
Charlemagne or Charles the Great, a member of the Carolingian dynasty, was King of the Franks from 768, King of the Lombards from 774, and was crowned as the Emperor of the Romans by the Papacy in 800. Charlemagne succeeded in uniting the majority of western and central Europe and was the first recognized emperor to rule from western Europe after the fall of the Western Roman Empire approximately three centuries earlier. The expanded Frankish state that Charlemagne founded was the Carolingian Empire, which is considered the first phase in the history of the Holy Roman Empire. He was canonized by Antipope Paschal III—an act later treated as invalid—and he is now regarded by some as beatified in the Catholic Church.

Einhard was a Frankish scholar and courtier. Einhard was a dedicated servant of Charlemagne and his son Louis the Pious; his main work is a biography of Charlemagne, the Vita Karoli Magni, "one of the most precious literary bequests of the early Middle Ages".

Louis I, better known as Louis the Pious, also called the Fair and the Debonaire, was King of the Franks and co-emperor with his father, Charlemagne, from 813. He was also King of Aquitaine from 781. As the only surviving son of Charlemagne and Hildegard, he became the sole ruler of the Franks after his father's death in 814, a position that he held until his death except from 833 to 834, when he was deposed.
The 780s decade ran from January 1, 780, to December 31, 789.

Louis the German, also known as Louis II of Germany and Louis II of East Francia, was the first king of East Francia, and ruled from 843 to 876 AD. Grandson of emperor Charlemagne and the third son of Louis the Pious, emperor of Francia, and his first wife, Ermengarde of Hesbaye, he received the appellation Germanicus shortly after his death, when East Francia became known as the kingdom of Germany.
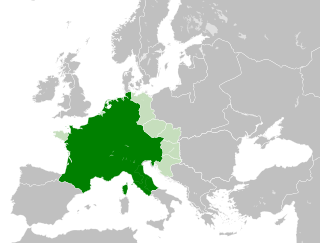
The Carolingian Empire (800–888) was a Frankish-dominated empire in Western and Central Europe during the Early Middle Ages. It was ruled by the Carolingian dynasty, which had ruled as kings of the Franks since 751 and as kings of the Lombards in Italy from 774. In 800, the Frankish king Charlemagne was crowned emperor in Rome by Pope Leo III in an effort to transfer the Roman Empire from the Byzantine Empire to Western Europe. The Carolingian Empire is considered the first phase in the history of the Holy Roman Empire.

Irene of Athens, surname Sarantapechaina (Σαρανταπήχαινα), was Byzantine empress consort to Emperor Leo IV from 775 to 780, regent during the childhood of their son Constantine VI from 780 until 790, co-ruler from 792 until 797, and finally empress regnant and sole ruler of the Eastern Roman Empire from 797 to 802. A member of the politically prominent Sarantapechos family, she was selected as Leo IV's bride for unknown reasons in 768. Even though her husband was an iconoclast, she harbored iconophile sympathies. During her rule as regent, she called the Second Council of Nicaea in 787, which condemned iconoclasm as heretical and brought an end to the first iconoclast period (730–787). Her public figure was very polarizing during her 5 year reign, as most saw a woman not right to rule solely. Her reign as such made her the first ever empress regnant, ruling in her own right, in Roman and Byzantine imperial history.

The Thuringii, Toringi or Teuriochaimai were an early Germanic people that appeared during the late Migration Period in the Harz Mountains of central Germania, a region still known today as Thuringia. It became a kingdom, which came into conflict with the Merovingian Franks, and it later came under their influence and Frankish control. The name is still used for one of modern Germany's federal states (Bundesländer).

Carloman I, also Karlmann, was king of the Franks from 768 until his death in 771. He was the second surviving son of Pepin the Short and Bertrada of Laon and was a younger brother of Charlemagne. His death allowed Charlemagne to take all of Francia and begin his expansion into other kingdoms.

Gudfred was a ninth century Danish king who reigned from at least 804 to 810. Alternate spellings include Godfred (Danish), Göttrick (German), Gøtrik (Danish), Gudrød (Danish), and Godofredus (Latin). He stands at the threshold of the History of Denmark in the sense that he is the first ruler about whom there is substantial knowledge from contemporary sources. He waged offensive war against the Carolingian Empire with some success, but was murdered under murky circumstances before a major confrontation had taken place. There is no unambiguous trace of Gudfred in the later Norse sagas, and his history can only be traced from the hostile Frankish texts which makes an assessment of his role problematic. His paternity is unknown but he may have been closely related to Sigfred, who preceded him as king of Denmark c. 770–804. He was the uncle of the later Danish King Hemming (810–812) and the father of King Horik I (813–854).

Conrad I, called the Younger, was the king of East Francia from 911 to 918. He was the first king not of the Carolingian dynasty, the first to be elected by the nobility and the first to be anointed. He was chosen as the king by the rulers of the East Frankish stem duchies after the death of young King Louis the Child. Ethnically Frankish, prior to this election he had ruled the Duchy of Franconia from 906.

The Royal Frankish Annals, also called the Annales Laurissenses maiores, are a series of annals composed in Latin in the Carolingian Francia, recording year-by-year the state of the monarchy from 741 to 829. Their authorship is unknown, though Wilhelm von Giesebrecht suggested that Arno of Salzburg was the author of an early section surviving in the copy at Lorsch Abbey. The Annals are believed to have been composed in successive sections by different authors, and then compiled.

Bernard was the King of Italy from 810 to 818. He plotted against his uncle, Emperor Louis the Pious, when the latter's Ordinatio Imperii made Bernard a vassal of his cousin Lothair. When his plot was discovered, Louis had him blinded, a procedure which killed him.
Henry was the leading military commander of the last years of the Carolingian Empire. He was commander-in-chief under Kings Louis the Younger and Charles the Fat. His early career was mostly restricted to East Francia, his homeland, but after Charles inherited West Francia in 884 he was increasingly active there. During his time, raids by the Vikings peaked in Francia. The sources describe at least eight separate campaigns waged by Henry against the Vikings, most of them successful.
Pepin, or Pippin the Hunchback was a Frankish prince. He was the eldest son of Charlemagne and noblewoman Himiltrude. He developed a humped back after birth, leading early medieval historians to give him the epithet "hunchback". He lived with his father's court after Charlemagne dismissed his mother and took another wife, Hildegard. Around 781, Pepin's half brother Carloman was rechristened as "Pepin of Italy"—a step that may have signaled Charlemagne's decision to disinherit the elder Pepin, for a variety of possible reasons. In 792, Pepin the Hunchback revolted against his father with a group of leading Frankish nobles, but the plot was discovered and put down before the conspiracy could put it into action. Charlemagne commuted Pepin's death sentence, having him tonsured and exiled to the monastery of Prüm instead. Since his death in 811, Pepin has been the subject of numerous works of historical fiction.
Drogo was a Frankish nobleman of the Pippinid family and the eldest son of Carloman, mayor of the palace of Austrasia under the Merovingian king Childeric III. He succeeded to his father's office in 747, but was soon squeezed out of power by his uncle, Pippin III, the mayor in Neustria. He resisted his uncle's takeover, but in 753 was captured and forced to become a monk.

Louis the Younger, sometimes called Louis the Saxon or Louis III, was the second eldest of the three sons of Louis the German and Hemma. He succeeded his father as the King of Eastern Francia on 28 August 876 and his elder brother Carloman as King of Bavaria from 876 to 882. He died in 882 and was succeeded in all his territories, which encompassed most of East Francia, by his younger brother, Charles the Fat, already king of Italy and emperor.
The Duchy of Thuringia was an eastern frontier march of the Merovingian kingdom of Austrasia, established about 631 by King Dagobert I after his troops had been defeated by the forces of the Slavic confederation of Samo at the Battle of Wogastisburg. It was recreated in the Carolingian Empire and its dukes were appointed by the king until it was absorbed by the Saxon dukes in 908. From about 1111/12 the territory was ruled by the Landgraves of Thuringia as Princes of the Holy Roman Empire. When Frederick IV, the last independent ruler of Thuringia died in 1440, the territory passed to his nephew, the saxon elector Frederick II.
Baugulf was a prominent Benedictine abbot in the Carolingian church. He was the second abbot of the Abbey of Fulda in present-day Germany. He served from 779 to 802 CE and was succeeded by Ratgar.











