBS) terminal elements, the Statement of work, or a Contract Data Requirements List.

In systems engineering, information systems and software engineering, the systems development life cycle (SDLC), also referred to as the application development life-cycle, is a process for planning, creating, testing, and deploying an information system. The systems development life cycle concept applies to a range of hardware and software configurations, as a system can be composed of hardware only, software only, or a combination of both. There are usually six stages in this cycle: requirement analysis, design, development and testing, implementation, documentation, and evaluation.
The Project Management Institute (PMI) is a global nonprofit professional organization for project management.

Organizational architecture has two very different meanings. In one sense it literally refers to the organization's built environment and in another sense it refers to architecture metaphorically, as a structure which fleshes out the organizations. The various features of a business's organizational architecture has to be internally consistent in strategy, architecture and competitive environment.
Task management is the process of managing a task through its life cycle. It involves planning, testing, tracking, and reporting. Task management can help either individual achieve goals, or groups of individuals collaborate and share knowledge for the accomplishment of collective goals. Tasks are also differentiated by complexity, from low to high.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to management:
In project management, level of effort (LOE) is a support-type project activity that must be done to support other work activities or the entire project effort. It usually consists of short amounts of work that must be repeated periodically. Examples of such an activity may be project budget accounting, customer liaison, or oiling machinery during manufacturing.
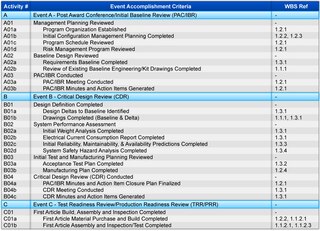
In the United States Department of Defense, the Integrated Master Plan (IMP) and the Integrated Master Schedule (IMS) are important program management tools that provide significant assistance in the planning and scheduling of work efforts in large and complex materiel acquisitions. The IMP is an event-driven plan that documents the significant accomplishments necessary to complete the work and ties each accomplishment to a key program event. The IMP is expanded to a time-based IMS to produce a networked and multi-layered schedule showing all detailed tasks required to accomplish the work effort contained in the IMP. The IMS flows directly from the IMP and supplements it with additional levels of detail——both then form the foundations to implement an Earned Value Management System.
Budgeted cost for work performed (BCWP) also called earned value (EV), is the budgeted cost of work that has actually been performed in carrying out a scheduled task during a specific time period. The BCWP is the sum of the budgets for completed work packages and completed portions of open work packages, plus the applicable portion of the budgets for level of effort and apportioned effort.
A glossary of terms relating to project management and consulting.
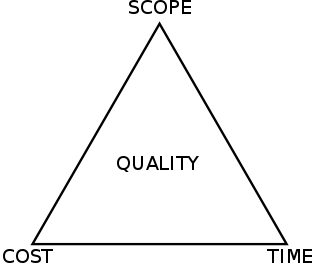
The project management triangle is a model of the constraints of project management. While its origins are unclear, it has been used since at least the 1950s. It contends that:
- The quality of work is constrained by the project's budget, deadlines and scope (features).
- The project manager can trade between constraints.
- Changes in one constraint necessitate changes in others to compensate or quality will suffer.

ClearTrial is a multinational software developer headquartered in Chicago, Illinois, USA. The company develops and markets a software as a service (SaaS) system designed for biopharmaceutical and medical device manufacturers for the planning, outsourcing, and tracking of clinical trials.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to project management:
References
- ↑ "COST ENGINEERING TERMINOLOGY, AACE® International Recommended Practice No. 10S-90" . Retrieved 10 June 2014.
- ↑ "A Glossary of Project Management Terms".
- ↑ "How to Build a Hammock Task".
- ↑ "Project Management Knowledge Summary" . Retrieved 10 June 2014.
- ↑ "Project Management Questions - Hammock Activity" . Retrieved 27 Apr 2016.
- ↑ A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK Guide) (4th ed.). Project Management Institute. 2009. p. 450. ISBN 978-1933890517.
- ↑ ""Level of Effort" in Primavera P6" . Retrieved 10 June 2014.
- ↑ "Level of Effort Activity - Primavera P6 step by step tutorial" . Retrieved 10 June 2014.
- ↑ Kerzner, Harold (March 2009). Project Management: A Systems Approach to Planning, Scheduling, and Controlling (10th ed.). Wiley. ISBN 978-0470278703.
- ↑ Manazanera, Ignacio (2013). "Planning & Scheduling References Book". p. 120. Retrieved 5 May 2017.