An object-modeling language is a standardized set of symbols used to model a software system using an object-oriented framework. The symbols can be either informal or formal ranging from predefined graphical templates to formal object models defined by grammars and specifications.

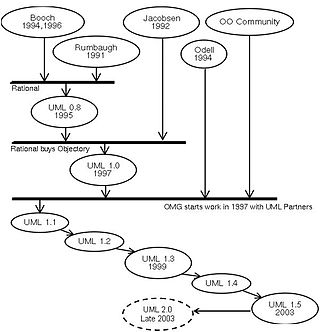
The unified modeling language (UML) is a general-purpose visual modeling language that is intended to provide a standard way to visualize the design of a system.

The Meta-Object Facility (MOF) is an Object Management Group (OMG) standard for model-driven engineering. Its purpose is to provide a type system for entities in the CORBA architecture and a set of interfaces through which those types can be created and manipulated. MOF may be used for domain-driven software design and object-oriented modelling.
In software and systems engineering, the phrase use case is a polyseme with two senses:
- A usage scenario for a piece of software; often used in the plural to suggest situations where a piece of software may be useful.
- A potential scenario in which a system receives an external request and responds to it.
Model Driven Architecture (MDA) is a software design approach for the development of software systems. It provides a set of guidelines for the structuring of specifications, which are expressed as models. Model Driven Architecture is a kind of domain engineering, and supports model-driven engineering of software systems. It was launched by the Object Management Group (OMG) in 2001.
The common warehouse metamodel (CWM) defines a specification for modeling metadata for relational, non-relational, multi-dimensional, and most other objects found in a data warehousing environment. The specification is released and owned by the Object Management Group, which also claims a trademark in the use of "CWM".

Ivar Hjalmar Jacobson is a Swedish computer scientist and software engineer, known as a major contributor to UML, Objectory, Rational Unified Process (RUP), aspect-oriented software development and Essence.
A functional software architecture (FSA) is an architectural model that identifies enterprise functions, interactions and corresponding IT needs. These functions can be used as a reference by different domain experts to develop IT-systems as part of a co-operative information-driven enterprise. In this way, both software engineers and enterprise architects can create an information-driven, integrated organizational environment.
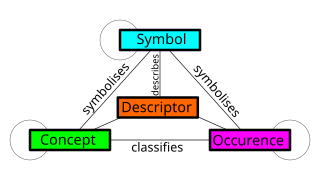
A metamodel is a model of a model, and metamodeling is the process of generating such metamodels. Thus metamodeling or meta-modeling is the analysis, construction and development of the frames, rules, constraints, models and theories applicable and useful for modeling a predefined class of problems. As its name implies, this concept applies the notions of meta- and modeling in software engineering and systems engineering. Metamodels are of many types and have diverse applications.
Object-oriented analysis and design (OOAD) is a technical approach for analyzing and designing an application, system, or business by applying object-oriented programming, as well as using visual modeling throughout the software development process to guide stakeholder communication and product quality.

Activity diagrams are graphical representations of workflows of stepwise activities and actions with support for choice, iteration and concurrency. In the Unified Modeling Language, activity diagrams are intended to model both computational and organizational processes, as well as the data flows intersecting with the related activities. Although activity diagrams primarily show the overall flow of control, they can also include elements showing the flow of data between activities through one or more data stores.

ATL is a model transformation language and toolkit developed and maintained by OBEO and AtlanMod. It was initiated by the AtlanMod team. In the field of Model-Driven Engineering (MDE), ATL provides ways to produce a set of target models from a set of source models.
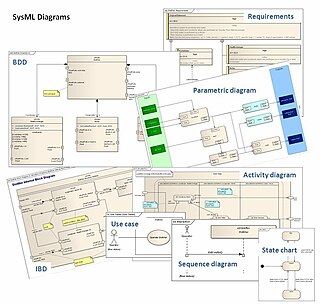
The systems modeling language (SysML) is a general-purpose modeling language for systems engineering applications. It supports the specification, analysis, design, verification and validation of a broad range of systems and systems-of-systems.
The UML profile for Enterprise Distributed Object Computing (EDOC) is a standard of the Object Management Group in support of open distributed computing using model-driven architecture and service-oriented architecture. Its aim is to simplify the development of component based (EDOC) systems by providing a UML-based modeling framework conforming to the MDA of the OMG.
The Business Process Definition Metamodel (BPDM) is a standard definition of concepts used to express business process models, adopted by the OMG. Metamodels define concepts, relationships, and semantics for exchange of user models between different modeling tools. The exchange format is defined by XSD and XMI, a specification for transformation of OMG metamodels to XML. Pursuant to the OMG's policies, the metamodel is the result of an open process involving submissions by member organizations, following a Request for Proposal (RFP) issued in 2003. BPDM was adopted in initial form in July 2007, and finalized in July 2008.
In computer science, the role class model is a role analysis pattern described by Francis G. Mossé in his article on Modelling Roles. The role class pattern provides the ability for a class to play multiple roles and to embed the role characteristic in a dedicated class.
Knowledge Discovery Metamodel (KDM) is a publicly available specification from the Object Management Group (OMG). KDM is a common intermediate representation for existing software systems and their operating environments, that defines common metadata required for deep semantic integration of Application Lifecycle Management tools. KDM was designed as the OMG's foundation for software modernization, IT portfolio management and software assurance. KDM uses OMG's Meta-Object Facility to define an XMI interchange format between tools that work with existing software as well as an abstract interface (API) for the next-generation assurance and modernization tools. KDM standardizes existing approaches to knowledge discovery in software engineering artifacts, also known as software mining.
The Semantics of Business Vocabulary and Business Rules (SBVR) is an adopted standard of the Object Management Group (OMG) intended to be the basis for formal and detailed natural language declarative description of a complex entity, such as a business. SBVR is intended to formalize complex compliance rules, such as operational rules for an enterprise, security policy, standard compliance, or regulatory compliance rules. Such formal vocabularies and rules can be interpreted and used by computer systems. SBVR is an integral part of the OMG's model-driven architecture (MDA).
Enterprise engineering is the body of knowledge, principles, and practices used to design all or part of an enterprise. An enterprise is a complex socio-technical system that comprises people, information, and technology that interact with each other and their environment in support of a common mission. One definition is: "an enterprise life-cycle oriented discipline for the identification, design, and implementation of enterprises and their continuous evolution", supported by enterprise modelling. The discipline examines each aspect of the enterprise, including business processes, information flows, material flows, and organizational structure. Enterprise engineering may focus on the design of the enterprise as a whole, or on the design and integration of certain business components.
Process map is a global-system process model that is used to outline the processes that make up the business system and how they interact with each other. Process map shows the processes as objects, which means it is a static and non-algorithmic view of the processes. It should be differentiated from a detailed process model, which shows a dynamic and algorithmic view of the processes, usually known as a process flow diagram. There are different notation standards that can be used for modelling process maps, but the most notable ones are TOGAF Event Diagram, Eriksson-Penker notation, and ARIS Value Added Chain.







