External links
| International | |
|---|---|
| National | |
| Other | |
| | This University of Oklahoma-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
Harrison Kerr (b. Cleveland, Ohio, October 13, 1897; d. Norman, Oklahoma, August 1978) was an American composer of contemporary classical music, editor, administrator, and educator.
He studied in Cleveland, Ohio with James H. Rogers, in Paris with Nadia Boulanger. From 1949 to 1969, he served as professor of music and dean at the University of Oklahoma in Norman, Oklahoma.
He also served as the first Executive Secretary of the American Music Center (which he helped to found) as well as the first Executive Secretary of the American Composers Alliance. In addition, he served on the editorial boards of New Music Editions and New Music Quarterly Recordings.
Among his many works are four symphonies and an opera entitled The Tower of Kel (1958–60). His music is recorded on the Composers Recordings, Inc. label.

William Henry Harrison served as the ninth president of the United States from March 4 to April 4, 1841, the shortest presidency in U.S. history. He was also the first U.S. president to die in office, causing a brief constitutional crisis since presidential succession was not then fully defined in the U.S. Constitution. Harrison was the last president born as a British subject in the Thirteen Colonies and was the grandfather of Benjamin Harrison, the 23rd U.S. president.
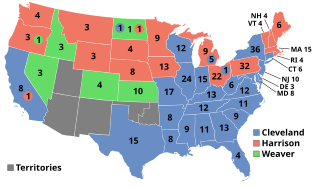
The 1892 United States presidential election was the 27th quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 8, 1892. In the fourth rematch in American history, the Democratic nominee, former president Grover Cleveland, defeated the Republican incumbent, President Benjamin Harrison. Cleveland's victory made him the first president in American history to be elected to a non-consecutive second term, a feat that would not be repeated until Donald Trump was elected again in 2024. This was the first of two occasions when incumbents were defeated in consecutive elections—the second being Gerald Ford's loss in 1976 to Jimmy Carter followed by Carter's loss in 1980 to Ronald Reagan.
Ralph Sylvester Peer was an American talent scout, recording engineer, record producer and music publisher in the 1920s and 1930s. Peer pioneered field recording of music when in June 1923 he took remote recording equipment south to Atlanta, Georgia, to record regional music outside the recording studio in such places as hotel rooms, ballrooms, or empty warehouses.

George Szell, originally György Széll, György Endre Szél, or Georg Szell, was a Hungarian-born American conductor and composer. Considered one of the twentieth century's greatest conductors, he was music director of the Cleveland Orchestra of Cleveland, Ohio, and recorded much of the standard classical repertoire in Cleveland and with other orchestras.

Howard Harold Hanson was an American composer, conductor, educator, music theorist, and champion of American classical music. As director for 40 years of the Eastman School of Music, he built a high-quality school and provided opportunities for commissioning and performing American music. In 1944, he won a Pulitzer Prize for his Symphony No. 4, and received numerous other awards including the George Foster Peabody Award for Outstanding Entertainment in Music in 1946.
New Mexico is a state of the Southwest United States. The state has music traditions dating back to the ancient Anasazi and Pueblo people, Navajo, Apache, and the Spanish Santa Fe de Nuevo México; these old traditions are found in both their original folk forms and as a modern folk genre known as New Mexico music.

James Edward Cleveland was an American gospel singer, musician, and composer. Known as the "King of Gospel," Cleveland was a driving force behind the creation of the modern gospel sound by incorporating traditional black gospel, soul, pop, and jazz in arrangements for mass choirs.

George Washington Steele was an American lawyer, soldier, and politician who twice served as a Representative for Indiana, from 1881 to 1889 and again from 1895 to 1903. Steele was also the first governor of Oklahoma Territory and was instrumental in developing the state's public education system and its two largest universities.

Robert Martin (1833–1897), a Republican lawyer and native of Pennsylvania who moved to Oklahoma Territory in 1889 and served as Secretary (1890–1893) and acting governor of Oklahoma Territory.

Benjamin Harrison was the 23rd president of the United States, serving from 1889 to 1893. He was a member of the Harrison family of Virginia—a grandson of the ninth president, William Henry Harrison, and a great-grandson of Benjamin Harrison V, a Founding Father. A Union Army veteran and a Republican, he defeated incumbent Grover Cleveland to win the presidency in 1888 and was defeated for a second term by Cleveland in 1892.
Paul William Whear was an American composer, conductor, music educator, and double-bassist.

Fletcher B. Swank was an American politician and a U.S. Representative from Oklahoma.
William Remsen Strickland was an American conductor and organist, noted for his lifelong promotion of American composers.

Harrison Leslie Adams Jr. was an American composer. His works have been performed by the Prague Radio Symphony Orchestra, Iceland Symphony Orchestra, Buffalo Philharmonic, and Indianapolis Symphony, and commissioned by The Cleveland Orchestra, Ohio Chamber Orchestra, Cleveland Chamber Symphony, and the Center for Black Music Research, among others. Metropolitan Opera artists have performed his vocal works internationally. He has also received composition awards from the National Association of Negro Women and the Christian Arts National Competition for Choral Music. Adams is best known for writing music for voice but has also written numerous purely instrumental compositions as well. Adams's music is composed largely within the tradition of Western classical music and also incorporates elements unique to African-American music.

John Sherman was an American politician from Ohio who served in federal office throughout the Civil War and into the late nineteenth century. A member of the Republican Party, he served in both houses of the U.S. Congress. He also served as Secretary of the Treasury and Secretary of State. Sherman sought the Republican presidential nomination three times, coming closest in 1888, but was never chosen by the party.

The 1892 United States elections was held on November 8, electing member to the 53rd United States Congress, taking place during the Third Party System. Democrats retained the House and won control of the presidency and the Senate. Following the election, Democrats controlled the presidency and a majority in both chambers of Congress for the first time since the 1858 elections.

Evelyn LaRue Pittman was an American composer, choral director and music educator.
Cass Harrison is an American jazz pianist and composer. He had two trio albums released by MGM Records in the 1950s.
Jane Corner Young was an American composer, music therapist, and pianist. She was born in Athens, Ohio, and graduated with a Bachelor of Music degree from Ohio University in 1936. She completed a master of music degree in piano and composition in 1953 at the Cleveland Institute of Music. Young studied piano with Beryl Rubinstein and Arthur Loesser; composition with Marcel Dick; and Dalcroze eurythmics with Elsa Findlay and Ann Lombardo.
Katharine Mulky Warne was an American composer, pianist and teacher, who founded the Darius Milhaud Society and organized 15 Milhaud festivals in Cleveland, Ohio, to promote his music. She was born in Oklahoma City, Oklahoma. On June 27, 1953, She married Clinton L. Warne and they had three children: Kate, Clinton Jr. and Carolyn.