
Allah is the common Arabic word for God. In the English language, the word generally refers to God in Islam. The word is thought to be derived by contraction from al-ilāh, which means "the god", and is linguistically related to the Aramaic words Elah and ܐܲܠܵܗܵܐ (ʼEl (Elohim) for God.
Agnosticism is the view or belief that the existence of God, of the divine or the supernatural is unknown or unknowable. Another definition provided is the view that "human reason is incapable of providing sufficient rational grounds to justify either the belief that God exists or the belief that God does not exist."

Abraham is the common patriarch of the Abrahamic religions, including Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. In Judaism he is the founding father of the special relationship between the Jews and God; in Christianity, he is the spiritual progenitor of all believers, Jewish or gentile (non-Jewish); and in Islam he is a link in the chain of prophets that begins with Adam and culminates in Muhammad.

Calvinism is a major branch of Protestantism that follows the theological tradition and forms of Christian practice set down by John Calvin and other Reformation-era theologians. It emphasises the sovereignty of God and the authority of the Bible.

A devil is the personification of evil as it is conceived in various cultures and religious traditions. It is seen as the objectification of a hostile and destructive force. Jeffrey Burton Russell states that the different conceptions of the devil can be summed up as 1) a principle of evil independent from God 2) an aspect of God 3) a created being turning evil; a fallen angel 4) a symbol of human evil.
Monotheism is the belief that there is only one deity, an all-supreme being that is universally referred to as God. A distinction may be made between exclusive monotheism, in which the one God is a singular existence, and both inclusive and pluriform monotheism, in which multiple gods or godly forms are recognized, but each are postulated as extensions of the same God.

Sunni Islam is the largest branch of Islam, followed by 85–90% of the world's Muslims. Its name comes from the word Sunnah, referring to the tradition of Muhammad. The differences between Sunni and Shia Muslims arose from a disagreement over the succession to Muhammad and subsequently acquired broader political significance, as well as theological and juridical dimensions. According to Sunni traditions, Muhammad left no successor and the participants of the Saqifah event appointed Abu Bakr as the next-in-line. This contrasts with the Shia view, which holds that Muhammad appointed his son-in-law and cousin Ali ibn Abi Talib as his successor.
Rabbinic Judaism considers some names of God so holy that, once written, they should not be erased: YHWH, Adonai, El ("God"), Elohim ("God"), Shaddai ("Almighty"), and Tzevaot ; some also include Ehyeh. Early authorities considered other Hebrew names mere epithets or descriptions of God and wrote that they and names in other languages may be written and erased freely. However, some moderns advise special care even in these cases, and many Orthodox Jews have adopted the Chumras of the writing "G-d" instead of "God" in English or saying Ṭēt-Vav instead of Yōd-Hē for the number fifteen or Ṭēt-Zayin instead of Yōd-Vav for the number sixteen in Hebrew.
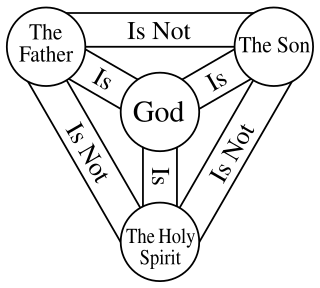
The Christian doctrine of the Trinity defines God as being one god existing in three coequal, coeternal, consubstantial divine persons: God the Father, God the Son and God the Holy Spirit, three distinct persons sharing one homoousion (essence). In this context, the three persons define who God is, while the one essence defines what God is.

Jehovah's Witnesses is a millenarian restorationist Christian denomination with nontrinitarian beliefs distinct from mainstream Christianity. The group reports a worldwide membership of approximately 8.7 million adherents involved in evangelism and an annual Memorial attendance of over 21 million. Jehovah's Witnesses are directed by the Governing Body of Jehovah's Witnesses, a group of elders in Warwick, New York, United States, which establishes all doctrines based on its interpretations of the Bible. They believe that the destruction of the present world system at Armageddon is imminent, and that the establishment of God's kingdom over the earth is the only solution for all problems faced by humanity.

An archangel is an angel of the highest rank. The word archangel itself is usually associated with the Abrahamic religions, but beings that are very similar to archangels are found in a number of other religious traditions. Archangels also appear in the religious texts of Gnosticism. The four most common archangels are Michael, Gabriel, Raphael, and Uriel.

Jesus, also referred to as Jesus of Nazareth or Jesus Christ, was a first-century Jewish preacher and religious leader. He is the central figure of Christianity, the world's largest religion. Most Christians believe he is the incarnation of God the Son and the awaited messiah, prophesied in the Hebrew Bible.

The Ten Commandments, also known as the Decalogue, are a set of biblical principles relating to ethics and worship that play a fundamental role in Judaism and Christianity. The text of the Ten Commandments appears twice in the Hebrew Bible: at Exodus 20:2–17 and Deuteronomy 5:6–21.

Adam is the name given in Genesis 1-5 to the first human. Beyond its use as the name of the first man, adam is also used in the Bible as a pronoun, individually as "a human" and in a collective sense as "mankind". Genesis 1 tells of God's creation of the world and its creatures, including adam, meaning humankind; in Genesis 2 God forms "Adam", this time meaning a single male human, out of "the dust of the ground", places him in the Garden of Eden, and forms a woman as his helpmate; in Genesis 3 Adam and the woman eat the fruit of the tree of knowledge and God condemns Adam to labour on the earth for his food and to return to it on his death; Genesis 4 deals with the birth of Adam's sons, and Genesis 5 lists his descendants from Seth to Noah.

In monotheistic thought, God is usually conceived of as the supreme being, creator, and principal object of faith. God is usually conceived of as being omnipotent, omniscient, omnipresent and omnibenevolent as well as having an eternal and necessary existence. God is most often held to be incorporeal, with said characteristic being related to conceptions of transcendence or immanence.

God in Islam is the eternal Supreme Being who originated the creation, preserves all things and then will repeat it. In Islam, God is conceived as absolutely one, unique, and perfect, free from all faults, deficiencies, and defects, and further held to be omnipotent, omniscient, and completely infinite in all of his attributes, who has no partner or equal, being the sole creator of everything in existence. Islam emphasizes that God is strictly singular, all-merciful and all-compassionate, whose mercy embraces everything; who neither slumbers nor sleeps, nor is obnoxious to decay nor death.
The Abrahamic religions are a group of mostly monotheistic religions that endorse worship of the God of Abraham. These most notably include Judaism, Christianity, and Islam, as well as the Baháʼí Faith, Samaritanism, the Druze, and others. The namesake for this group's identity is Abraham, a Hebrew patriarch and prophet who is extensively mentioned in many prominent Abrahamic scriptures, such as the Bible and Quran.
Atheism, in the broadest sense, is an absence of belief in the existence of deities. Less broadly, atheism is a rejection of the belief that any deities exist. In an even narrower sense, atheism is specifically the position that there are no deities. Atheism is contrasted with theism, which in its most general form is the belief that at least one deity exists.

Prophets in Islam are individuals in Islam who are believed to spread God's message on Earth and to serve as models of ideal human behaviour. Some prophets are categorized as messengers, those who transmit divine revelation, most of them through the interaction of an angel. Muslims believe that many prophets existed, including many not mentioned in the Quran. The Quran states: "There is a Messenger for every community". Belief in the Islamic prophets is one of the six articles of the Islamic faith.













