
A toothbrush is an oral hygiene tool used to clean the teeth, gums, and tongue. It consists of a head of tightly clustered bristles, atop of which toothpaste can be applied, mounted on a handle which facilitates the cleaning of hard-to-reach areas of the mouth. They should be used in conjunction with something to clean between the teeth where the bristles of the toothbrush cannot reach - for example floss, tape or interdental brushes.

Toothpaste is a paste or gel dentifrice used with a toothbrush to clean and maintain the aesthetics and health of teeth. Toothpaste is used to promote oral hygiene: it is an abrasive that aids in removing dental plaque and food from the teeth, assists in suppressing halitosis, and delivers active ingredients to help prevent tooth decay and gum disease (gingivitis). Owing to differences in composition and fluoride content, not all toothpastes are equally effective in maintaining oral health. The decline of tooth decay during the 20th century has been attributed to the introduction and regular use of fluoride-containing toothpastes worldwide. Large amounts of swallowed toothpaste can be poisonous. Common colors for toothpaste include white and blue.
Teeth cleaning is part of oral hygiene and involves the removal of dental plaque from teeth with the intention of preventing cavities, gingivitis, and periodontal disease. People routinely clean their own teeth by brushing and interdental cleaning, and dental hygienists can remove hardened deposits (tartar) not removed by routine cleaning. Those with dentures and natural teeth may supplement their cleaning with a denture cleaner.

Tooth decay, also known as cavities or caries, is the breakdown of teeth due to acids produced by bacteria. The cavities may be a number of different colors from yellow to black. Symptoms may include pain and difficulty with eating. Complications may include inflammation of the tissue around the tooth, tooth loss and infection or abscess formation.
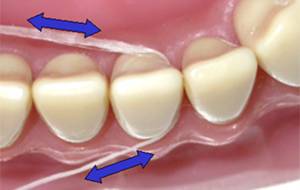
Dental floss is a cord of thin filaments used in interdental cleaning to remove food and dental plaque from between teeth or places a toothbrush has difficulty reaching or is unable to reach. Its regular use as part of oral cleaning is designed to maintain oral health.

Acid erosion is a type of tooth wear. It is defined as the irreversible loss of tooth structure due to chemical dissolution by acids not of bacterial origin. Dental erosion is the most common chronic condition of children ages 5–17, although it is only relatively recently that it has been recognised as a dental health problem. There is generally widespread ignorance of the damaging effects of acid erosion; this is particularly the case with erosion due to consumption of fruit juices because they tend to be considered as healthy. Acid erosion begins initially in the enamel, causing it to become thin, and can progress into dentin, giving the tooth a dull yellow appearance and leading to dentin hypersensitivity.

Streptococcus mutans is a facultatively anaerobic, gram-positive coccus commonly found in the human oral cavity and is a significant contributor to tooth decay. It is part of the "streptococci", an informal general name for all species in the genus Streptococcus. The microbe was first described by James Kilian Clarke in 1924.
Periodontology or periodontics is the specialty of dentistry that studies supporting structures of teeth, as well as diseases and conditions that affect them. The supporting tissues are known as the periodontium, which includes the gingiva (gums), alveolar bone, cementum, and the periodontal ligament. A periodontist is a dentist that specializes in the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of periodontal disease and in the placement of dental implants.
Dental plaque is a biofilm of microorganisms that grows on surfaces within the mouth. It is a sticky colorless deposit at first, but when it forms tartar, it is often brown or pale yellow. It is commonly found between the teeth, on the front of teeth, behind teeth, on chewing surfaces, along the gumline (supragingival), or below the gumline cervical margins (subgingival). Dental plaque is also known as microbial plaque, oral biofilm, dental biofilm, dental plaque biofilm or bacterial plaque biofilm. Bacterial plaque is one of the major causes for dental decay and gum disease.
The tooth-friendly label distinguishes products which are non-cariogenic and non-erosive, i.e. safe for teeth. To replace sugar, toothfriendly products often contain sweeteners that are not fermented by the microflora of the dental plaque. Products that are certified as toothfriendly also do not contain excessive amounts of food acids.
Toothfriendly International is a non-profit association which was established in 1989 in Basel, Switzerland. The purpose of the association is to advance oral health, particularly through preventive measures which include regular oral hygiene, appropriate dietary habits and regular check-ups by a dentist. It is governed by an executive board of dental professionals.

Pericoronitis is inflammation of the soft tissues surrounding the crown of a partially erupted tooth, including the gingiva (gums) and the dental follicle. The soft tissue covering a partially erupted tooth is known as an operculum, an area which can be difficult to access with normal oral hygiene methods. The hyponym operculitis technically refers to inflammation of the operculum alone.

Early childhood caries (ECC), formerly known as nursing bottle caries, baby bottle tooth decay, night bottle mouth and night bottle caries, is a disease that affects teeth in children aged between birth and 71 months. ECC is characterized by the presence of 1 or more decayed, missing, or filled tooth surfaces in any primary tooth. ECC has been shown to be a very common, transmissible bacterial infection, usually passed from the primary caregiver to the child. The main bacteria responsible for dental caries are Streptococcus mutans and Lactobacillus. There is also evidence that supports that those who are in lower socioeconomic populations are at greater risk of developing ECC.

Tooth brushing is the act of scrubbing teeth with a toothbrush, usually equipped with toothpaste. Interdental cleaning can be useful with tooth brushing, and together these two activities are the primary means of cleaning teeth, one of the main aspects of oral hygiene.The recommended amount of time for tooth brushing is two minutes.
Oral microbiology is the study of the microorganisms (microbiota) of the oral cavity and their interactions between oral microorganisms or with the host. The environment present in the human mouth is suited to the growth of characteristic microorganisms found there. It provides a source of water and nutrients, as well as a moderate temperature. Resident microbes of the mouth adhere to the teeth and gums to resist mechanical flushing from the mouth to stomach where acid-sensitive microbes are destroyed by hydrochloric acid.

Oral hygiene is the practice of keeping one's oral cavity clean and free of disease and other problems by regular brushing of the teeth and adopting good hygiene habits. It is important that oral hygiene be carried out on a regular basis to enable prevention of dental disease and bad breath. The most common types of dental disease are tooth decay and gum diseases, including gingivitis, and periodontitis.

Tooth remineralization is the natural repair process for non-cavitated tooth lesions, in which calcium, phosphate and sometimes fluoride ions are deposited into crystal voids in demineralised enamel. Remineralization can contribute towards restoring strength and function within tooth structure.

Amine fluorides are dental drugs.

Tooth wear refers to loss of tooth substance by means other than dental caries. Tooth wear is a very common condition that occurs in approximately 97% of the population. This is a normal physiological process occurring throughout life; but with increasing lifespan of individuals and increasing retention of teeth for life, the incidence of non-carious tooth surface loss has also shown a rise. Tooth wear varies substantially between people and groups, with extreme attrition and enamel fractures common in archaeological samples, and erosion more common today.
Hans Rudolf Mühlemann was a Swiss dentist and medical academic. He was professor and director of the Dental Instituts University of Zurich.













