Related Research Articles
The forearm is the region of the upper limb between the elbow and the wrist. The term forearm is used in anatomy to distinguish it from the arm, a word which is most often used to describe the entire appendage of the upper limb, but which in anatomy, technically, means only the region of the upper arm, whereas the lower "arm" is called the forearm. It is homologous to the region of the leg that lies between the knee and the ankle joints, the crus.

The tibia, also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates, and it connects the knee with the ankle bones. The tibia is found on the medial side of the leg next to the fibula and closer to the median plane or centre-line. The tibia is connected to the fibula by the interosseous membrane of the leg, forming a type of fibrous joint called a syndesmosis with very little movement. The tibia is named for the flute tibia. It is the second largest bone in the human body next to the femur. The leg bones are the strongest long bones as they support the rest of the body.

The fibula or calf bone is a leg bone on the lateral side of the tibia, to which it is connected above and below. It is the smaller of the two bones and, in proportion to its length, the slenderest of all the long bones. Its upper extremity is small, placed toward the back of the head of the tibia, below the knee joint and excluded from the formation of this joint. Its lower extremity inclines a little forward, so as to be on a plane anterior to that of the upper end; it projects below the tibia and forms the lateral part of the ankle joint.

The capitate bone is found in the center of the carpal bone region, colloquially known as the wrist, which is at the distal end of the radius and ulna bones. It articulates with the third metacarpal bone and forms the third carpometacarpal joint. The capitate bone is the largest of the carpal bones in the human hand. It presents, above, a rounded portion or head, which is received into the concavity formed by the scaphoid and lunate bones; a constricted portion or neck; and below this, the body. The bone is also found in many other mammals, and is homologous with the "third distal carpal" of reptiles and amphibians.

The radius or radial bone is one of the two large bones of the forearm, the other being the ulna. It extends from the lateral side of the elbow to the thumb side of the wrist and runs parallel to the ulna. The ulna is shorter and smaller than the radius. It is a long bone, prism-shaped and slightly curved longitudinally.

A bone fracture is a medical condition in which there is a partial or complete break in the continuity of the bone. In more severe cases, the bone may be broken into several pieces. A bone fracture may be the result of high force impact or stress, or a minimal trauma injury as a result of certain medical conditions that weaken the bones, such as osteoporosis, osteopenia, bone cancer, or osteogenesis imperfecta, where the fracture is then properly termed a pathologic fracture.

The olecranon from the Greekolene meaning elbow and kranon meaning head is the large, thick, curved bony eminence of the ulna, a long bone in the forearm that projects behind the elbow. It forms the most pointed portion of the elbow and is opposite to the cubital fossa or elbow pit. The olecranon serves as a lever for the extensor muscles that straighten the elbow joint.

The talus, talus bone, astragalus, or ankle bone is one of the group of foot bones known as the tarsus. The tarsus forms the lower part of the ankle joint. It transmits the entire weight of the body from the lower legs to the foot.

The ischium forms the lower and back part of the hip bone.

Hangman's fracture is the colloquial name given to a fracture of both pedicles, or pars interarticulares, of the axis vertebra (C2).
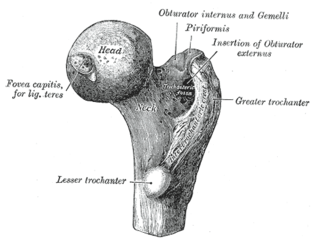
The femoral neck is a flattened pyramidal process of bone, connecting the femoral head with the femoral shaft, and forming with the latter a wide angle opening medialward.

A malleolus is the bony prominence on each side of the human ankle.

A calcaneal fracture is a break of the calcaneus. Symptoms may include pain, bruising, trouble walking, and deformity of the heel. It may be associated with breaks of the hip or back.

A trimalleolar fracture is a fracture of the ankle that involves the lateral malleolus, the medial malleolus, and the distal posterior aspect of the tibia, which can be termed the posterior malleolus. The trauma is sometimes accompanied by ligament damage and dislocation.
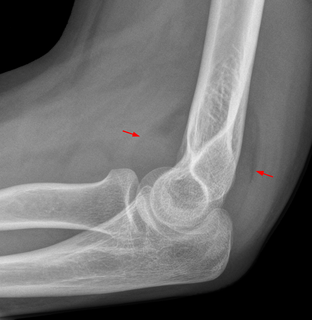
The fat pad sign, also known as the sail sign, is a potential finding on elbow radiography which suggests a fracture of one or more bones at the elbow. It is may indicate an occult fracture that is not directly visible. Its name derives from the fact that it has the shape of a spinnaker (sail). It is caused by displacement of the fat pad around the elbow joint. Both anterior and posterior fat pad signs exist, and both can be found on the same X-ray.

A Le Fort fracture of the skull is a classic transfacial fracture of the midface, involving the maxillary bone and surrounding structures in either a horizontal, pyramidal or transverse direction. The hallmark of Lefort fractures is traumatic pterygomaxillary separation, which signifies fractures between the pterygoid plates, horseshoe shaped bony protuberances which extend from the inferior margin of the maxilla, and the maxillary sinuses. Continuity of this structure is a keystone for stability of the midface, involvement of which impacts surgical management of trauma victims, as it requires fixation to a horizontal bar of the frontal bone. The pterygoid plates lie posterior to the upper dental row, or alveolar ridge, when viewing the face from an anterior view. The fractures are named after French surgeon René Le Fort (1869–1951), who discovered the fracture patterns by examining crush injuries in cadavers.

A supracondylar humerus fracture is a fracture of the distal humerus just above the elbow joint. The fracture is usually transverse or oblique and above the medial and lateral condyles and epicondyles. This fracture pattern is relatively rare in adults, but is the most common type of elbow fracture in children. In children, many of these fractures are non-displaced and can be treated with casting. Some are angulated or displaced and are best treated with surgery. In children, most of these fractures can be treated effectively with expectation for full recovery. Some of these injuries can be complicated by poor healing or by associated blood vessel or nerve injuries with serious complications.
The Bosworth fracture is a rare fracture of the distal fibula with an associated fixed posterior dislocation of the proximal fibular fragment which becomes trapped behind the posterior tibial tubercle. The injury is caused by severe external rotation of the ankle. The ankle remains externally rotated after the injury, making interpretation of X-rays difficult which can lead to misdiagnosis and incorrect treatment. The injury is most commonly treated by open reduction internal fixation as closed reduction is made difficult by the entrapment of the fibula behind the tibia.
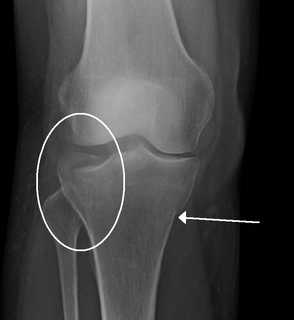
A crus fracture is a fracture of the lower legs bones meaning either or both of the tibia and fibula.

The intercondylar area is the separation between the medial and lateral condyle on the upper extremity of the tibia. The anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments and the menisci attach to the intercondylar area.
References
- ↑ Haraguchi N, Haruyama H, Toga H, Kato F (2006). "Pathoanatomy of posterior malleolar fractures of the ankle". J Bone Joint Surg Am. 88 (5): 1085–92. doi:10.2106/jbjs.e.00856. PMID 16651584.