An Internet filter is software that restricts or controls the content an Internet user is capable to access, especially when utilized to restrict material delivered over the Internet via the Web, Email, or other means. Such restrictions can be applied at various levels: a government can attempt to apply them nationwide, or they can, for example, be applied by an Internet service provider to its clients, by an employer to its personnel, by a school to its students, by a library to its visitors, by a parent to a child's computer, or by an individual user to their own computers. The motive is often to prevent access to content which the computer's owner(s) or other authorities may consider objectionable. When imposed without the consent of the user, content control can be characterised as a form of internet censorship. Some filter software includes time control functions that empowers parents to set the amount of time that child may spend accessing the Internet or playing games or other computer activities.

A hacker is a person skilled in information technology who achieves goals by non-standard means. The term has become associated in popular culture with a security hacker – someone with knowledge of bugs or exploits to break into computer systems and access data which would otherwise be inaccessible to them. In a positive connotation, though, hacking can also be utilized by legitimate figures in legal situations. For example, law enforcement agencies sometimes use hacking techniques to collect evidence on criminals and other malicious actors. This could include using anonymity tools to mask their identities online and pose as criminals.

Iran's telecommunications industry is almost entirely state-owned, dominated by the Telecommunication Company of Iran (TCI). Fixed-line penetration in 2004 was relatively well-developed by regional standards, standing at 22 lines per 100 people, higher than Egypt with 14 and Saudi Arabia with 15, although behind the UAE with 27. Iran had more than 1 mobile phone per inhabitant by 2012.
Computer and network surveillance is the monitoring of computer activity and data stored locally on a computer or data being transferred over computer networks such as the Internet. This monitoring is often carried out covertly and may be completed by governments, corporations, criminal organizations, or individuals. It may or may not be legal and may or may not require authorization from a court or other independent government agencies. Computer and network surveillance programs are widespread today and almost all Internet traffic can be monitored.
Deep packet inspection (DPI) is a type of data processing that inspects in detail the data being sent over a computer network, and may take actions such as alerting, blocking, re-routing, or logging it accordingly. Deep packet inspection is often used for baselining application behavior, analyzing network usage, troubleshooting network performance, ensuring that data is in the correct format, checking for malicious code, eavesdropping, and internet censorship, among other purposes. There are multiple headers for IP packets; network equipment only needs to use the first of these for normal operation, but use of the second header is normally considered to be shallow packet inspection despite this definition.
Hacktivismo is an offshoot of Cult of the Dead Cow (cDc), whose beliefs include access to information as a basic human right. It was founded in 1999.
In programming and software development, fuzzing or fuzz testing is an automated software testing technique that involves providing invalid, unexpected, or random data as inputs to a computer program. The program is then monitored for exceptions such as crashes, failing built-in code assertions, or potential memory leaks. Typically, fuzzers are used to test programs that take structured inputs. This structure is specified, e.g., in a file format or protocol and distinguishes valid from invalid input. An effective fuzzer generates semi-valid inputs that are "valid enough" in that they are not directly rejected by the parser, but do create unexpected behaviors deeper in the program and are "invalid enough" to expose corner cases that have not been properly dealt with.
Xcitium, formerly known as Comodo Security Solutions, Inc., is a cybersecurity company headquartered in Bloomfield, New Jersey. Under the brand Sectigo, the company acts as a web Certificate authority (CA) and issues SSL/TLS certificates.

Psiphon is a free and open-source Internet censorship circumvention tool that uses a combination of secure communication and obfuscation technologies, such as a VPN, SSH, and a Web proxy. Psiphon is a centrally managed and geographically diverse network of thousands of proxy servers, using a performance-oriented, single- and multi-hop routing architecture.
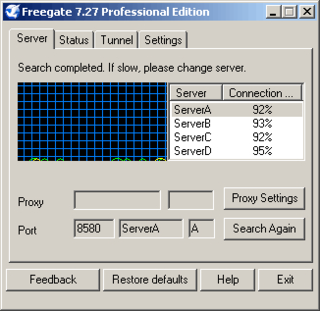
Freegate is a software application developed by Dynamic Internet Technology (DIT) that enables internet users to view websites blocked by their governments. The program takes advantage of a range of proxy servers called Dynaweb. This allows users to bypass Internet firewalls that block web sites by using DIT's Peer-to-peer (P2P)-like proxy network system. FreeGate's anti-censorship capability is further enhanced by a new, unique encryption and compression algorithm in the versions of 6.33 and above. Dynamic Internet Technology estimates Freegate had 200,000 users in 2004. The maintainer and CEO of DIT is Bill Xia.

Internet censorship is the legal control or suppression of what can be accessed, published, or viewed on the Internet. Censorship is most often applied to specific internet domains but exceptionally may extend to all Internet resources located outside the jurisdiction of the censoring state. Internet censorship may also put restrictions on what information can be made internet accessible. Organizations providing internet access – such as schools and libraries – may choose to preclude access to material that they consider undesirable, offensive, age-inappropriate or even illegal, and regard this as ethical behavior rather than censorship. Individuals and organizations may engage in self-censorship of material they publish, for moral, religious, or business reasons, to conform to societal norms, political views, due to intimidation, or out of fear of legal or other consequences.
Iran is known for having one of the world's most comprehensive Internet censorship systems. The Iranian government and the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC) have blocked access to many popular websites and online services, including YouTube, Twitter, Facebook Instagram and Telegram. Internet traffic in the country is heavily restricted and monitored. Internet Filtering Committee (Iran) headed by Prosecutor-General of Iran decides which websites must be censored and implements this vast censorship.
Internet activism and, specifically, social networking has been instrumental in organizing many of the 2009 Iranian election protests. Online sites have been uploading amateur pictures and video, and Twitter, Facebook, and blogs have been places for protesters to gather and exchange information. Although some scholars in the West stress that Twitter has been used to organize protests, Iranian scholars argue that Twitter was hardly used by Iranian citizens in the midst of the 2009 protests.
The splinternet is a characterization of the Internet as splintering and dividing due to various factors, such as technology, commerce, politics, nationalism, religion, and divergent national interests. "Powerful forces are threatening to balkanise it", wrote the Economist weekly in 2010, arguing it could soon splinter along geographic and commercial boundaries. The Chinese government erected the "Great Firewall" for political reasons, and Russia has enacted the Sovereign Internet Law that allows it to partition itself from the rest of the Internet. Other nations, such as the US and Australia, have discussed plans to create a similar firewall to block child pornography or weapon-making instructions.

An Internet outage or Internet blackout or Internet shutdown is the complete or partial failure of the internet services. It can occur due to censorship, cyberattacks, disasters, police or security services actions or errors.
Internet censorship circumvention, also referred to as going over the wall or scientific browsing in China, is the use of various methods and tools to bypass internet censorship.
A national intranet is an Internet Protocol-based walled garden network maintained by a nation state as a national substitute for the global Internet, with the aim of controlling and monitoring the communications of its inhabitants, as well as restricting their access to outside media. Other names have been used, such as the use of the term halal internet in Iran.

Lantern is a free internet censorship circumvention tool that operates in some of the most extreme censorship environments, such as China, Iran, and Russia. It uses wide variety of protocols and techniques that obfuscate network traffic and/or co-mingle traffic with protocols censors are reluctant to block. It also uses domain fronting. It is not an anonymity tool like Tor.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to computer security:
The National Information Network (NIN) (Persian: شبکۀ ملی اطلاعات, Shabake-ye Melli-ye Ettelā'āt), also known as National Internet in Iran and the Iranian intranet, is an ongoing project to develop a secure, stable infrastructure network and national intranet in Iran.







