Related Research Articles

The Roman Empire was the state ruled by the Romans following Octavian's assumption of sole rule under the Principate in 27 BC, the post-Republican state of ancient Rome. It included territories in Europe, North Africa, and Western Asia and was ruled by emperors. The fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476 AD conventionally marks the end of classical antiquity and the beginning of the Middle Ages.

Ancient Roman architecture adopted the external language of classical ancient Greek architecture for the purposes of the ancient Romans, but was different from Greek buildings, becoming a new architectural style. The two styles are often considered one body of classical architecture. Roman architecture flourished in the Roman Republic and to an even greater extent under the Empire, when the great majority of surviving buildings were constructed. It used new materials, particularly Roman concrete, and newer technologies such as the arch and the dome to make buildings that were typically strong and well engineered. Large numbers remain in some form across the former empire, sometimes complete and still in use today.

An amphitheatre or amphitheater is an open-air venue used for entertainment, performances, and sports. The term derives from the ancient Greek ἀμφιθέατρον, from ἀμφί, meaning "on both sides" or "around" and θέατρον, meaning "place for viewing".

Mediolanum, the ancient city where Milan now stands, was originally an Insubrian city, but afterwards became an important Roman city in Northern Italy.

The Amphitheatrum Castrense is a Roman amphitheatre in Rome, next to the church of Santa Croce in Gerusalemme. Both the Amphiteatrum and the Circus Varianus were part of the palatial villa known as the Horti Spei Veteris and later the Palatium Sessorium. The Regionary Catalogues name it as the "Amphitheatrum Castrense", which could mean it was an amphitheatre connected to an imperial residence.

The Forma Urbis Romae or Severan Marble Plan is a massive marble map of ancient Rome, created under the emperor Septimius Severus between 203 and 211 CE. Matteo Cadario gives specific years of 205–208, noting that the map was based on property records.
"Bread and circuses" is a metonymic phrase referring to superficial appeasement. It is attributed to Juvenal, a Roman poet active in the late first and early second century AD, and is used commonly in cultural, particularly political, contexts.

The Circus of Maxentius is an ancient structure in Rome, Italy, part of a complex of buildings erected by emperor Maxentius on the Via Appia between AD 306 and 312. It is situated between the second and third miles of the Via Appia, between the basilica and catacombs of San Sebastiano and the imposing late republican tomb of Caecilia Metella, which dominates the hill that rises immediately to the east of the complex. It is part of the Appian Way Regional Park.

Peter William Connolly FSA was a British scholar of the ancient world, Greek and Roman military equipment historian, reconstructional archaeologist and illustrator. He was a regular contributor to such periodicals as the Journal of Roman Military Equipment Studies and Roman Frontier Studies.

The Ludus Magnus, also known as the Great Gladiatorial Training School, was the largest of the gladiatorial schools in Rome. It was built by the emperor Domitian in the late first century C.E., alongside other building projects undertaken by him such as three other gladiatorial schools across the Roman Empire.

Approximately 100 years after the destruction of Punic Carthage in 146 BC, a new city of the same name was built on the same land by the Romans in the period from 49 to 44 BC. By the 3rd century, Carthage had developed into one of the largest cities of the Roman Empire, with a population of several hundred thousand. It was the center of the Roman province of Africa, which was a major breadbasket of the empire. Carthage briefly became the capital of an usurper, Domitius Alexander, in 308–311. Conquered by the Vandals in 439, Carthage served as the capital of the Vandal Kingdom for a century. Re-conquered by the Eastern Roman Empire in 533–534, it continued to serve as an Eastern Roman regional center, as the seat of the praetorian prefecture of Africa. The city was sacked and destroyed by Umayyad Arab forces after the Battle of Carthage in 698 to prevent it from being reconquered by the Byzantine Empire. A fortress on the site was garrisoned by Muslim forces until the Hafsid period, when it was captured by Crusaders during the Eighth Crusade. After the withdrawal of the Crusaders, the Hafsids decided to destroy the fortress to prevent any future use by a hostile power. Roman Carthage was used as a source of building materials for Kairouan and Tunis in the 8th century.

Publia Fulvia Plautilla was the wife of the Roman emperor Caracalla, her paternal second cousin. After her father was condemned for treason, she was exiled and eventually killed, possibly on Caracalla's orders.

David John Mattingly, FBA is an archaeologist and historian of the Roman world. He is currently Professor of Roman Archaeology at the University of Leicester.

The Castra Nova equitum singularium was an ancient Roman fort in Rome housing part of the emperor's cavalry bodyguard. The site of the fort now lies beneath the Basilica of St John Lateran. The Castra Nova, or "new fort", was one of two cavalry forts that provided a base in Rome for the mounted bodyguard of the Roman emperors.
Lucius Aelius Helvius Dionysius was a Roman statesman who served as the Proconsul of Africa from 296 to 300 and as the Praefectus urbi from 301 to 302.
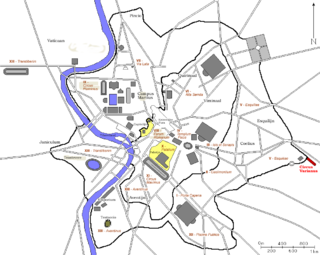
Circus Varianus was a large Roman circus, started during the reign of Caracalla and located in the palatial villa complex known as the Horti Spei Veteris, which included the Amphitheatrum Castrense. This circus was where Elagabalus raced chariots under the family name of Varius, giving the site its name. The circus was later restructured by Elagabalus, who removed the western end to create more space for the palace by moving the starting gates (carcares) back and building two towers at the end.

The Palace of Domitian was built as Roman emperor Domitian's official residence in 81–92 AD and was used as such by subsequent emperors. Its remains sit atop and dominate the Palatine Hill in Rome, alongside other palaces.
Annalisa Marzano, FRHistS FSA, MAE is an Italian-American archaeologist and academic. She is Professor of Classical Archaeology at the University of Bologna and has been Professor of Ancient History at the University of Reading in England. She specializes in Roman social and economic history.
Lea Margaret Stirling is a Canadian classical scholar and professor in the Department of Classics at the University of Manitoba. Her research focuses on Roman archaeology and Roman art with particular emphases on Roman sculpture, Late Antique art, and cemetery archaeology, and Roman North Africa.
Jonathan "Jon" Charles Nelson Coulston was a British archaeologist and lecturer who specialised in Roman army studies and Roman art and architecture. He was Senior Lecturer in the School of Classics at the University of St Andrews.
References
- ↑ "Dr. Hazel Dodge - Staff : Department of Classics:Trinity College Dublin, the University of Dublin, Ireland". www.tcd.ie. Archived from the original on 21 November 2017. Retrieved 14 January 2022.
- ↑ "Hazel Dodge - Archaeological Institute of America". www.archaeological.org. Archived from the original on 21 April 2019. Retrieved 14 January 2022.
- ↑ "Corresponding Members - Archaeological Institute of America". www.archaeological.org. Retrieved 10 November 2018.