
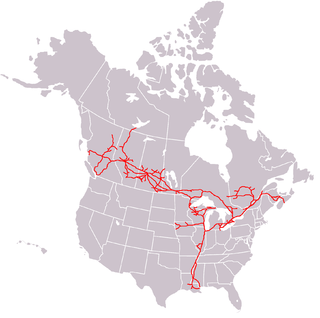
The Canadian Pacific Railway, also known simply as CPR or Canadian Pacific and formerly as CP Rail (1968–1996), is a Canadian Class I railway incorporated in 1881. The railway is owned by Canadian Pacific Railway Limited, which began operations as legal owner in a corporate restructuring in 2001.

A threshing machine or a thresher is a piece of farm equipment that threshes grain, that is, it removes the seeds from the stalks and husks. It does so by beating the plant to make the seeds fall out.

There has been a significant history of Chinese immigration to Canada, with the first settlement of Chinese people in Canada being in the 1780s. The major periods of Chinese immigration would take place from 1858 to 1923 and 1947 to the present day, reflecting changes in the Canadian government's immigration policy.
The Canadian National Railway Company is a Canadian Class I freight railway headquartered in Montreal, Quebec, which serves Canada and the Midwestern and Southern United States.

The Kettle Valley Railway was a subsidiary of the Canadian Pacific Railway (CPR) that operated across southern British Columbia, west of Midway running to Rock Creek, then north to Myra Canyon, down to Penticton over to Princeton, Coalmont, Brookmere, Coquihalla and finally Hope where it connected to the main CPR line.

BC Rail is a railway in the Canadian province of British Columbia.

A coolie is a term for a low-wage labourer, typically of South Asian or East Asian descent.

Canadian historians until the 1960s tended to focus on the history of Canada's economy because of the far fewer political, economic, religious and military conflicts present in Canadian history than in other societies. Many of the most prominent English Canadian historians from this period were economic historians, such as Harold Innis, Donald Creighton and Arthur R. M. Lower.

Andrew Onderdonk was an American construction contractor who worked on several major projects in the West, including the San Francisco seawall in California and the Canadian Pacific Railway in British Columbia. He was born on August 30, 1848 in New York City to an established ethnic Dutch family. He received his education at the Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute.

The Royal Hudsons are a series of semi-streamlined 4-6-4 "Hudson" type steam locomotives owned by the Canadian Pacific Railway (CPR) and built by Montreal Locomotive Works (MLW). The engines were built in 1937. In 1939, King George VI allowed the CPR to use the term after Royal Hudson number 2850 transported the royal train across Canada with no need of replacement. These locomotives were in service between 1937 and 1960. Four of them have been preserved. No. 2839 was used to power excursions for the Southern Railway Steam Program between 1979 and 1980. No. 2860 was used for excursion service in British Columbia between 1974 and 1999, then again between 2006 and 2010.

Charles Melville Hays was the president of the Grand Trunk Railway. He began working in the railroad business as a clerk at the age of 17 and quickly rose through the ranks of management to become the General Manager of the Wabash, St. Louis and Pacific Railway. He became Vice-President of that company in 1889 and remained as such until 1896 when he became General Manager of the Grand Trunk Railway (GTR) of Canada.

Mechanised agriculture is the process of using agricultural machinery to mechanise the work of agriculture, greatly increasing farm worker productivity. In modern times, powered machinery has replaced many farm jobs formerly carried out by manual labour or by working animals such as oxen, horses and mules.

The Mineral Revolution is a term used by historians to refer to the rapid industrialisation and economic changes which occurred in South Africa from the 1860s onwards. The Mineral Revolution was largely driven by the need to create a permanent workforce to work in the mining industry, and saw South Africa transformed from a patchwork of agrarian states to a unified, industrial nation. In political terms, the Mineral Revolution had a significant impact on diplomacy and military affairs. Finally, the policies and events of the Mineral Revolution had an increasingly negative impact on race relations in South Africa, and formed the basis of the apartheid system, which dominated South African society for a century. The Mineral Revolution was caused by the discovery of diamonds in Kimberly in 1867 and also by the discovery of gold in Witwatersrand in 1886. The mineral mining revolution laid the foundations of racial segregation and the control of white South Africans over black South Africans. The Mineral Revolution changed South Africa from being an agricultural society to becoming the largest gold producing country in the world.

The history of immigration to Canada details the movement of people to modern-day Canada. The modern Canadian legal regime was founded in 1867 but Canada also has legal and cultural continuity with French and British colonies in North America going back to the seventeenth century, and during the colonial era immigration was a major political and economic issue and Britain and France competed to fill their colonies with loyal settlers. Prior to that, the land that now makes up Canada was inhabited by many distinct indigenous nations for thousands of years. Indigenous peoples contributed significantly to the culture and economy of the early European colonies, to which was added several waves of European immigration. More recently, the source of migrants to Canada has shifted away from Europe and towards Asia and Africa. Canada's cultural identity has evolved constantly in tandem with changes in immigration patterns.

The Chinese Labour Corps was a force of workers recruited by the British government in the First World War to free troops for front line duty by performing support work and manual labour. The French government also recruited a significant number of Chinese labourers, and although those labourers working for the French were recruited separately and not part of the CLC, they are often considered to be so. In all, some 140,000 men served for both British and French forces before the war ended and most of the men were repatriated to China between 1918 and 1920.

Saskatchewan Highway 641 is a highway in the province of Saskatchewan, Canada, beginning at Highway 39 near Rouleau, and traveling north ending at Highway 15 at Semans. The highway intersects the Trans Canada Highway, Saskatchewan Highway 1 south of Pense and east of Belle Plaine, Highway 20 at Lumsden, and Highway 22 at Earl Grey. Local Improvement Districts were the precursors of rural municipalities which initially established and maintained roads in their area. Early settlers helped to construct and maintain the route and would get paid road improvement wages from the local rural municipality. The 8 kilometres (5.0 mi) concurrency between Highway 20 and Highway 641 was constructed in 1927 following the removal of the Canadian National Railway line between Lumsden and Craven. The remainder of the road followed Dominion land survey township and range lines.

Racialization of labour in the Okanagan refers to the growing relationship between particular racial identities and agricultural labour in the Okanagan Valley of British Columbia. In brief, the continued growth and operation of the agricultural industry in the Okanagan evidently depends on the employment of temporary migrant workers. In 2009, there were 3,000 Mexican migrant labourers working in the Okanagan.
The Georgian Bay and Seaboard Railway (GB&S) was a former short-line railway in Ontario, Canada, owned and operated by Canadian Pacific Railway (CPR). The first sections opened in 1908, and the entire 140 kilometres (87 mi) route was fully completed in 1912.
The United Brotherhood of Railway Employees (UBRE) was an industrial labor union established in Canada in 1898, and a separate union established in Oregon in 1901. The two combined in 1902. The union signed up lesser-skilled railway clerks and laborers, but had the ambition of representing all railway workers regardless of trade. The Canadian Pacific Railway (CPR) was determined to break the UBRE and provoked a major strike in Vancouver in 1903. The CPR used strikebreakers, spies and secret police to break the strike. The crafts brotherhoods of engineers, conductors, firemen and brakemen would not support the UBRE. The strike failed, and the UBRE disintegrated over the next year.

Indian migrant workers during the COVID-19 pandemic have faced multiple hardships. With factories and workplaces shut down due to the lockdown imposed in the country, millions of migrant workers had to deal with the loss of income, food shortages and uncertainty about their future. Following this, many of them and their families went hungry. Thousands of them then began walking back home, with no means of transport due to the lockdown. In response, the Central and State Governments took various measures to help them, and later arranged transport for them. 198 migrant workers died due to the lockdown, with reasons of road accidents.














